 Öne Çıkan
Öne Çıkan
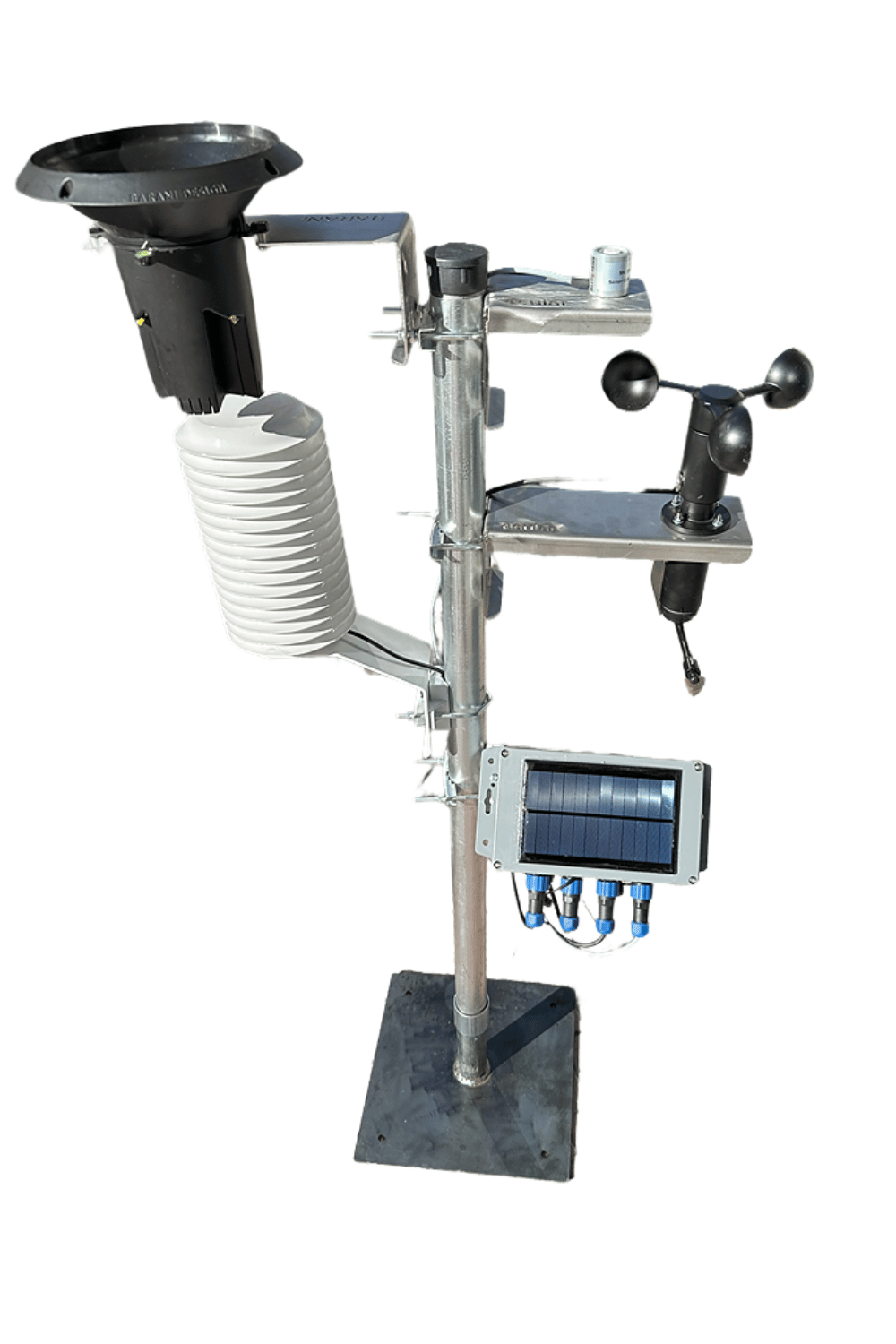
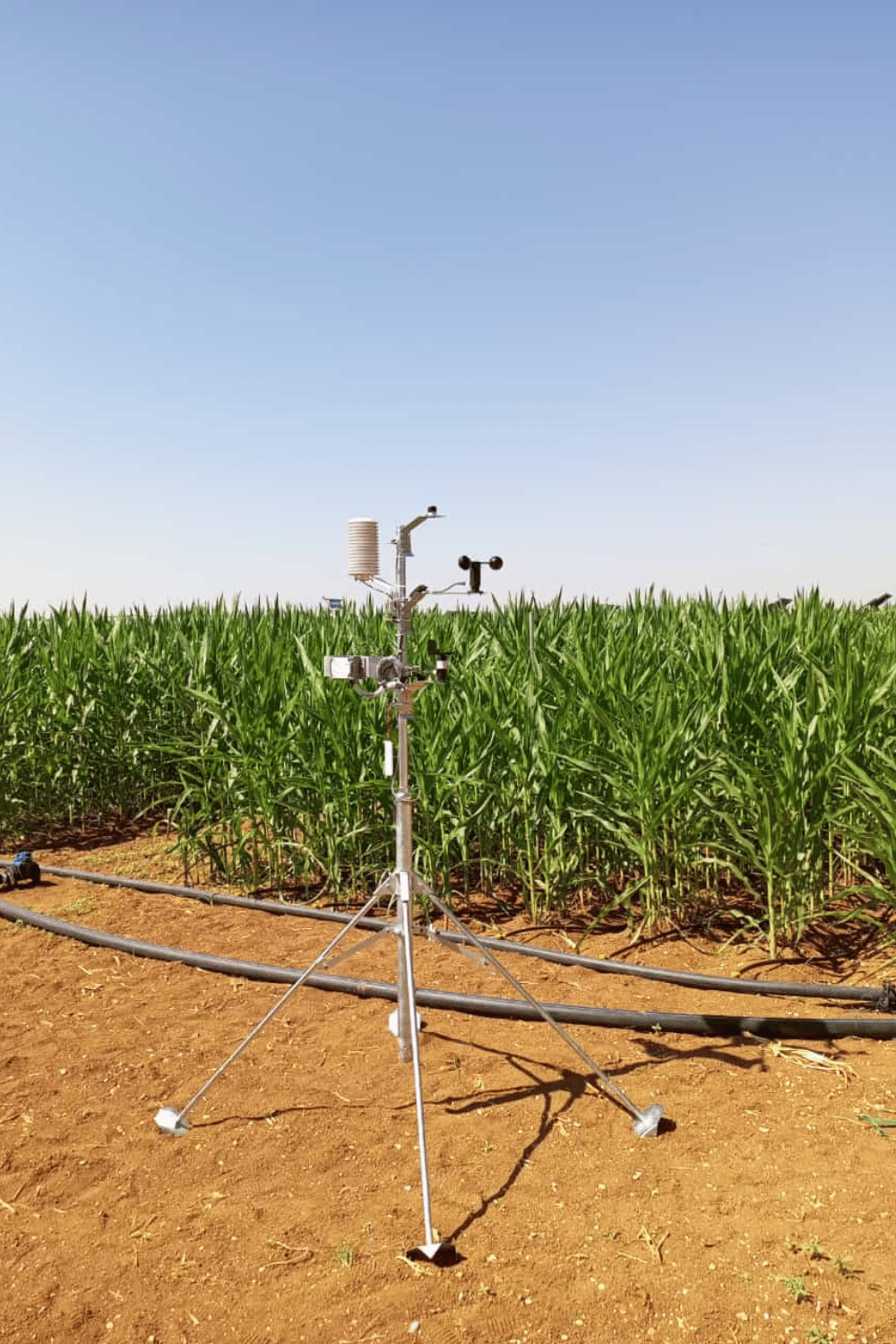
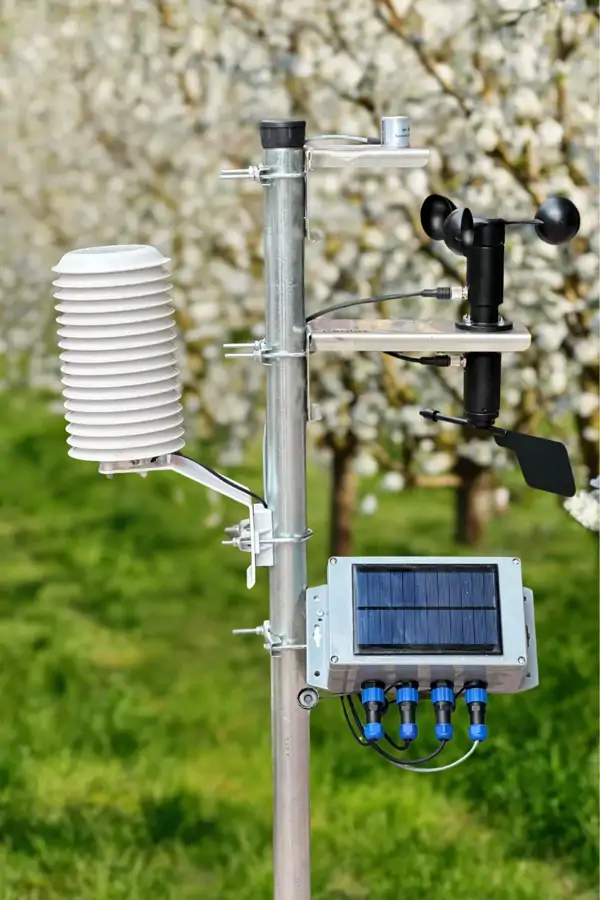
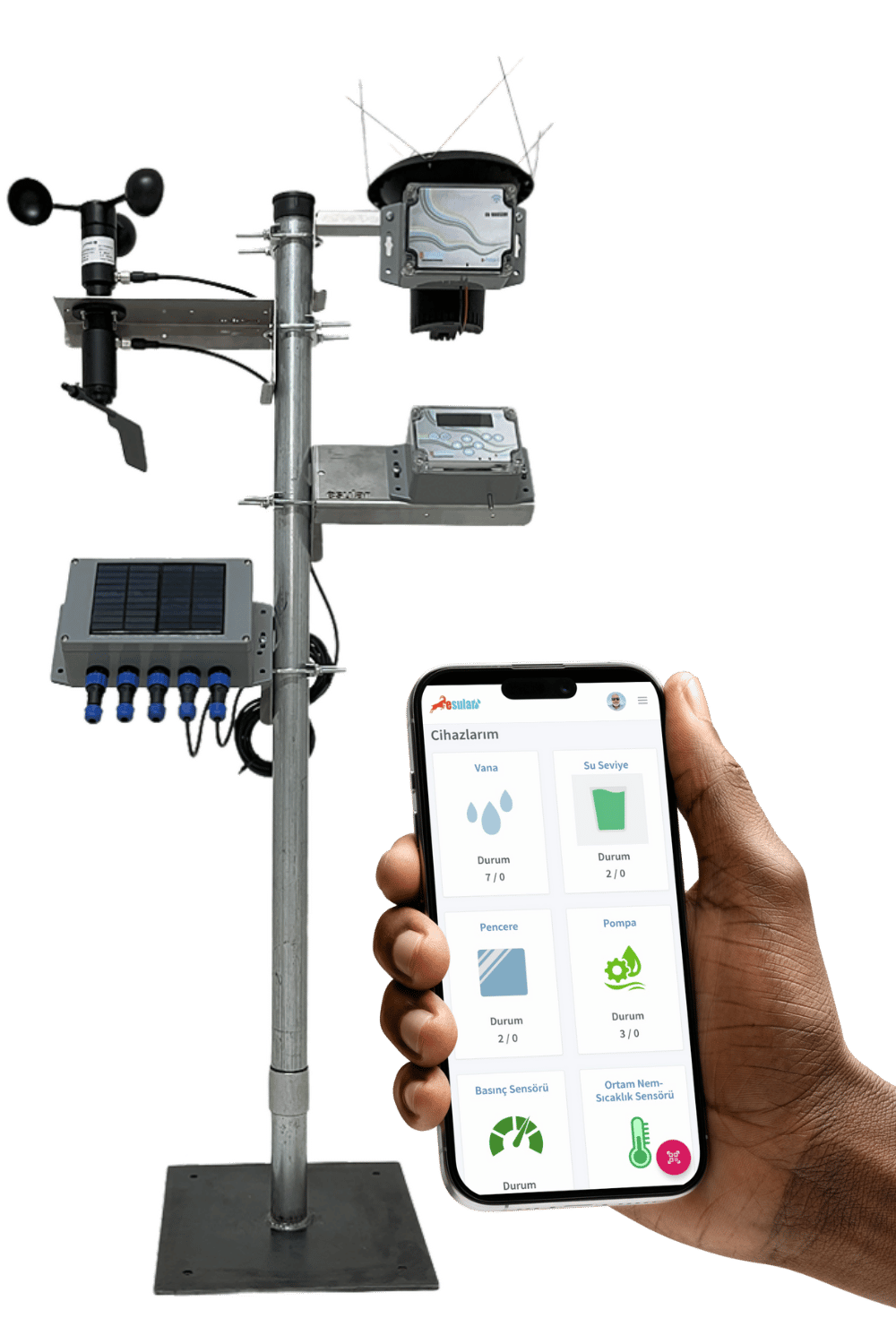



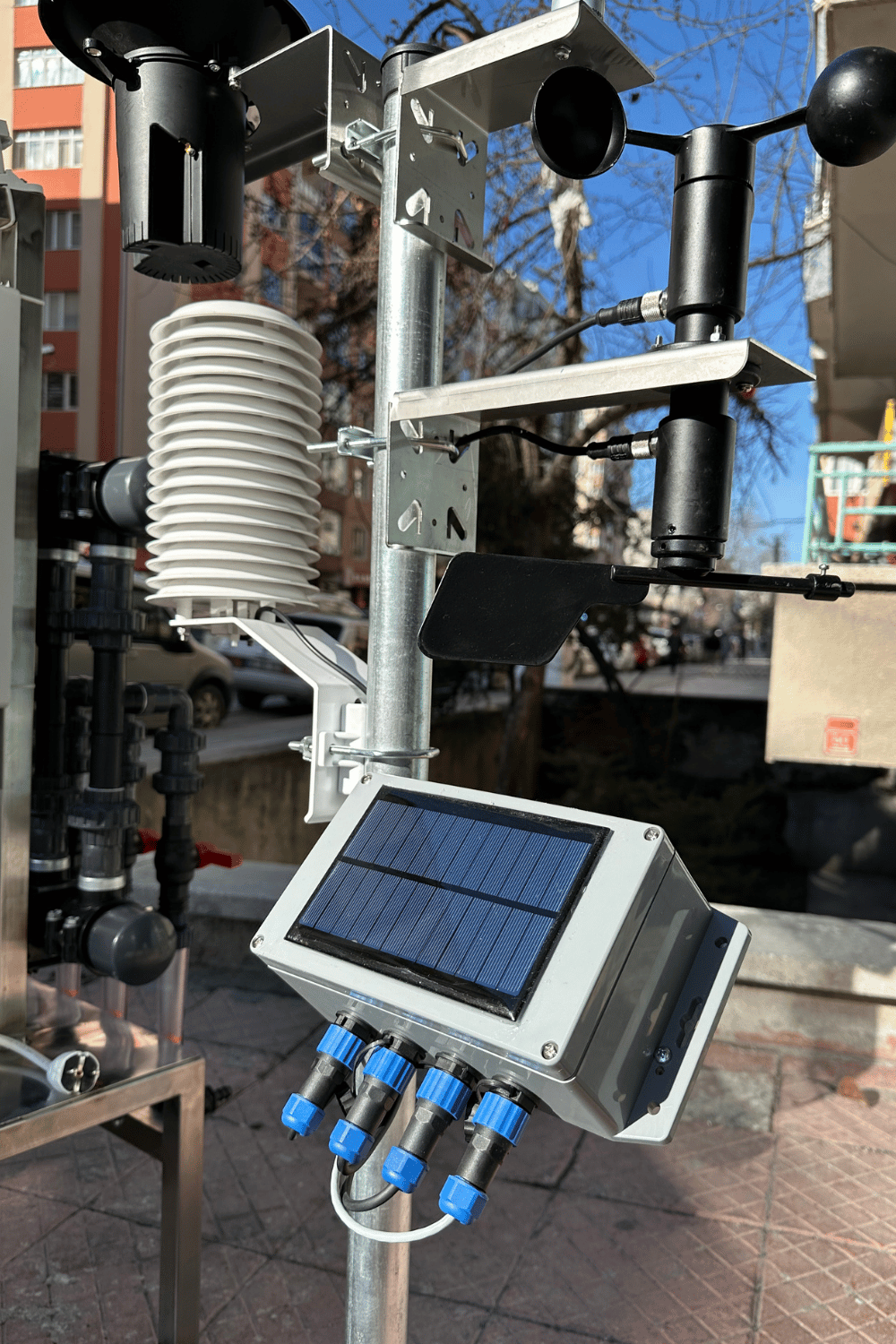


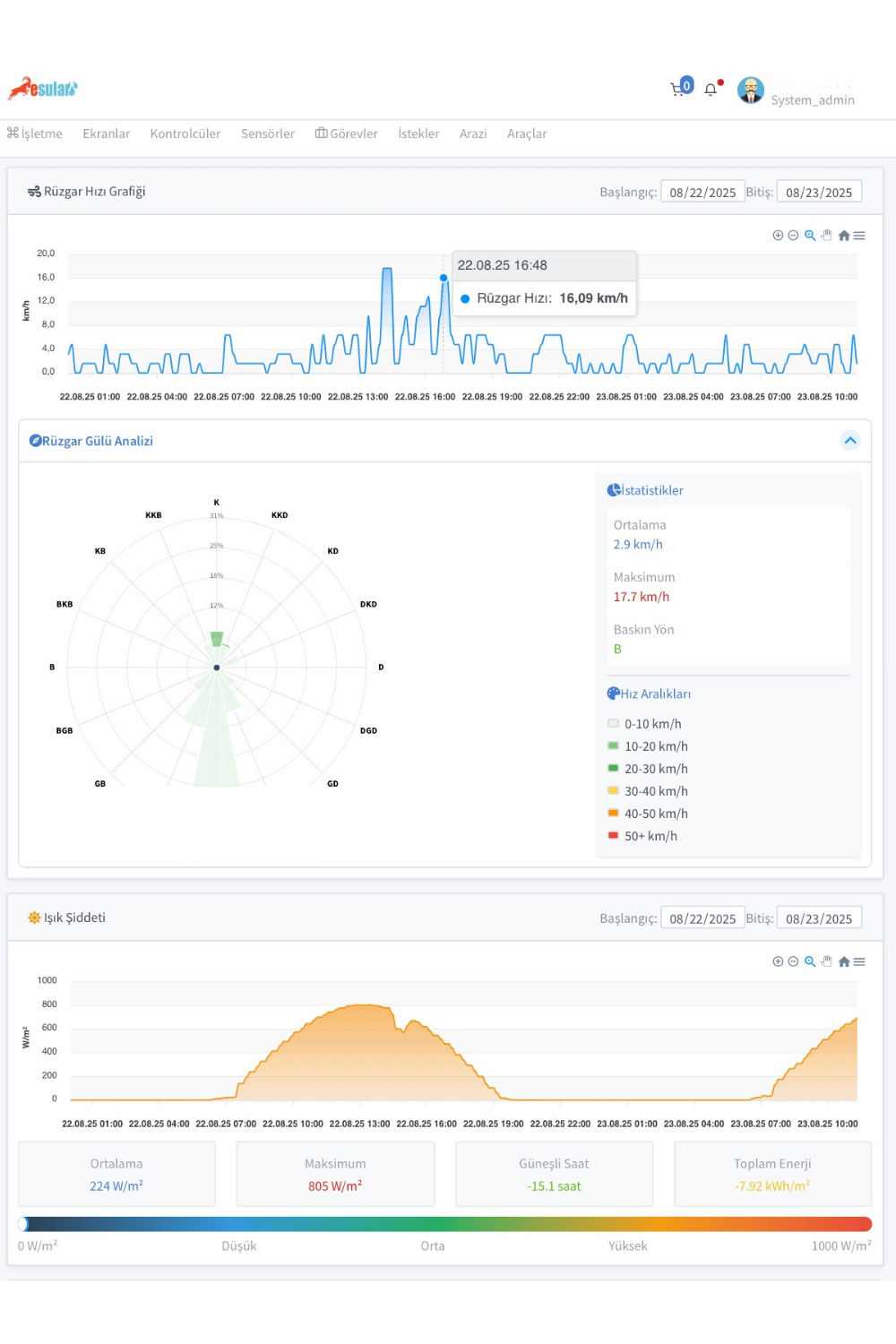

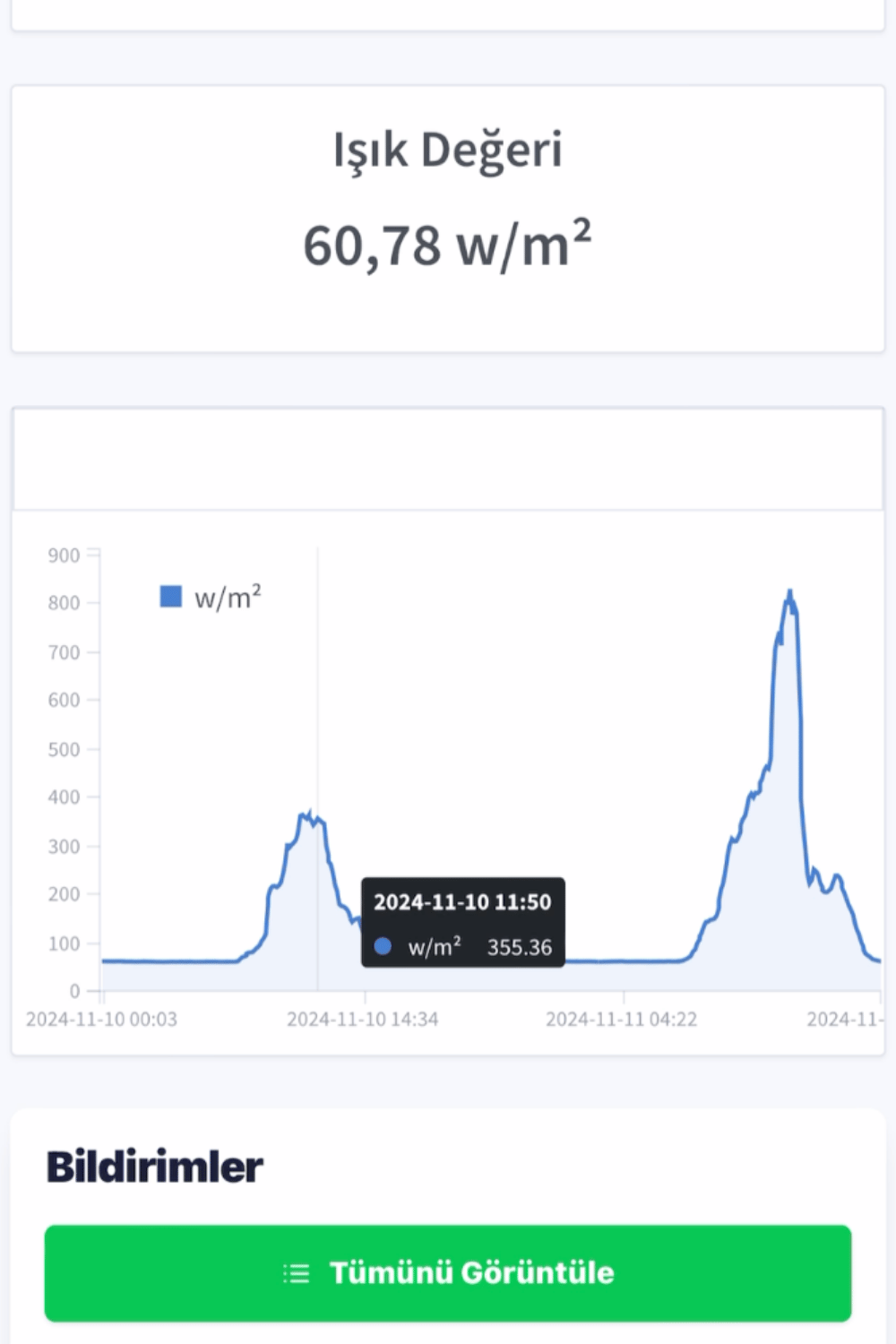
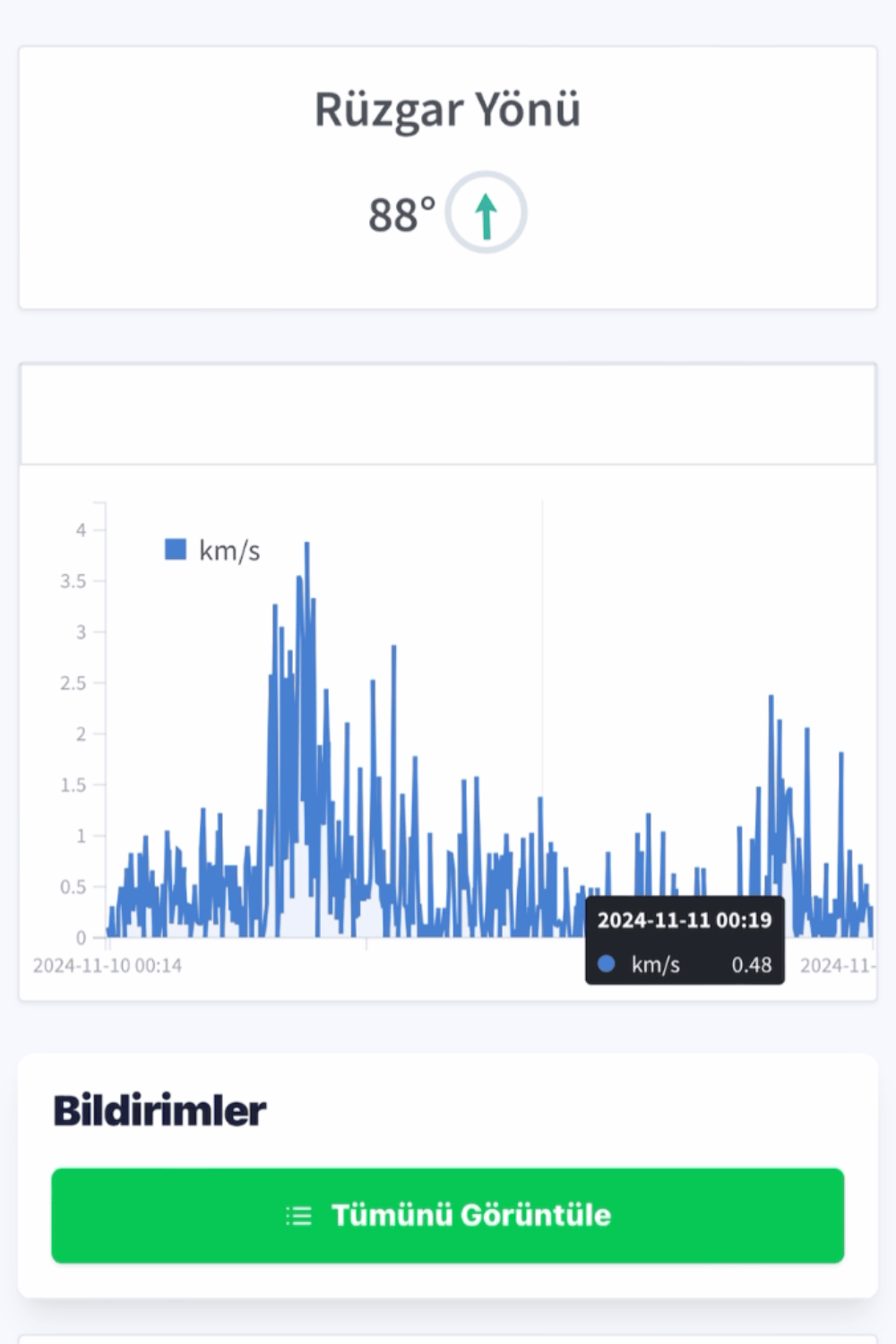
İklim-Meteoroloji İstasyonu
İklim-meteoroloji istasyonu, atmosferin fiziksel durumunu izlemek ve kaydetmek için kullanılan ölçüm cihazıdır. Bu istasyonlar, çeşitli sensörleri kullanarak çeşitli meteorolojik parametreleri ölçer ve kaydeder. Bu ölçülen veriler arasında sıcaklık, basınç, rüzgâr hızı ve yönü, nem, yağış türü ve...
Teknik Özellikler
| Boyut | 217 x 30 |
|---|---|
| Doküman | Teknik Dokümantasyon Mevcut |
Ürün Açıklaması
İklim-meteoroloji istasyonu, atmosferin fiziksel durumunu izlemek ve kaydetmek için kullanılan ölçüm cihazıdır. Bu istasyonlar, çeşitli sensörleri kullanarak çeşitli meteorolojik parametreleri ölçer ve kaydeder. Bu ölçülen veriler arasında sıcaklık, basınç, rüzgâr hızı ve yönü, nem, yağış türü ve yoğunluğu gibi parametreler bulunur. Kablosuz sistemlerimiz sayesinde, kablolamanın yaratacağı zorluklar olmadan hızlı ve pratik şekilde iklim istasyonunu arazinizde devreye alabilirsiniz. İklim ve Meteoroloji İstasyonu, çeşitli meteorolojik verileri anlık, saatlik ve günlük olarak ölçme işlevine sahiptir. Kendinden solar panelli ve şarjlı pilli yapısı sayesinde kolayca ölçekleyebilirsiniz.
İklim-Meteoroloji İstasyonu
İklim istasyonları, tarım sektöründe oldukça önemli bir rol oynar. Bu istasyonlar, hava durumu ve iklim koşulları hakkında detaylı veriler toplayarak çiftçilere değerli bilgiler sunar. Sıcaklık, nem, yağış miktarı, rüzgar hızı ve güneş ışınımı gibi faktörler, bitki büyümesini ve verimini doğrudan etkiler. İklim istasyonları sayesinde çiftçiler, ekim ve hasat zamanlarını daha doğru bir şekilde planlayabilir, sulama ve gübreleme stratejilerini optimize edebilir ve zararlı böcekler veya hastalıklar için önleyici tedbirler alabilirler. Bu sayede, tarımsal verimlilik artar ve kaynak kullanımı daha sürdürülebilir bir hale gelir. Ayrıca, uzun vadeli iklim verileri, tarım politikalarının ve stratejilerinin geliştirilmesine de katkı sağlar.
İklim-Meteoroloji İstasyonu Kullanmanın Faydaları:
Bu sensörler sayesinde tarımsal, sera, bahçe ve diğer açık alanlardaki faaliyetlerinizi daha verimli, sürdürülebilir ve karlı hale getirebilirsiniz!
Daha fazla bilgi için lütfen Esular ile iletişime geçin.
İklim-Meteoroloji istasyonu Genel Özellikler:
- İklim istasyonu sıcaklık, nem oranı, ruzgar hızı ve yönu, solar radyasyon, hava basıncı, yağış miktarı gibi verileri ölçer.
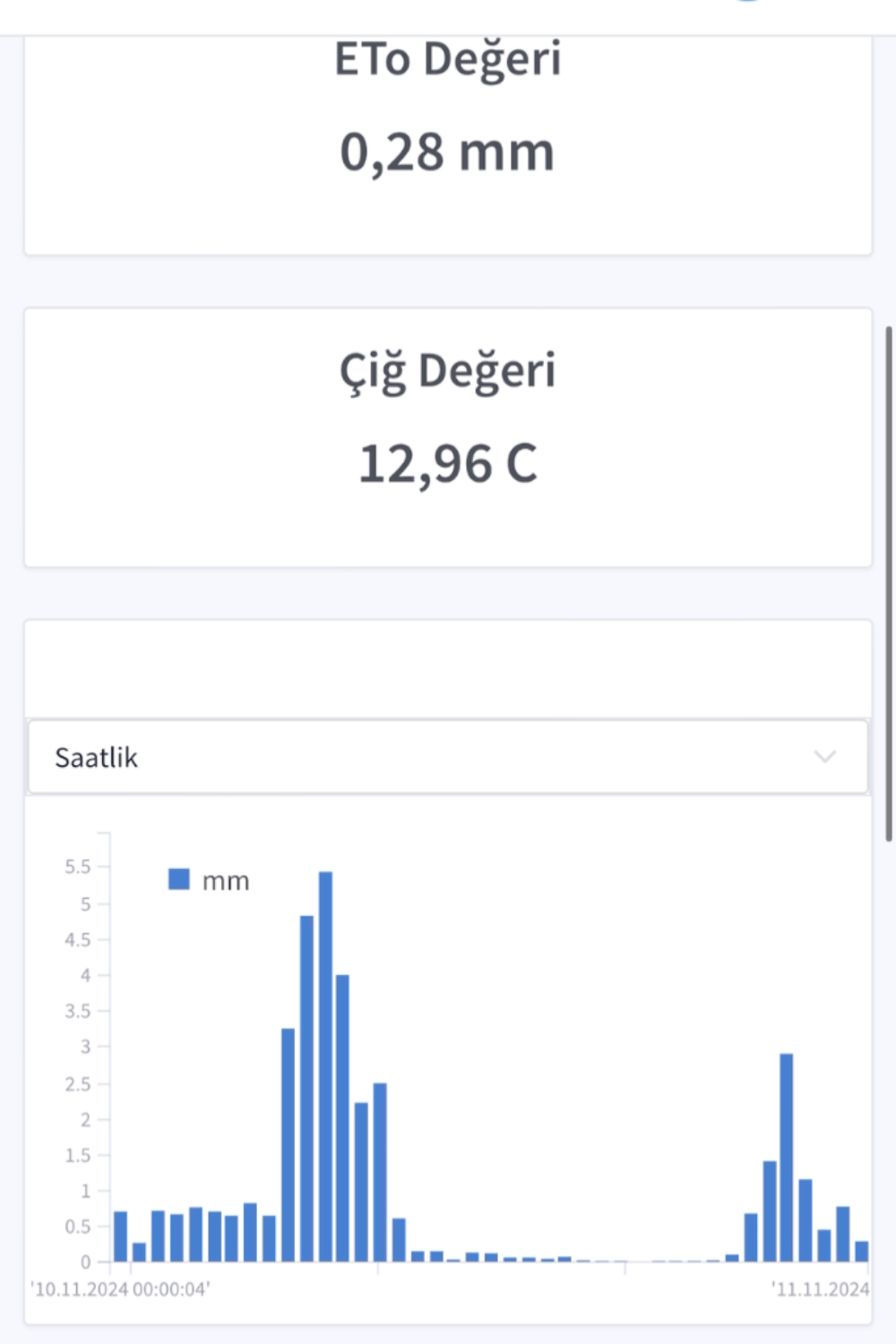
- Yağış miktarı sensöru, mm cinsinden yağan yağışın miktarını ölçer. Yağış tespit amacı ile kullanılabilir. En az 0.2mm yağış olmalıdır.
- Sulama takvimi oluşturma
- Verileri gece gündüz sürekli ölçer.
- Buharlaşma(Eto) ve bitki su ihtiyacı takibi
- RS485 çıkış ve modbus haberleşme özelliği vardır.
- Kablosuz, kendinden güneş panelli şarjlı pil ile güneş olmasa dahi 1 yıl boyunca çalışmasına devam eder.
- Kendinden güneş panelli şarjlı pil ile ek enerji ihtiyacı olmadan çalışır.
- 5000 mAh dahili şarjlı pile sahiptir.
- Alarmlar ve izlemler
- İnternet uzerinden sürekli takip IP65 su geçirmez yapıdadır.
- Kapanıp açılması durumunda herhangi bir veri kaybı olmaz.
- Cihaz LoRa modülasyonu ve LoRaWAN protokolu ile çalışmaktadır. EU-868 Mhz frekans bandı ve 14dB çıkış gucune sahiptir.
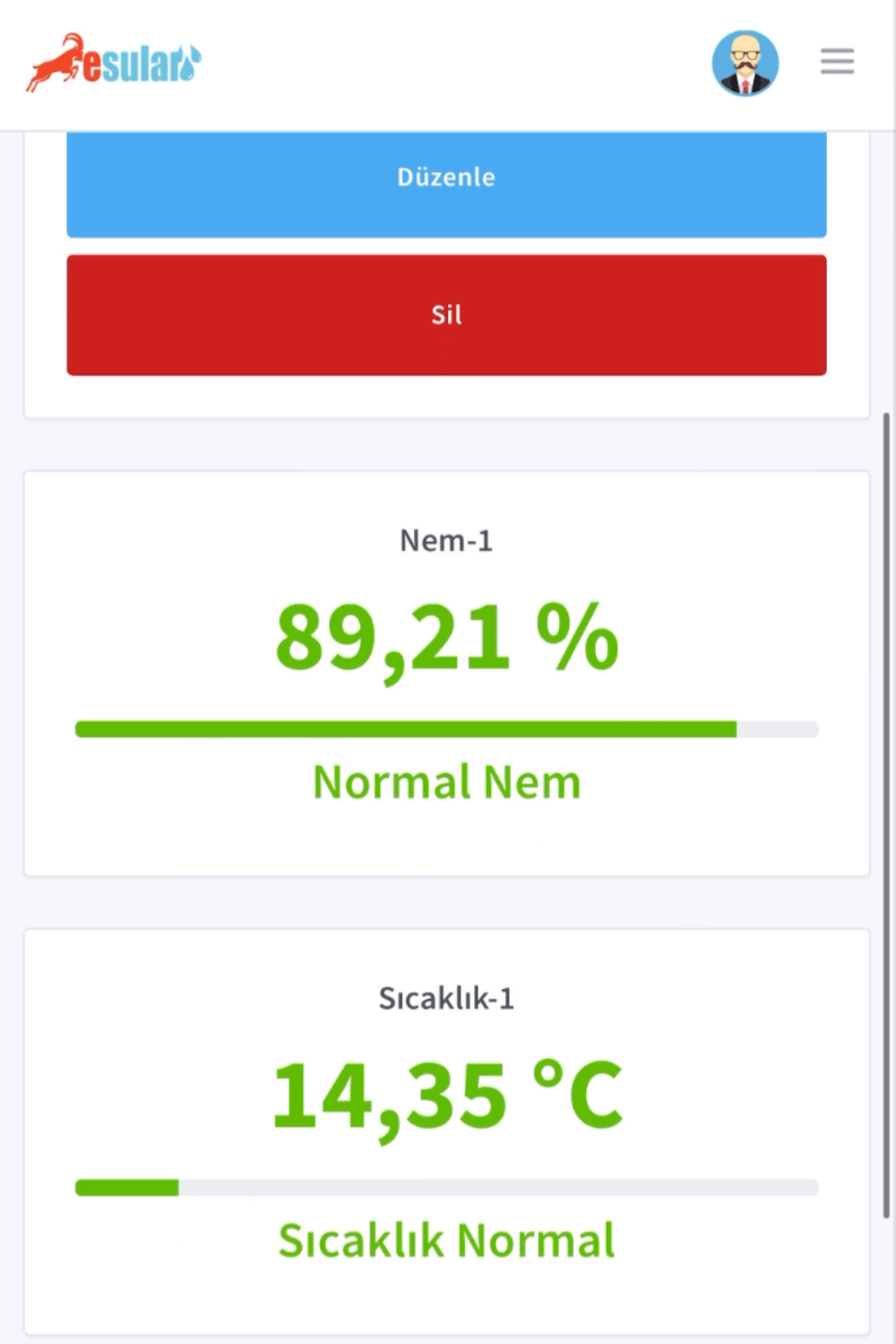
Dış Ortam Nem-Sıcaklık Ölçümü
- Havadaki nemin yoğunlaşmaya başladığı sıcaklığı ölçer.
- Havanın sıcaklığını ve nemini ölçer.
- Verileri gece gündüz sürekli ölçer.
- Nem ölçüm aralığı: 0 – 100% RH
- Nem ölçüm hassasiyeti: ±2% Bağıl Nem @ 0 Bağıl Nem ~ %100 Bağıl Nem (25°C’de)
- Sıcaklık ölçüm aralığı: -40 – 125°C
- Sıcaklık ölçüm doğruluğu: ±0.2°C@0°C-90°C (Tipik)
Solar Radyasyon Sensörü (Piranometre)
- Güneşten gelen ışınım değerlerinin ölçümünü yapar.
- Çalışma Ortamı: -25°C – 60°C, %0-100%RH
- Spektral aralığı: güneş ışığı
- Ölçüm Aralığı: 0-1800W/m²
- Çözünürlük: 1W/m²
- Tepki Süresi: 320S
- Doğrusal Olmayan: <±3%
- Yıllık Kararlılık: ≤±3%
Yağış Miktarı Sensörü
- Yağmur miktarını ve yağmur yoğunluğunu ölçer.
- Ölçüm aralığı: Sıfırın üzerindeki koşullarda saatte 600mm’ye kadar.
- Çalışma Sıcaklığı: -40°C…80°C
- Çözünürlük: 0.1, 0.2, 0.25 mm (0.01”)
- Kararlılık: <0.0125 mm her yıl
- Doğruluk: <100 mm/saat yağmur oranlarında %1’den az
- Başlangıç Eşiği: Çözünürlük + 0.07 mm (0.0027”)
- Yağmur Algılama Alanı: 200 cm² (0.16 m², 6.3”)
- Kablosuz Ağ Uyumluluğu: Tüm bölgeler LoRaWAN
Rüzgar Hız Sensörü
- 0.5 m/s ile 55 m/s arasındaki yatay rüzgar hızını ölçer.
- Ölçüm Aralığı: 0.5 m/s – 50 m/s
- Ölçüm: ≤ 0.5 m/s, 0.05 m/s (≤5 m/s)
- Hassasiyet: ±0.5 m/s (≤5 m/s)
- Çalışma Sıcaklık Aralığı: -20 … +85°C, ≤95% bağıl nem
- Maksimum Rüzgar Hızı: Maksimum 30 dakikada 70 m/s
- Koruma: IP65
Rüzgar Yön Sensörü
- Yatay rüzgarın 360° derece yönünü doğru şekilde ölçer.
- Ölçüm Aralığı: 0°-360°
- Başlangıç rüzgar hızı: <0.5m/s
- Limit Rüzgar Hızı: >70m/s
- Yön: 16 yön
- Çözünürlük: 22.5°
- Doğruluk: ±3°
- Çalışma nemi: 0 % – 95 % RH
- Çalışma sıcaklığı: -20 °C- +85 °C
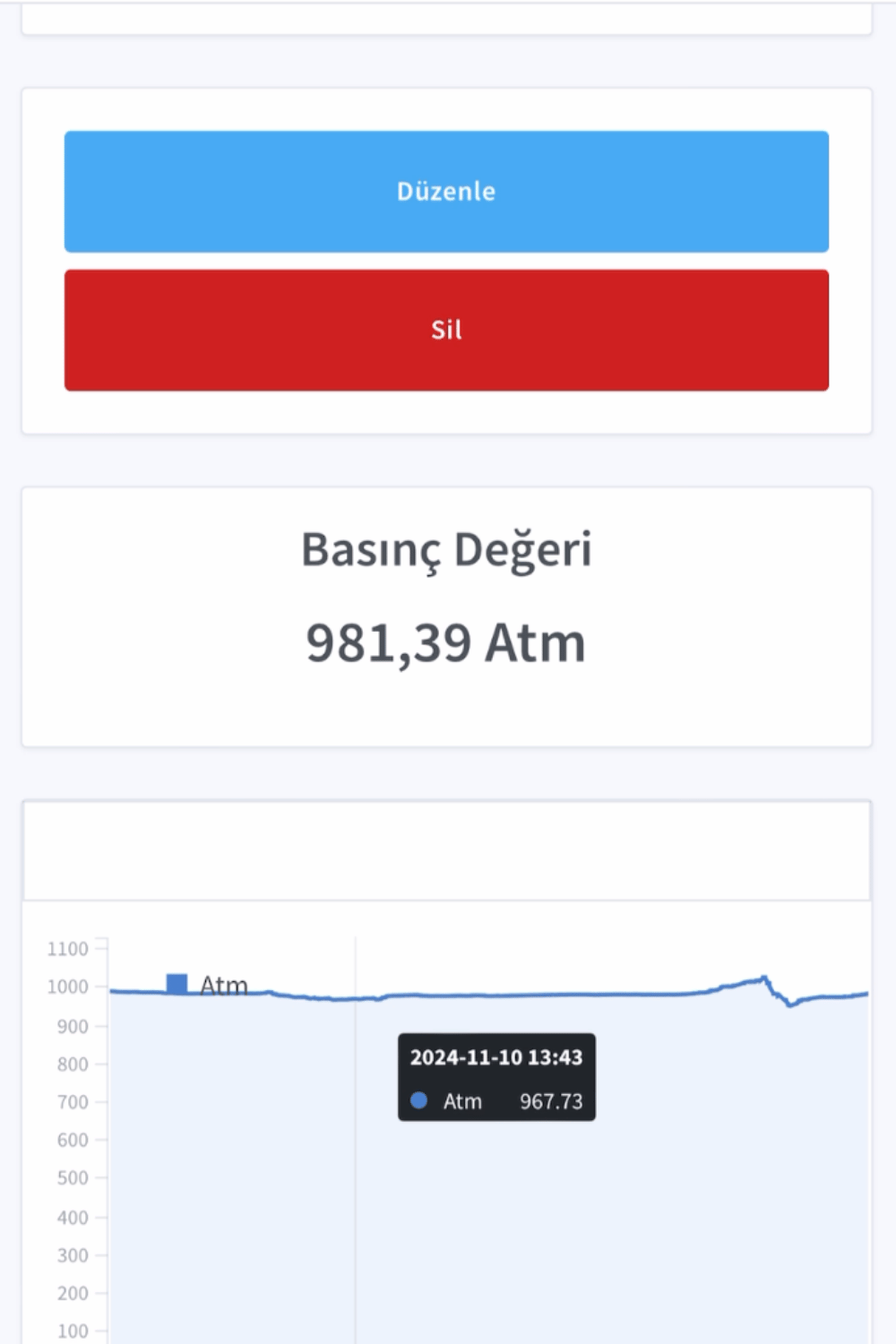
Atmosferik Basınç Sensörü
- Ortamdaki anlık hava basıncını ölçer.
- 300-1100hPa arasındaki basınç değerini ölçer
- 0.03 hPa (0,25metre) gibi çok yüksek bir çözünürlüğe sahiptir
Uygulama Alanları
- Akıllı Tarım Uygulamaları
- Akıllı Sera Uygulamaları
- Akıllı Peyzaj Uygulamaları
- Dikey Tarım Uygulamaları
- Akıllı Sulama Sistemleri
- Topraksız Tarım Uygulamaları
- SCADA Sistemleri
- IoT (Internet of Things)
- Park, Bahçe Akıllı Sulama Çözümleri
- LoRa / LoRaWAN Sensör Uygulamaları
- Çimlendirme, Köklendirme Otomasyonu
Teknik Dökümanlar
Ürün hakkında detaylı bilgi için dökümanları indirin
