What Are Smart Irrigation Technologies?
Smart irrigation technologies are modern irrigation solutions that operate with sensor data, data analytics, and automation systems. These systems analyze the plant's actual needs and ensure irrigation is done at the right time and in the right amount.
Main features:
- Analysis of soil moisture and environmental data
- Automatic irrigation planning
- Water and energy saving
- Remote control and real-time data tracking
- Automation structure that reduces human error
- Continuous learning with an AI-supported analysis system
Thanks to smart irrigation, production costs decrease while efficiency increases. Additionally, a more resilient agricultural model is created against risks caused by climate change.
How Does a Smart Irrigation System Work?
A smart irrigation system gains functionality through the collaborative operation of sensors, control units, automation, and artificial intelligence software. The system continuously collects data and dynamically updates irrigation decisions.
Operating principle:
1. Sensors measure soil moisture and weather conditions.
2. The control unit analyzes the incoming data.
3. The plant's water need is determined.
4. Valves and pumps are automatically activated.
5. The user can monitor the system 24/7 via mobile application or web panel and intervene instantly.
Thanks to this structure:
· Unnecessary irrigation is prevented
· Rainfall data is taken into account
· Plant root health is protected
· Water resources are used efficiently
· Irrigation planning is done
· Loss, leakage, and fault situations are minimized
· More controlled and efficient irrigation is performed thanks to the smart irrigation system
· Time and labor are saved
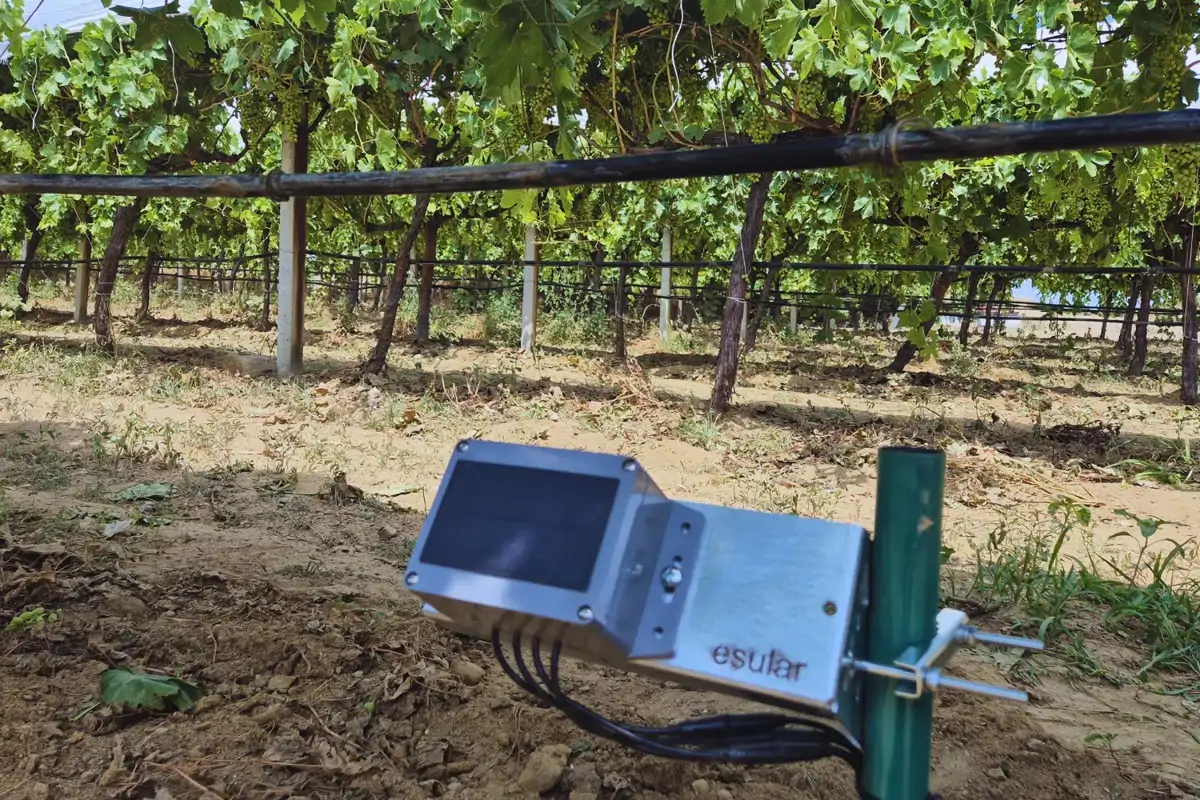

What Are the Components of a Smart Irrigation System?
Smart irrigation systems are formed by the integrated operation of different technological parts. Each component increases the accuracy and efficiency of the system.

1. Sensors
It is the data collection center of the system.
· Soil moisture sensor
· Soil temperature sensor
· Ambient humidity sensor
· Ambient temperature sensor
· pH sensor
· EC sensor
· Rain sensor
· Solar radiation sensor
· Wind speed and direction sensor
· Pressure sensor
2. Control Unit
It functions as the brain of the system.
· Analyzes sensor data
· Determines irrigation timing
· Creates an automatic decision mechanism
· Ensures automatic operation of irrigation planning and irrigation schedule
3. Valves and Pump Systems
· Controls water flow
· Ensures irrigation with correct pressure
4. Climate Meteorology Stations
· Analyzes external environment data
· Evaporation (Evapotranspiration) ETo is calculated
· Creates an irrigation plan based on ETo and precipitation forecasts
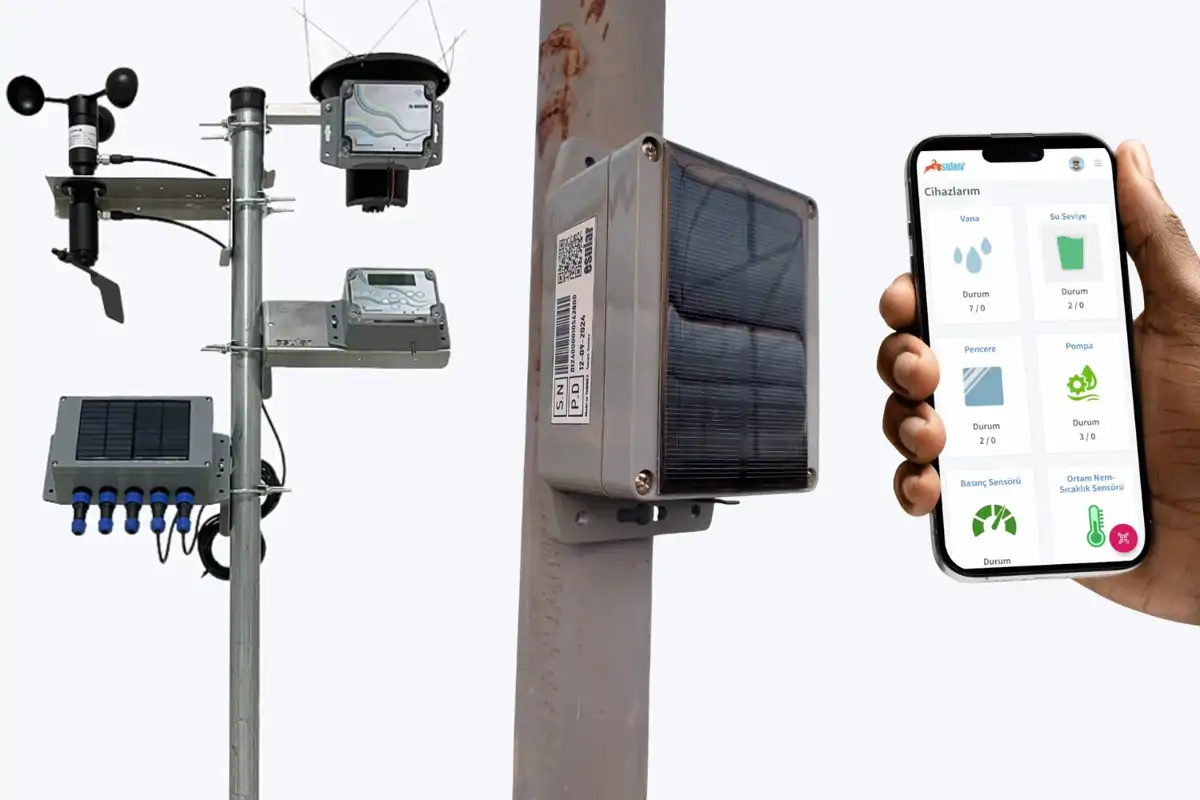
5. Data Communication and Remote Management
· Web&Mobile application integration
· IoT connectivity infrastructure
· Wireless digital infrastructure
· Thanks to its self-contained solar panel and rechargeable battery structure, it does not create additional energy costs
· Real-time data tracking
· Instant management
Sensor Solutions and Their Use in Agriculture
Sensor solutions and technologies form the foundation of smart irrigation systems. Sensor solutions strengthen the decision-making mechanism by instantly measuring environmental conditions.
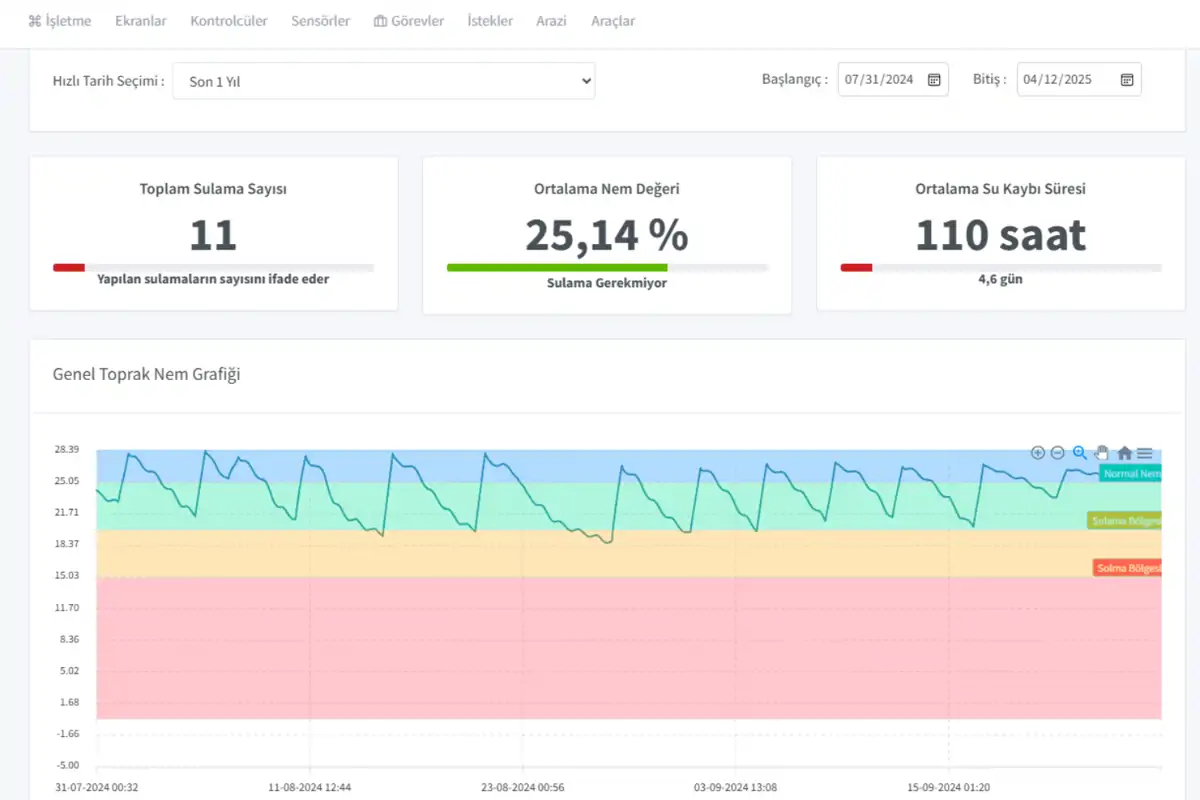
Prominent sensors:
Soil Moisture Sensors
Thanks to soil moisture sensors, the plant's instant water need is determined. It directly determines the plant's water need. It prevents over or under irrigation.
Temperature and Humidity Sensors
Temperature and humidity sensors continuously measure the ambient temperature and humidity values. They monitor environmental conditions to prevent plant stress. This ensures the plant is grown at optimum temperature and humidity levels.
Rain Sensors
Rain sensors measure the amount of rainfall. When sufficient rainfall is detected, it automatically stops irrigation. A rain sensor is very important in irrigation planning. Thanks to this sensor, unnecessary irrigation is prevented, and plant yield and quality are not negatively affected by excessive irrigation.
Solar Radiation Sensors
Solar radiation sensors analyze photosynthesis conditions and optimize the irrigation strategy. Does the plant receive enough light for favorable photosynthesis? It answers questions like how is the plant's photosynthesis efficiency. It is used in ETo calculation.
Wind Sensors
Wind speed and direction sensors are among the foremost climatic data. They play a vital role in planning both irrigation processes and processes such as fertilization and spraying. It ensures that agricultural processes such as irrigation, fertilization, and spraying are carried out at the most appropriate time.
In this way, many agricultural sensor solutions work in an integrated manner. The Esular ecosystem also supports all these sensors and various other agricultural sensors. All sensors provide practical installation and ease of use thanks to Esular's wireless digital infrastructure. Thanks to the cloud-based central software infrastructure, processes such as irrigation and fertilization can be monitored, controlled, and managed from any desired location and time. With web&mobile applications, it becomes possible to manage the system 24/7. Remote monitoring is possible in large agricultural areas thanks to wireless sensor systems.
Benefits of Smart Irrigation Systems
Smart irrigation systems are indispensable for efficient agricultural production. They offer both economic and environmental advantages.
Main benefits:
· Water savings of up to 30-50%
· Reduction in energy costs
· Improvement in plant development
· Reduction in disease risk
· Time saving thanks to remote control
· Increase in agricultural productivity
· Protection of natural resources
· Reduction in labor costs
· Increase in product quality
· Enables climate-resilient production
Furthermore, thanks to the data-based decision mechanism, producers can develop more accurate strategies.

Contribution of Smart Irrigation Systems to Sustainable Agriculture
Smart irrigation systems are at the heart of sustainability goals. Sustainable agriculture requires the balanced use of natural resources. Smart irrigation systems play an important role in achieving this goal.
Contributions:
· Protection of water resources
· Provides irrigation-related energy optimization
· Reduction of carbon footprint
· Protection of soil structure
· Reduction of chemical use necessity
· Adaptation to climate change
· Environmental damage is minimized
· More predictable and controlled production is achieved
· Increased production efficiency supports the continuity and sustainability of the agricultural sector
These systems are one of the fundamental building blocks of the future digital agriculture model.

The Future of Smart Irrigation Technologies
With the development of IoT, artificial intelligence, and data analytics technologies, smart irrigation systems are further evolving.
Expected trends:
· AI-supported irrigation decisions
· Satellite data integration
· Autonomous farming systems
· Multi-sensor analyses
· Energy-efficient solar-powered solutions
Thanks to these developments, agriculture will become more digital, more sustainable, and more efficient.
Conclusion
With the widespread adoption of smart farming practices, the question "What are Smart Irrigation Technologies and Systems?" is becoming increasingly important. Thanks to sensor technologies, automation systems, and data analysis, modern irrigation solutions provide great advantages in terms of both efficiency and sustainability.
Smart irrigation systems:
· Provide water and energy savings
· Protect plant health
· Reduce production costs
· Increase production efficiency
· Save labor and time
· Support environmentally friendly agriculture
Understanding and implementing smart irrigation technologies correctly is of critical importance for the agriculture of the future.

Sıkça Sorulan Sorular
How does a smart irrigation system work?
Smart irrigation systems analyze soil and weather data from sensors to perform irrigation processes smartly and automatically.
Do smart irrigation systems require manual intervention?
No, the system operates automatically. It can be controlled remotely 24/7 instantly.
Which sensors are used?
Soil moisture, temperature, rain, solar radiation, light, and wind speed and direction sensors are common.
What is the energy source?
It operates wirelessly. Thanks to its self-contained solar panel and rechargeable battery structure, it does not require additional energy.
What are the components of smart irrigation systems?
Wireless sensors, control units, central station, and web&mobile applications.
For which plants are smart irrigation systems suitable?
They are suitable for field and garden crops, greenhouse plants, parks, gardens, landscape areas, and all plants and processes where water is used in industrial facilities.
Does it save water?
Yes, it provides significant savings by irrigating only when needed.
Can it be controlled from a mobile phone?
Yes, the system is managed via web and mobile applications.
How do smart irrigation systems support sustainable agriculture?
They prevent the waste of natural resources such as water and energy. This prevents the plant from being under or over-irrigated. The controlled and smart execution of the irrigation process increases crop yield. Environmental damage is prevented. Resource optimization both increases efficiency and reduces carbon emissions.
Is smart irrigation system installation difficult?
Esular system and solutions operate completely wirelessly. They do not require any cabling. They do not need an additional energy source. Thanks to its plug&play structure, installation is done quickly. Installation and use are practical.
What exactly are smart irrigation technologies and what are their differences from traditional methods?
Smart irrigation technologies are modern systems that analyze information from various sources such as soil moisture sensors and meteorological data to determine the actual water needs of plants and automatically optimize irrigation accordingly. Unlike traditional irrigation methods, these systems minimize human error, prevent unnecessary water usage, and dynamically update irrigation schedules to maximize both efficiency and resource savings. In this way, farmers can use valuable resources such as water and energy much more consciously and efficiently.
What is the operating principle of a smart irrigation system and how does it increase efficiency in agriculture?
Smart irrigation systems work by continuously collecting data from sensors in the field (soil moisture, temperature, etc.) and climate stations (rainfall, wind, etc.). This data is analyzed by a central control unit, and after the plant's instant water need is determined, irrigation valves and pumps are automatically activated or deactivated. Thanks to this principle, plants are always kept at ideal moisture levels, water and fertilizer waste is prevented, disease risk is reduced, and as a result, product quality and efficiency are significantly increased.
What are the main components of a smart irrigation system and what are their functions?
A smart irrigation system typically consists of sensors, a control unit, valves and pump systems, climate/meteorology stations, and data communication and remote management infrastructure. Sensors collect environmental data, while the control unit analyzes this data to make irrigation decisions and manages the valves and pumps. Climate stations evaluate external environmental conditions, and thanks to the IoT-based communication infrastructure, users can monitor and control the system 24/7 via mobile or web applications.
How much water and energy savings can be achieved with smart irrigation systems?
Smart irrigation systems can achieve water savings of 30% to 50% by irrigating only when and in the amount the plant needs. This optimization also leads to significant reductions in energy costs, as irrigation pumps operate less. These savings both reduce operating expenses and directly contribute to the conservation of natural resources.
In what types of agricultural areas or for which plants can smart irrigation systems be used?
Smart irrigation systems have a very wide range of applications and can be implemented in all types of areas where water is used, from field crops to garden plants, from greenhouses to parks and landscape areas. Thanks to versatile sensor and automation solutions, they can be customized according to the specific water needs of different plant species. This flexibility ensures that Esular solutions are preferred in agricultural and urban areas of various scales, including industrial facilities.
How easy is the installation and use of smart irrigation systems?
Modern smart irrigation systems like Esular are designed with a user-friendly approach; they operate completely wirelessly, thus requiring no complex cabling, and can be quickly installed using a plug-and-play principle. Systems generally do not require an external energy source, thanks to integrated solar panels and rechargeable batteries, which reduces installation and operating costs. As they can be easily managed via mobile and web applications, users can monitor and control the system from anywhere.
How do smart irrigation systems contribute to sustainable agriculture goals?
Smart irrigation systems form the basis of sustainable agriculture by preventing the waste of critical natural resources such as water and energy. These systems prevent over or under-irrigation of plants, thereby protecting soil structure, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, and lowering the carbon footprint. Through resource optimization, they support the continuity of agricultural production while also offering a more resilient and environmentally friendly production model against climate change.
What are the main types of sensors used in smart irrigation systems and what are their functions?
In smart irrigation systems, soil moisture sensors determine the plant's instant water needs, while temperature and humidity sensors monitor environmental conditions to prevent plant stress. Rain sensors prevent unnecessary irrigation, solar radiation sensors analyze photosynthesis conditions, and wind sensors ensure that processes such as irrigation, fertilization, and spraying are carried out at the most appropriate time. The integrated operation of these sensors ensures that irrigation decisions are based on scientific data and agricultural efficiency is increased.