Classification of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Sensors
There are several types of classification for carbon dioxide (CO2) sensors, and understanding CO2 sensor types is useful in the selection process. Generally, CO2 sensors can be classified according to their operating principles as electrochemical, infrared, and photoacoustic. The operating principles and general characteristics of each type are explained in the table below:

| Sensor type | Principle | General characteristics |
| Electrochemical Sensor | Converts the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) into an electrical signal through electrochemical reactions. |
|
| Infrared sensor | Measures CO2 concentration by detecting the absorption of specific wavelengths of infrared light by carbon dioxide (CO2) molecules. | Non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) sensor:
|
| ||
| Photoacoustic Sensor | It measures CO2 concentration by detecting the absorption of light at certain wavelengths by CO2 molecules or the interaction between CO2 molecules and vibrations or sound waves. |
|

The Best Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Sensors for Greenhouses
Factors such as area, cultivated plants, and construction materials are effective in selecting the best carbon dioxide (CO2) sensors for greenhouses, and the selection can be made according to the actual situation. It is explained in detail in the table below.
Greenhouse factor | Important Factors | Selection of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Sensor | |
area | Small area (covers <100 square meters) | Measurement range, accuracy | NDIR sensor Important Factors |
Medium area (covers 100-1000 square meters) | Measurement range, accuracy | NDIR sensor or electrochemical sensor | |
Large area (covers >1000 square meters) | Measurement range, accuracy, energy consumption, price | Electrochemical sensor or dispersive infrared sensor | |
| Cultivated Plants | Plants with high carbon dioxide (CO2) needs (e.g., tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, and other C3 plants and vegetables) | Measurement range, accuracy, energy consumption | NDIR sensor |
Plants with low carbon dioxide (CO2) needs such as C4 plants and some shade-tolerant plants) | Measurement range, stability | NDIR sensor or electrochemical sensor | |
Construction materials | Materials with good carbon dioxide (CO2) retention capacity (double or multi-layer glass, polycarbonate panels, polyethylene film) | stability, accuracy | NDIR sensor |
Materials with significant CO2 loss (single-layer glass, transparent plastic film, metal materials) | Accuracy, response time | NDIR sensor or electrochemical sensor | |
Ventilation system | Well-ventilated system (adequate ventilation, uniform air distribution, good controllability) | Response time, stability, accuracy | NDIR sensor or electrochemical sensor |
Poor ventilation system (inadequate ventilation, non-uniform air distribution, lack of flexibility in control) | Measurement range, accuracy | NDIR sensor or dispersive infrared sensor | |
| Lighting system | More artificial light sources are used | Response time | NDIR sensor or electrochemical sensor |
| Primarily natural lighting | stability | NDIR sensor or dispersive infrared sensor | |
Control System | Used together with automatic control system | Accuracy, response time, stability | NDIR sensor or electrochemical sensor |
Used with an automatic control system | Accuracy, response time, stability | NDIR sensor or electrochemical sensor | |
| Location | indoor environment | Accuracy, response time | Photoacoustic sensor, infrared sensor or electrochemical sensor |
outdoor environment | Accuracy, response time, stability, energy consumption | infrared sensor or electrochemical sensor | |
In the greenhouse, photoacoustic sensors are relatively suitable for the indoor environment, while electrochemical sensors depend on some other factors. Among infrared sensor types, NDIR carbon dioxide (CO2) sensors are a widely used and versatile type. NDIR stands for Non-Dispersive Infrared Gas Analyzer, which uses the absorption properties of infrared light to measure gas concentration. It typically consists of an infrared light source, a sample chamber, a detector, and a signal processing circuit. This sensor can measure CO2 concentration quickly and accurately without being affected by other gases. It also has low energy consumption, long-term stability, and is suitable for long-term monitoring in greenhouse environments.

Installation of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Sensors in Greenhouses
During the installation of carbon dioxide (CO2) sensors in greenhouses, after selecting the appropriate carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor, proper installation and distribution are needed to effectively monitor the CO2 concentration in the greenhouse. Proper installation and distribution ensure the accuracy and stability of the sensor, allowing for accurate data collection and management in the smart greenhouse system. During installation, the following steps can be followed:
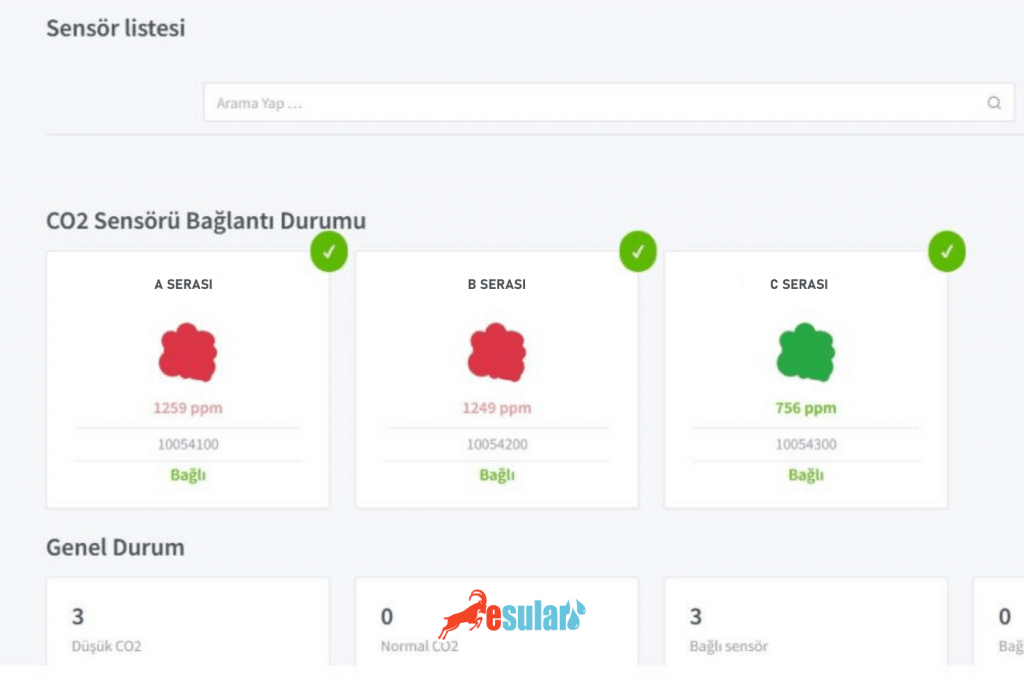
- Determining the sensor location
The sensor should be placed in the most representative area within the greenhouse, usually on walls or the ceiling at the height of plant growth. This allows for measuring the CO2 concentration around the plants. To prevent interference from fresh outdoor air that could cause inaccurate data within the greenhouse, the sensor should not be placed near ventilation ducts, exhaust pipes, or areas of high human activity.
- Installation of the sensor
Before installing the sensor, ensure that the installation site is level and that screws, expansion tubes, and other materials meet safety requirements. Additionally, some sensors may require connection to a power source or other devices. During installation, the instructions provided by the sensor manufacturer should be followed to ensure proper connection.
- Installation of the control unit
Connect the sensor to the data logger of the monitoring system to read and transmit CO2 concentration data. The connection method may vary depending on the sensor type; therefore, the sensor's instructions should be followed for guidance.
Sensor Parameterization
Calibration is required before using the sensor to ensure accurate CO2 readings. Some sensors have automatic calibration, while others require manual calibration. Before calibration, the accuracy and measurement range of the sensor should be checked. The calibration process should generally be carried out according to the instructions provided by the sensor manufacturer, which involves the use of its software.
- Parameterization of Sensor Signals
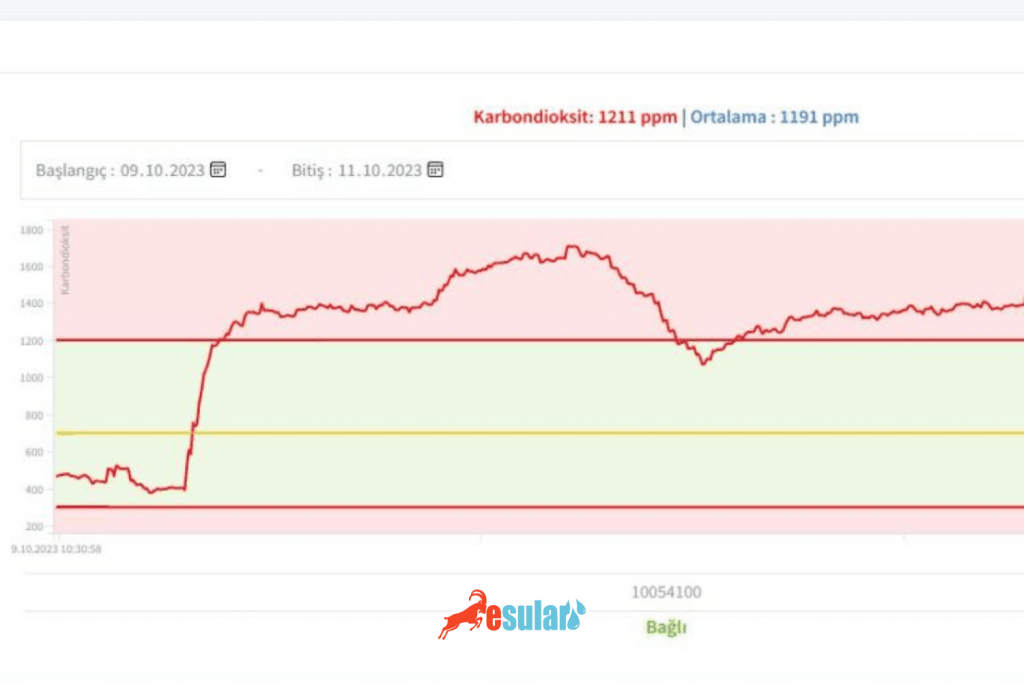
After installing and connecting the sensor, set up the monitoring system to start reading CO2 concentration data. Thresholds are often adjusted; thus, the system will generate alerts or automatically adjust CO2 levels within the greenhouse when the CO2 concentration exceeds or falls below specified limits.
- Sensor Monitoring and Maintenance
After the sensor is installed, the sensor's measurement results should be monitored regularly. Sensor batteries should be checked and replaced regularly to ensure proper operation.
Creating a carbon dioxide (CO2) monitoring system in a smart greenhouse and selecting an appropriate carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor is crucial for tracking CO2 concentration and supporting plant growth. When selecting a CO2 sensor, factors such as measurement range, accuracy, response time, stability, price, and energy consumption should be considered. While the use of versatile NDIR (Non-Dispersive Infrared) CO2 sensors is recommended in greenhouse scenarios, photoacoustic sensors can also be considered for indoor greenhouses. Proper installation and distribution are required to achieve optimal monitoring results with the appropriate CO2 sensor.


