Armillaria Root Rot
Symptoms
If the tree gets infected after reaching 5 years of age, typical symptoms include poor terminal growth and small leaves; in mid-summer the whole tree suddenly collapses; in orchards, trees usually die in a circular pattern; Infected trees usually have a fan-shaped white fungal mat growing between the crown bark and wood.
Causal Agent
Fungal
Development Conditions of the Disease
The fungus lives on dead roots; symptoms similar to Phytophthora root rot.
Control Methods
Once a tree is infected, there is no treatment and the tree must be removed, fumigants cannot adequately control fungi in the soil; Do not plant apricots in newly cleared forests or old orchards with a history of Armillaria.
Gray Mold in Apricots
Symptoms
Brown discoloration occurring under the fruit skin while flower parts are still attached to the fruit
Causal Agent
Fungal
Development Conditions of the Disease
Disease formation favored by wet conditions during flowering and jacket stage
Control Method
Fungicide treatment applied at full bloom.
Apricot Powdery Mildew
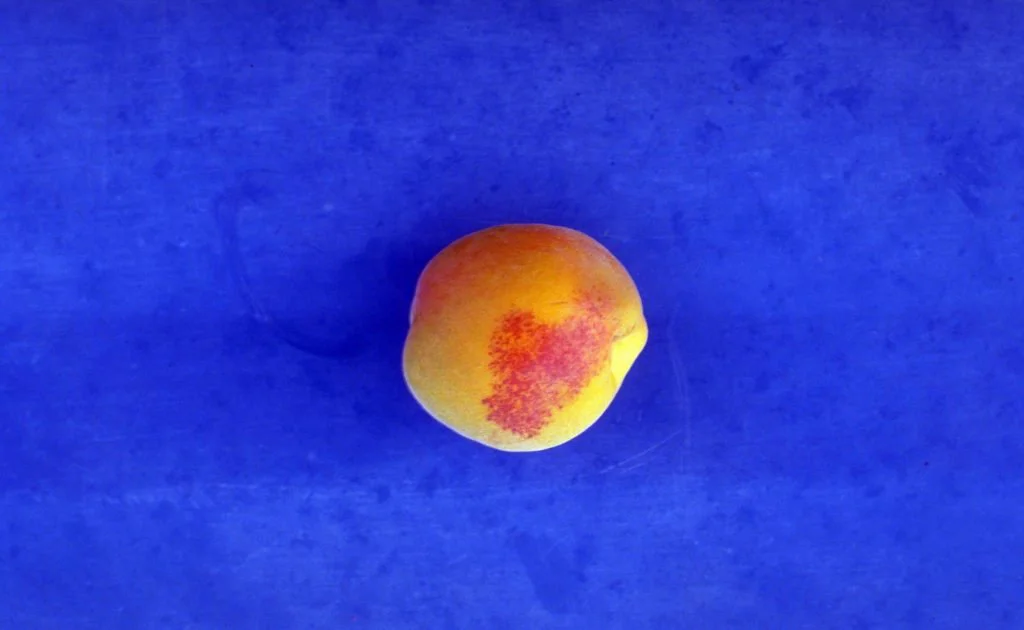
Symptoms
Round, powdery white fungal growth spots on fruit and leaves; rusty patches on fruits that turn brown and leathery and may crack.
Causal Agent
Fungal
Development Conditions of the Disease
Pannosa infects the plant in spring. P. tridactyla infects the plant in summer and autumn.
Control Methods
Apply fungicide during flowering and fruit development.
Monilia Disease in Apricots
Symptoms
Dark brown circular spots on the fruit; tan-colored spore masses may be visible in the center of the spots; diseased fruit may not fall from the tree
Causal Agent
Fungal
Development Conditions of the Disease
Fruit rot symptoms will appear 48 hours after rain.
Control Methods
If heavy rains are expected 2-3 weeks before harvest, a protective fungicide treatment may be necessary.
Apricot Rust
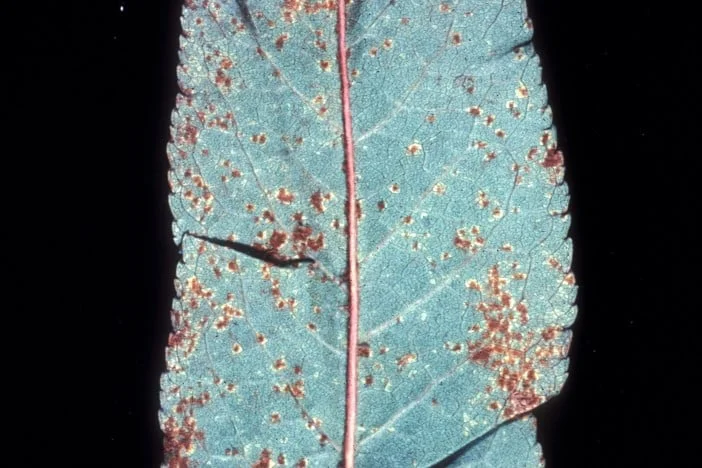
Symptoms
Pale yellow-green spots turning angular, bright yellow on the upper and lower surfaces of leaves; spots on the lower leaf surface develop orange-red spores.
Causal Agent
Fungal
Development Conditions of the Disease
The fungus overwinters on branches or leaves that remain attached to the tree.
Control Methods
Rust can be prevented by spraying trees with protective fungicides; In areas prone to disease outbreaks in the early season, application is usually made one, two, and three months before harvest, while in areas where the disease is less problematic or appears at the end of the season, it is done after harvest.
Shothole Disease in Apricots
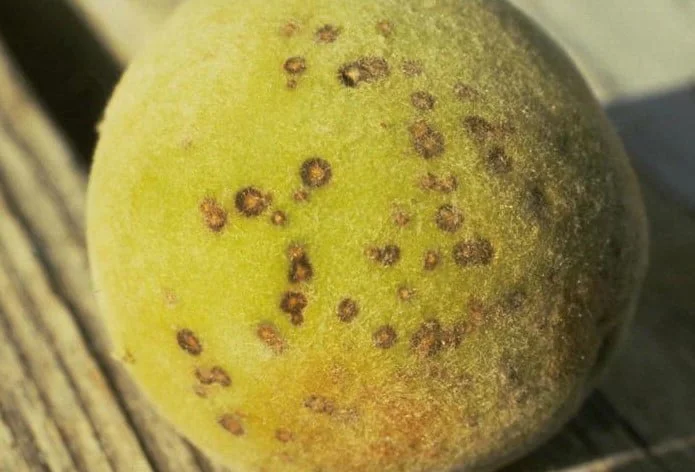

Symptoms
Brown lesions with purple margins on fruit, branches, and buds; holes in leaves due to dried and fallen lesions; brown lumps developing in the center of the lesion (visible with a hand lens); buds turning brown or black and exuding sap; tan lesions with brown margins exuding sap on branches.
Causal Agent
Fungal
Development Conditions of the Disease
The fungus survives in buds and branches; spores spread by splashing water.
Control Methods
Application of Bordeaux mixture in the fall before rains is sufficient to protect dormant buds and twigs throughout the winter.



Yorumlar