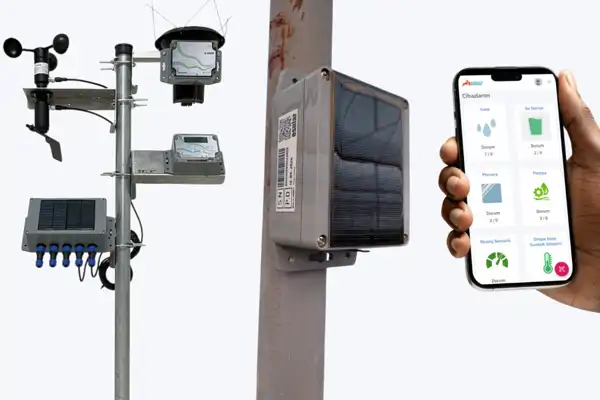
Smart Irrigation Technology-Controllers and Sensors
Smart irrigation technology offers revolutionary solutions in terms of efficient use of water resources and protection of plant health. Among the core components of this technology are controllers and sensors. While controllers function as the brain of the irrigation system, sensors collect soil moisture, weather, temperature, and other environmental data. Controllers analyze this data from sensors to determine irrigation time and amount, thus ensuring that water reaches the plants exactly when they need it and in the correct amount. Soil moisture sensors continuously monitor the moisture level in the root zone of plants, while weather sensors measure precipitation amount, temperature, and humidity, and sunlight sensors monitor the amount of sunlight plants receive. These two components work together to optimize irrigation processes and provide water in the most suitable way for the plants' needs. Consequently, smart irrigation technology prevents water waste, protects plant health, and contributes to environmental sustainability.
How Does a Smart Irrigation System Work?
The operating model of the smart irrigation system integrates advanced technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things), mobile internet, LORA (Long Range), and remote sensing monitoring. In these systems, automatic control valves are operated and managed wirelessly and remotely. By providing the correct amount of water according to plants, soil type, and weather conditions, water savings of more than 50% from irrigation water and 30-40% energy savings are achieved. The working principle of the smart irrigation system is based on the integration of various technologies such as sensor technology, wireless automatic control technology, and computer technology.
This system works by being combined with smart irrigation methods such as sprinkler irrigation and drip irrigation. Data obtained through soil moisture sensors, weather sensors, and other environmental sensors are transmitted to the central control unit. The control unit analyzes this data and automatically adjusts the irrigation schedule. Thus, the water needed by the plants is provided exactly on time and in the correct amount. Additionally, these systems are controlled remotely, minimizing the need for manual intervention and making irrigation processes more efficient. The smart irrigation system provides significant contributions to environmental sustainability by ensuring both water and energy savings and supports the healthy growth of plants.
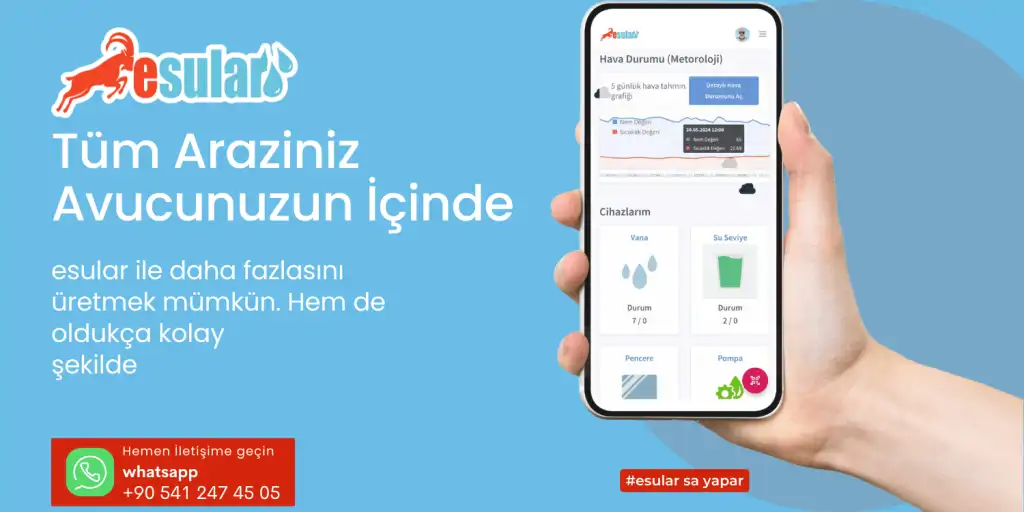
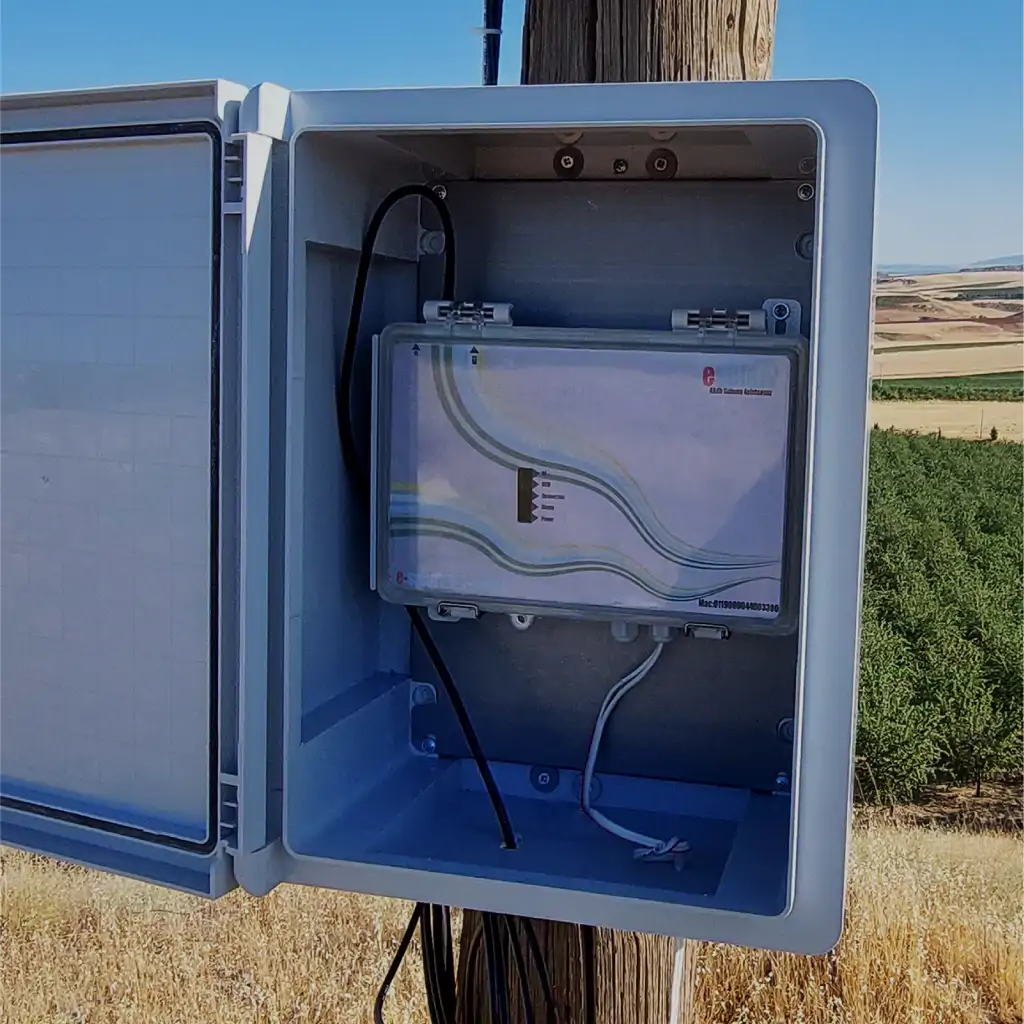
Smart Irrigation-Controllers
Controllers are the central management units of the irrigation system and play a role in the effective and accurate management of irrigation processes. As Esular, we offer advanced controller systems that work with GSM and are used as central stations. These controllers provide uninterrupted operation for up to 6 hours even in the event of a power outage, thanks to the rechargeable battery on them. Furthermore, they can read valves and sensors up to a distance of 10 km and control them up to a distance of 5 km; thus, the entire system has a completely expandable structure.
The controllers offered by Esular are equipped with 4 pump control outputs, 2 water meter inputs, and 2 4-20 ampere pressure sensor inputs. These features allow users to monitor and manage their irrigation systems in detail. Warnings can be created in cases such as excessive pressure or power failure, and these warnings are notified via SMS, so users are informed instantly. Our controllers support up to 128 valves and sensors, and up to 64 in-device automatic tasks can be added. These features increase the efficiency of the irrigation system while offering customized and automated solutions according to the needs of the users. As Esular, we are proud to offer advanced technologies that increase the efficiency and reliability of modern irrigation systems, contribute to environmental sustainability, and support the healthy growth of plants.

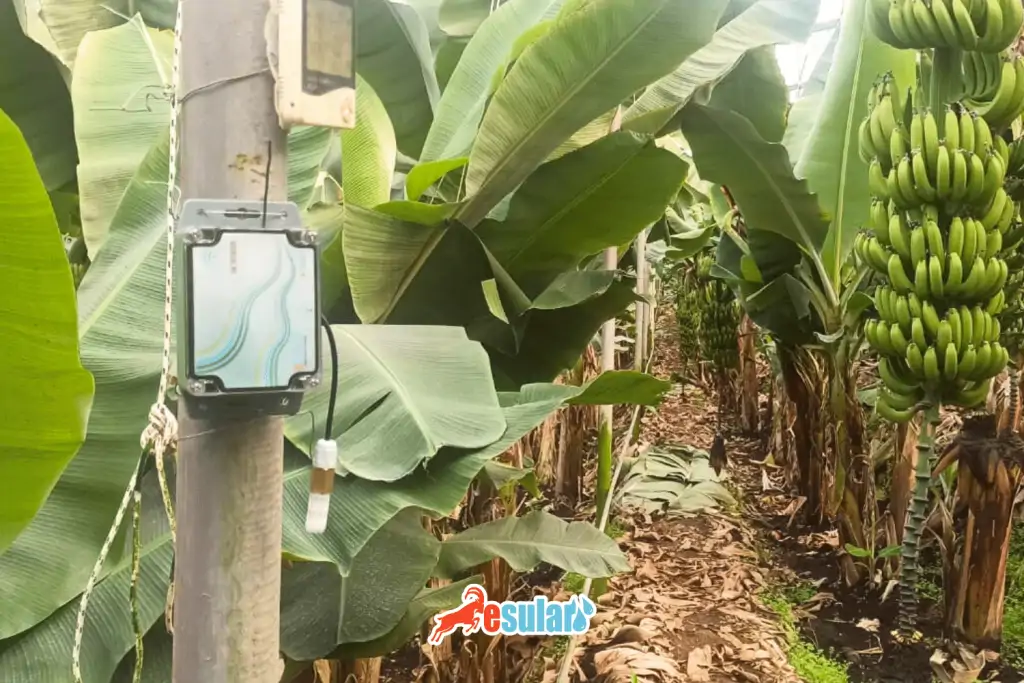
Smart Irrigation-Sensors
Smart irrigation systems use advanced sensor technologies for the efficient use of water resources and the protection of plant health. These sensors allow irrigation systems to collect and analyze environmental data, thus optimizing irrigation processes and adjusting them according to the needs of the plants. Here are the main sensors used in smart irrigation systems:
Pressure Sensors
Pressure sensors continuously monitor the water pressure in the irrigation system. These sensors measure pressure levels, send data to the controller, and prevent damage in cases of excessive pressure by adjusting the system's pressure when necessary. Additionally, they ensure the efficient operation of the system in cases of low pressure.
Soil Moisture Sensors
Soil moisture sensors continuously monitor the moisture level in the root zone of plants. These sensors measure the water content of the soil and send data to the controller. The controller analyzes this data and adjusts the irrigation time and amount. Thanks to soil moisture sensors, plants are given as much water as they need, and water waste is prevented. Additionally, plants are prevented from entering water stress, thus ensuring healthy and productive growth.

Ambient Humidity and Temperature Sensors
Ambient humidity and temperature sensors allow the irrigation system to accurately monitor environmental conditions. These sensors measure air temperature and humidity and transmit data to the controller. This data helps in adjusting irrigation schedules according to environmental conditions, so the water needs of the plants are met in the most suitable way.
EC and pH Sensors
Electrical conductivity (EC) and pH sensors monitor water and soil quality. EC sensors measure the salinity level of irrigation water, while pH sensors determine the acidity or alkalinity level of the water. This data is used to provide ideal water and soil conditions for the optimal growth of plants.
Precipitation Sensors
Precipitation sensors measure the amount of rain and send data to the irrigation system. Thanks to these sensors, irrigation can be stopped automatically when it rains, and water savings can be achieved. Additionally, precipitation sensors allow for more precise adjustment of irrigation schedules.

Wind Speed and Direction Sensors
Wind speed and direction sensors measure the speed and direction of the wind. This data is used to prevent water waste during irrigation. For example, irrigation can be postponed or adjusted in strong wind conditions.
Pool and Well Level Sensors
Pool and well level sensors monitor the water level at the source of the irrigation water. These sensors send a warning to the controller if the water level drops and ensure that necessary precautions are taken. This supports the sustainable use of water resources.
Solar Radiation Sensors
Solar radiation sensors monitor the amount of sunlight plants receive and optimize irrigation schedules based on this data. The water needs of the plants are determined according to the amount of sunlight, and irrigation durations are adjusted. These sensors support the photosynthesis process of plants and ensure the most efficient use of water.
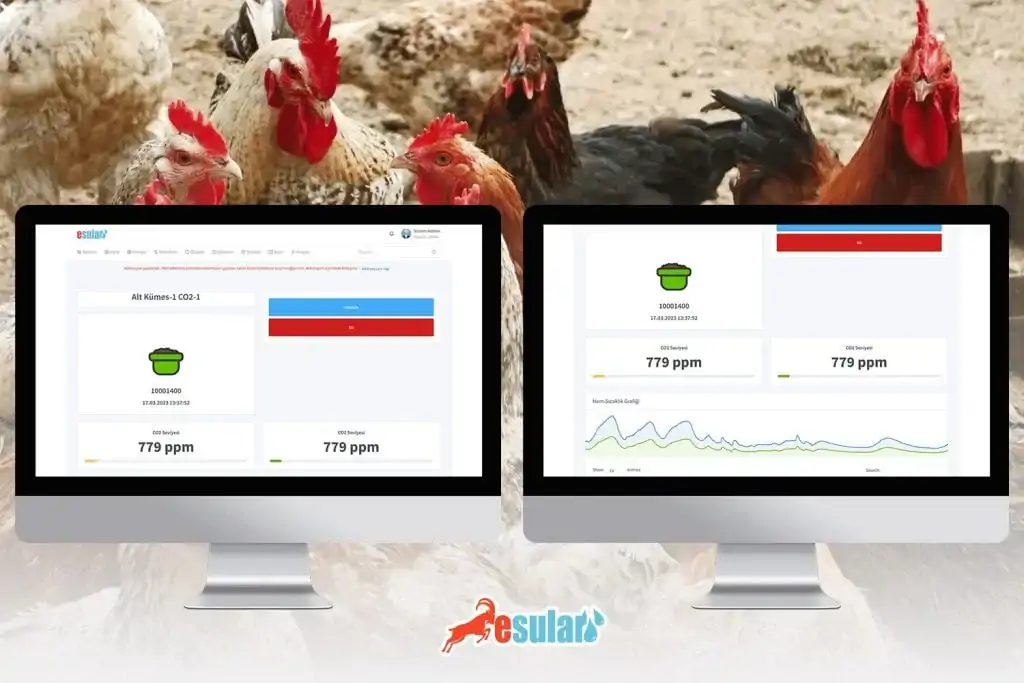
CO2 Sensors
CO2 sensors monitor carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in the air and send data to the controller. This data is vital for the photosynthesis process of plants. High CO2 levels can increase the growth rate of plants and support productivity. In addition to irrigation schedules, CO2 data can also be used to optimize the overall health and growth conditions of plants.
Benefits of Smart Irrigation Systems
Smart irrigation systems offer many advantages compared to traditional irrigation methods. Here are some benefits provided by smart irrigation systems:
Smart irrigation systems continuously monitor soil moisture and environmental conditions through sensors to determine irrigation needs. This ensures that water is provided at the right time and in the right amount, prevents unnecessary water consumption, and provides water savings.
Optimal irrigation increases productivity by enhancing plants' nutrient uptake and photosynthesis efficiency.
Less water usage and less energy consumption reduce irrigation costs. Additionally, labor costs also decrease as the need for manual labor is reduced.
Preventing water waste and using water correctly reduces the impact on the environment.
Smart irrigation systems offer remote access and control via internet connection. This feature allows business owners to monitor, adjust, and control the system from anywhere.
Data from sensors allows for more informed irrigation schedules and plant management. Data analysis helps in making future irrigation plans and agricultural decisions more accurately.
Smart irrigation systems can support various irrigation methods such as sprinkler irrigation, drip irrigation, and can combine these methods efficiently.
These benefits ensure that smart irrigation systems are accepted as an important solution in agricultural production, garden maintenance, and various irrigation needs. The continuous development of systems along with technological advancements has significant potential to increase agricultural productivity and sustainability.


