The Importance of Using Soil Moisture Sensor in Agricultural Irrigation
Irrigation in agriculture is the provision of water that the plant needs and cannot be met by rainfall to the root area of the plant in the soil in the required amount and time. Many regions of our country are located in arid and semi-arid climate zones, and in these arid agricultural areas, if natural rainfall is insufficient during the growth period of the plants, agricultural irrigation should be carried out with the most appropriate method for high yield and quality.
Agricultural irrigation ensures the germination of plants, the vitality of organs such as cells, stems, branches, and leaves, and ensures that the plant nutrients required by the plant are melted by the roots and carried to other parts of the plant.
In addition to the importance of irrigation for the plant, what is really important is the critical irrigation period, which is different for each plant, and the amount of water it needs. If the amount of moisture that plants need during their development and critical irrigation periods are not taken into consideration, serious yield losses and a decrease in product quality are observed. In order to eliminate such problems in agriculture and to use our decreasing water resources effectively, soil moisture sensors should be used.

Soil Moisture Sensor
The soil moisture sensor is a sensor that we can use to measure the amount of moisture in the soil. The moisture meter probes are inserted into the soil to be measured. The moisture values of different types of soil are measured gradually and from multiple points.
Soil Moisture Sensor Types
Thanks to developing technology, soil moisture measurement has started to be done using soil moisture sensors rather than the gravimetric approach. There are many soil moisture sensors developed for this purpose. We can group these sensors in 3 groups in terms of their working principle. These are; tensiometers, dielectric (electromagnetic reflection) sensors and neutron scattering method.
Tensiometers
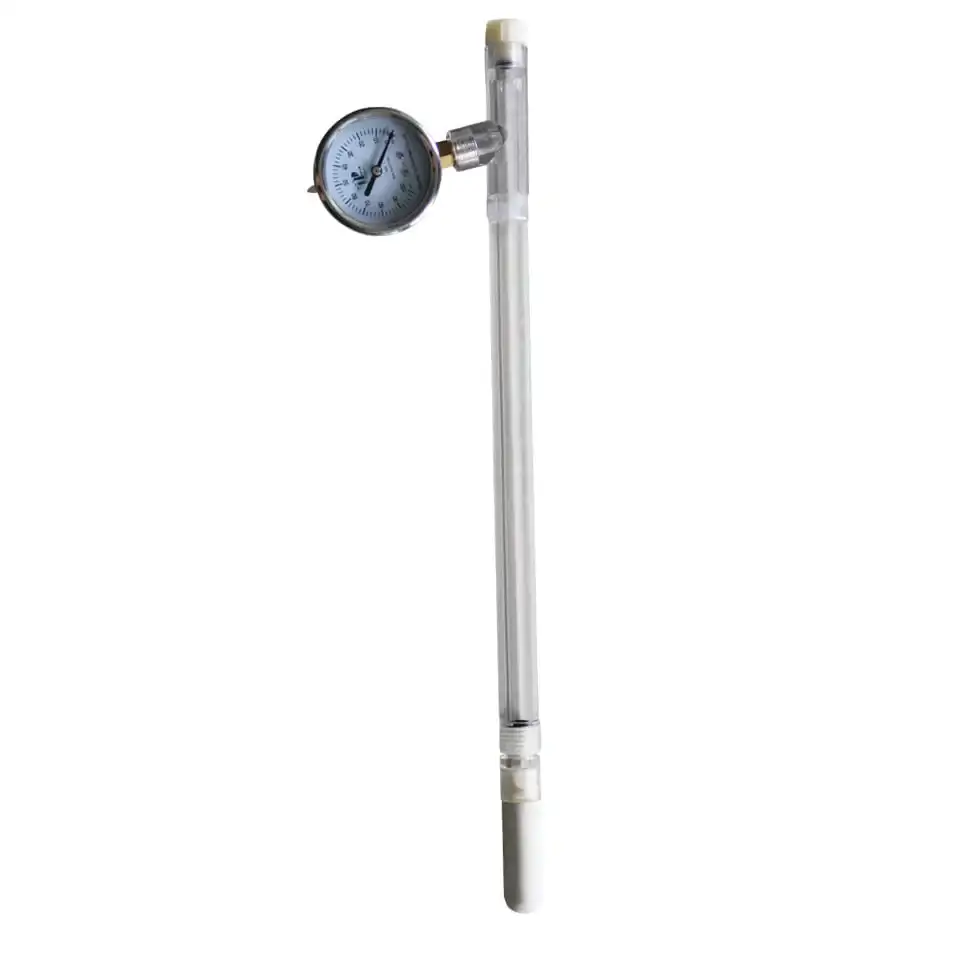
Tensiometers are soil moisture sensors that measure this tension between soil particles and water molecules. Tensiometers are instruments consisting of a plastic body filled with water, a permeable ceramic tip, and a vacuum gauge (manometer). As the amount of moisture in the soil decreases, the soil begins to dry out and the water held around the soil grains is held more strongly. After the tensiometer is placed in the soil, water begins to pass from the ceramic tip to the soil, depending on the amount of moisture in the soil. As the soil around the ceramic tip absorbs water, a vacuum is created inside the tensiometer. This vacuum is monitored on the manometer gauge.

Dielectric (Electromagnetic Reflection) Sensors
Dielectric sensors measure the dielectric constant of the soil, which is an electrical property that depends on the moisture content of the soil. The use of methods based on the dielectric property of the soil to measure soil moisture content has increased in recent years. The dielectric technique is based on the large difference between the dielectric constant of dry soil and the dielectric constant of pure water. Sensors such as TDR (Electromagnetic reflection time) and FDR (Electromagnetic reflection frequency) TDT (Electromagnetic transmission meter) are used to measure soil moisture based on the dielectric constant.
- TDR (Electromagnetic Reflection Time) Sensor It is based on the principle of sending electromagnetic signals from a source along two or three probes placed in the soil. The signal is in the form of a single movement (hit, impact-pulse). These electromagnetic waves travel along the probes and the signals hit the soil with the probes, returning to the source as a reflection. The path taken by this electromagnetic wave along the length of the probe and the time it takes to return to the source are measured. More water in the soil results in higher dielectric strengths (slower transmission speed).
- FDR (Electromagnetic Reflection Frequency) Sensor Soil moisture sensors based on the FDR method work very similarly to sensors based on the TDR method. However, while TDR measures the travel time of electromagnetic waves, FDR measures the frequency of electromagnetic waves. FDR sensors have two different types of electrodes: with two parallel tips or a circular metal ring. The parallel two-tip type is buried in the soil, while the circular metal ring is used in a tube.
- TDT (Electromagnetic Transmission Meter) Sensor The TDT-based soil moisture sensor measures the time for an electromagnetic pulse to propagate unidirectionally along a transmission line. Therefore, it is similar to TDR, but requires an electrical connection at the beginning and end of the transmission line.
Neutron Scattering Method
This method is based on the principle that hydrogen atoms with a high slowing capacity slow down the neutrons scattered from the radioactive source of the device and detect hydrogen atoms in the water in the soil. Since the source of hydrogen in the soil is mostly water, the slowed neutrons counted around the fast neutron source are used to measure the soil water content. In addition, the special training and attention required for the use of these devices and their expensiveness are disadvantages of use.
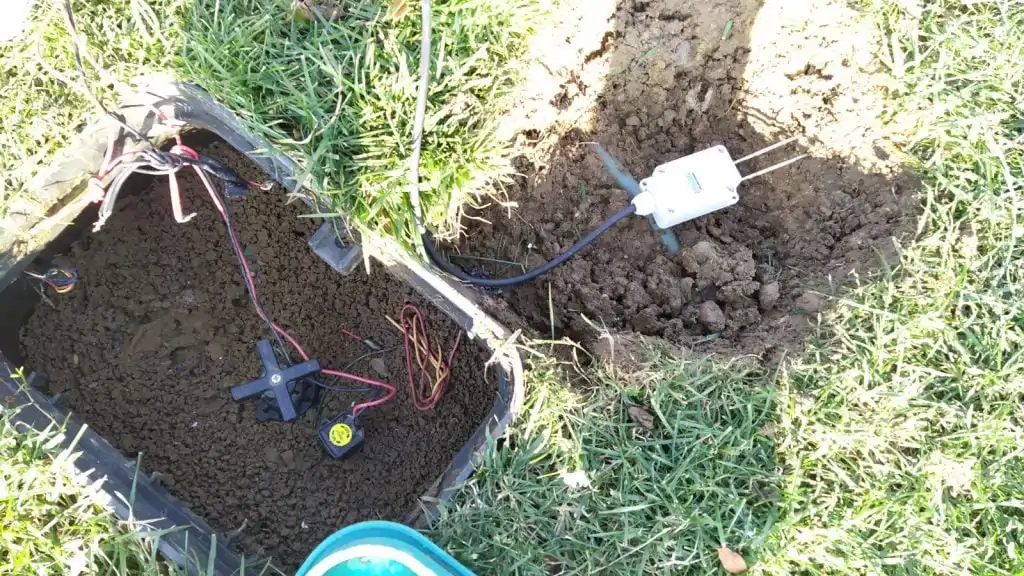
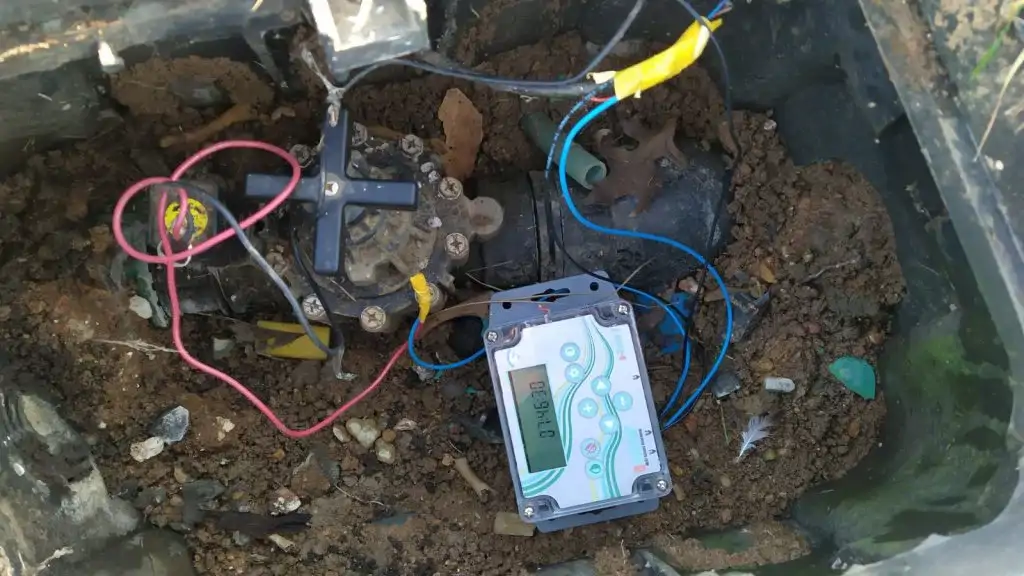
Esular Wireless Solar Panel Soil Moisture Sensor
Wireless battery-powered humidity sensor sensor It works with a solar panel rechargeable battery. It has 1 soil moisture sensor input. No external energy is required to feed the sensor. Humidity is measured at certain intervals and transmitted and humidity values can be monitored remotely.
It works wirelessly. Measurement values are transmitted to the server at certain intervals. At the same time, when these values exceed certain intervals, they are transmitted to the server and alarms can be created. Limit values can be set remotely wirelessly. Thanks to its wireless and battery-powered structure, it is possible to monitor and control from multiple points.
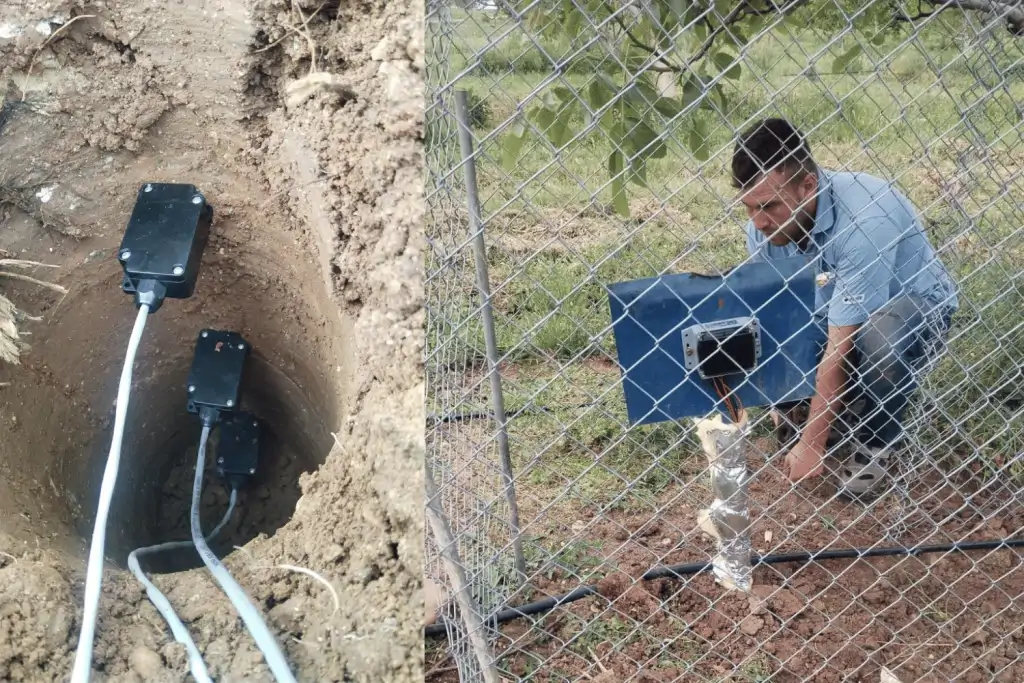

Irrigation System with Soil Moisture Sensor
Agricultural and landscape irrigation are the application areas where freshwater resources are consumed the most. Smart management of water contributes to increasing irrigation efficiency, reducing costs and environmental sustainability. In order to optimize water use, reduce energy consumption and improve the quality of crops, sensors such as humidity sensors should be added to the irrigation system.
The soil moisture sensor determines the appropriate irrigation time and irrigation duration by measuring the moisture value of the soil. Moisture sensors postpone the irrigation time in case of unexpected rainfall.
As Esular, the analysis of sensor data that can be recorded on the cloud system with our wireless, battery-powered smart soil moisture sensor and smart algorithms helps determine the ideal irrigation period and irrigation duration, and we also reduce water use and increase efficiency in agricultural production.
Advantages of Soil Moisture Sensor in Agricultural Irrigation
In irrigation applications, it is very important to measure the moisture in the plant root zone accurately and to evaluate the moisture change in the soil. The most effective and definitive solution for measuring soil moisture is the soil moisture sensor. The advantages of soil moisture sensors in agricultural irrigation are many and can be summarized as follows;
- Reduces Water Use: Since soil moisture sensors can calculate the moisture needed by the plant in the soil, they prevent the use of more water than necessary, thus reducing water use.
- Provides Increased Efficiency in Agricultural Production: Plants take water into their bodies through active or passive transport depending on the content of the growing environment. If there is not enough water in the soil, plants take water through active transport, and since active transport requires more energy, it causes losses in every period from seed germination to harvest. On the other hand, if there is more water in the environment than needed, the plant does not receive nutrients, microorganism activities decrease, and disease agents occur. Maintaining the soil moisture content at the level required by the plants grown, preventing product losses and ensuring production sustainability are extremely important.
- Stage and Multi-Point Measurement: The moisture values of different types of soils are measured stage by stage and multi-point, and effective irrigation optimization is provided by supporting them with artificial intelligence and machine learning solutions.
- Alarms Can Be Created: The measurement values are transmitted to the server at certain intervals. At the same time, these values are transmitted to the server when certain intervals are exceeded and alarms can be created.
- Wireless Battery: Thanks to its wireless, battery-powered structure, there is no need for additional energy to feed the sensor.
- Automatic Irrigation Delay According to Meteorological Data and Rainfall Information: Unexpected situations such as rain in the region are automatically detected and the activation of the irrigation system is delayed. The amount of moisture in the soil can be detected by moisture sensors, thus saving water.




