Why Should Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Levels Be Monitored in Greenhouses?
Why should carbon dioxide (CO2) levels be monitored in greenhouses? Monitoring carbon dioxide (CO2) levels is of critical importance for optimizing plant growth and greenhouse conditions.
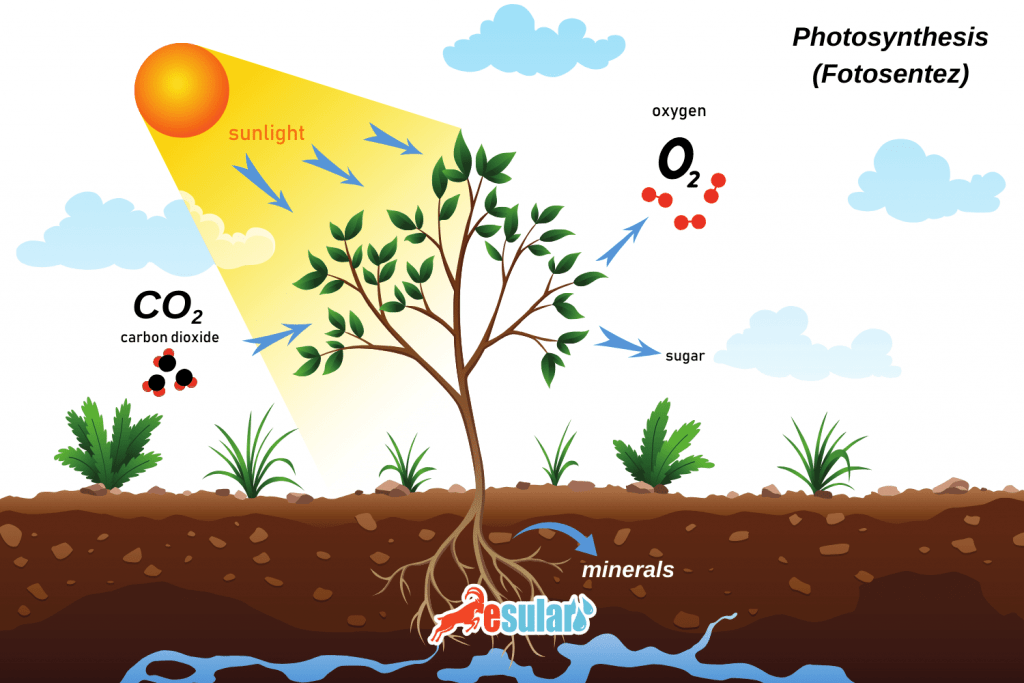
Carbon dioxide is the raw material for plant photosynthesis, and 95% of the dry weight of crops comes from photosynthesis. For this reason, carbon dioxide is an important factor affecting crop yield. In greenhouses, because plants are kept in a relatively closed place for a long time, the carbon dioxide concentration in the greenhouse varies greatly within a day. A serious carbon dioxide deficit in the greenhouse will become an important factor affecting the yield of greenhouse plants. Therefore, a carbon dioxide sensor should be used to monitor insufficient carbon dioxide concentration in the greenhouse.

Positive Effects of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) on Plant Growth
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is one of the necessary raw materials for photosynthesis in plants; plants convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds. Adequate carbon dioxide (CO2) levels increase the rate of photosynthesis and thus promote plant growth. Additionally, it increases crop yield, crop quality, and can improve fruit characteristics. Furthermore, appropriate carbon dioxide levels can increase plant resistance, meaning it increases resistance against diseases, drought, and cold. It positively affects the general survival ability of plants. CO2 also reduces plant transpiration, which allows for water saving and enables plants to grow normally under water-deficient conditions.
Negative Effects of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) on Plant Growth
It should not be forgotten that excessive or insufficient carbon dioxide (CO2) levels can cause various negative effects. When the CO2 concentration is too high, plant photosynthesis tends to saturate; this can lead to a decrease in nutritional value and overall plant quality. Additionally, if carbon dioxide (CO2) levels are excessively high, more ventilation may be needed to reduce the CO2 concentration inside the greenhouse, which can increase energy consumption and operating costs. If the CO2 concentration is too low, the rate of photosynthesis and plant growth decrease. This can lead to the stomata opening more, increased water transpiration, and restriction of plant growth and development; consequently, it affects the taste and nutritional composition of plants.
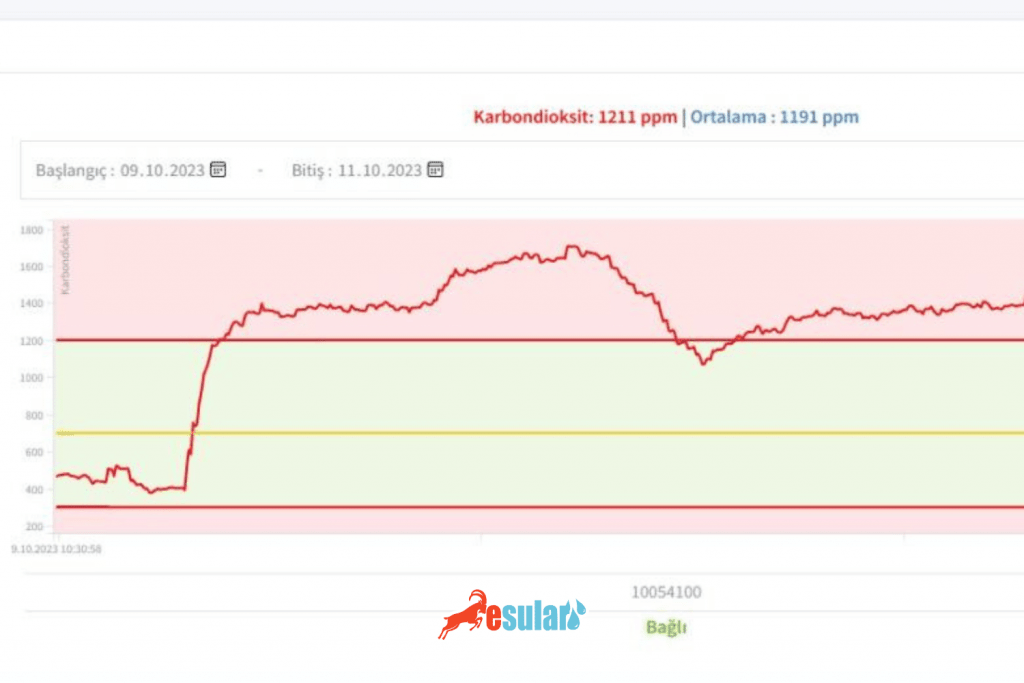
Different plants have different environmental requirements for growth. For example, tomatoes thrive in CO2 concentrations between 800 and 1200 ppm. When the concentration exceeds 1200 ppm, photosynthesis saturates. Long-term growth at high CO2 concentrations can lead to increased sugar content, decreased acidity, decreased vitamin C content, altered taste, accelerated ripening, and reduced storage capacity. On the other hand, when the concentration falls below 800 ppm, the rate of photosynthesis and fruit quantity decrease, and fruit sizes become smaller.
Therefore, it is extremely important to maintain appropriate CO2 concentrations to ensure healthy plant growth within the greenhouse. Understanding and monitoring CO2 levels in the greenhouse in real-time is of great importance.

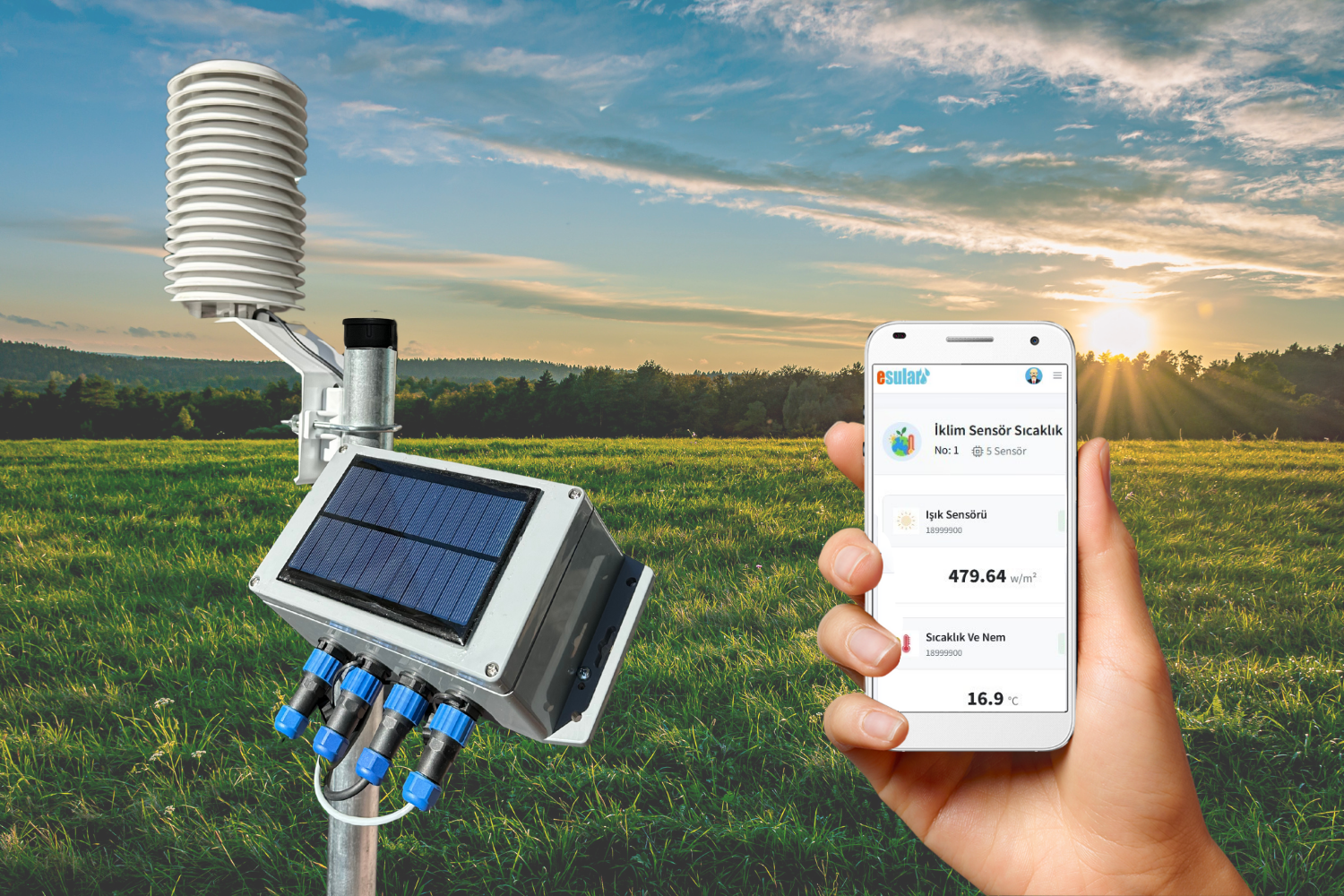
How is Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Monitoring Done in Greenhouses? Smart Greenhouse Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Monitoring System
A carbon dioxide (CO2) monitoring system in a smart greenhouse uses modern technologies to monitor the carbon dioxide concentration inside the greenhouse. Its basic function is to monitor CO2 concentration in real-time and, by performing data analysis, allow farmers to understand the climate conditions inside the greenhouse and improve the growth efficiency and quality of greenhouse crops.
Components of the Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Monitoring System in Greenhouses
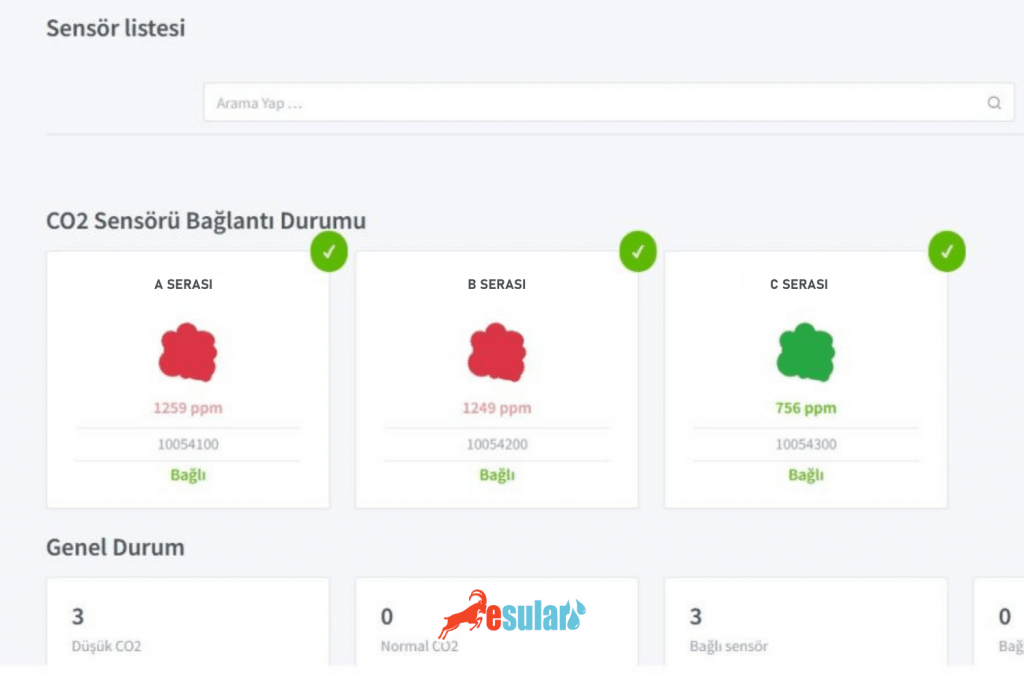
The components of the carbon dioxide (CO2) monitoring system in greenhouses basically consist of a carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor, data logger, wireless communication module, host computer or cloud server, and power module. The carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor is responsible for monitoring the CO2 concentration inside the greenhouse. The data logger receives the data collected by the carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor. The wireless communication module transmits the processed data wirelessly to the host computer or cloud server. The host computer or cloud server receives the data transmitted from the data logger, performs data analysis and processing, and presents the processed results to the user. The power module provides power to the system.

Operation Process of the Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Monitoring System in Greenhouses
In the operation process of the carbon dioxide (CO2) monitoring system in smart greenhouses, the sensor continuously collects data regarding the CO2 concentration inside the greenhouse. The data is then transmitted to the data collection module, which uses the wireless communication module to transmit the data to the server. After receiving the data, the server stores the data in a database and performs data analysis and processing. Finally, the processed data is presented to the user.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Sensor Selection in Greenhouses
The selection of carbon dioxide (CO2) sensors in a smart greenhouse carbon dioxide (CO2) monitoring system is of vital importance. When making a specific selection, it is important to understand the selection criteria and available sensor types, and then make the best decision based on the specific conditions of the greenhouse environment.
Selection Criteria for Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Sensors
Different types of sensors have different characteristics and their application areas vary. Therefore, choosing the right sensor type will have a great impact on monitoring results and plant growth. The following features should be considered in sensor selection:
Measurement Range
The measurement range of a carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor is an important factor to consider. A sensor with an appropriate measurement range should be selected based on the CO2 concentration that needs to be monitored. For example, while the measurement range of some sensors is 0-5000 ppm, others can measure high concentrations such as 100,000 ppm. Generally, if the greenhouse is small or the CO2 concentration changes relatively little, under natural ventilation conditions where the CO2 concentration may remain between 300-800 ppm, a CO2 sensor with a measurement range of 0-2000 ppm will be sufficient.
Accuracy
Accuracy refers to the deviation between the measurement result and the actual value. Usually, more sensitive measurements are required for higher accuracy. Since greenhouse environments have higher CO2 concentration requirements, it is typically necessary to select a sensor with an accuracy requirement of ±50 ppm or lower.
Response Time
Response time refers to the time it takes for the sensor to detect a change in CO2 concentration and provide the measurement result. For applications requiring real-time response, response time is a critical indicator. The CO2 concentration in the greenhouse can change with plant respiration and photosynthesis, so it is important to choose a sensor with a fast response speed, typically 1 minute or faster.
Stability
The stability of a carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor refers to its long-term measurement performance. The higher the stability of the sensor, the more reliable the measurement results. In greenhouse scenarios, it is important to choose a sensor with high stability. Additionally, the life of the sensor and maintenance costs should also be considered.
Price
Prices of carbon dioxide (CO2) sensors vary depending on the brand, model, accuracy, etc. A sensor with a good price/performance ratio should be selected based on actual needs.
Power Consumption
Power consumption refers to the energy consumed by the sensor during operation. Choosing a sensor with generally low power consumption can extend battery life, reduce maintenance frequency, and increase the usability and cost-effectiveness of the sensor within the greenhouse.
Other Features
Some carbon dioxide (CO2) sensors may have extra features, for example, a screen, alarm function, a specific output signal type, specific interface types, temperature and humidity compensation, etc. A sensor with appropriate features should be selected based on actual needs.

In conclusion, the best choice for a CO2 sensor will be the sensor that offers high accuracy, low power consumption, fast response time, high stability, and a good balance in terms of price/performance.
Classification of carbon dioxide sensors you can read our article.



Yorumlar