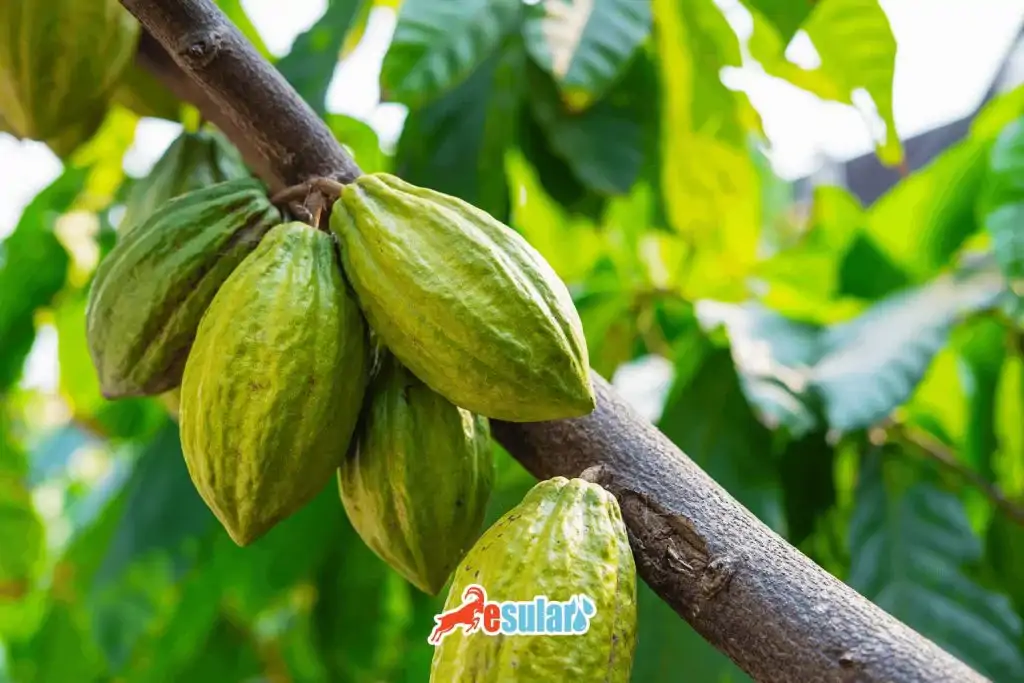
How Is Cocoa Cultivation Done?
Cocoa cultivation is an important agricultural activity that provides the basic raw material for chocolate, which is an indispensable flavor for millions of people worldwide. Cocoa trees generally have a height of 2 to 3 meters, with a dense foliage and branched structure. These trees grow best in well-drained soils that receive regular rainfall throughout the year and where temperatures are between 18 and 35 degrees. Cocoa cultivation has great economic importance. Especially West African countries strengthen their economies with the income they obtain from this product by providing a large part of the world's cocoa production. Countries such as Ivory Coast, Ghana, Cameroon, and Nigeria are important actors in the global cocoa trade. Cocoa trade is the livelihood of millions of people in these regions and contributes to agricultural development and the strengthening of local economies.
From a touristic perspective as well, cocoa cultivation and chocolate production form an important center of attraction for many tropical regions. Tours are organized for visitors to cocoa farms, showing them the cultivation processes, harvesting techniques, and stages of chocolate making, and providing information about local culture and traditions. These tours, in addition to contributing to the local economy, help promote sustainable tourism by offering tourists an unforgettable experience.
Where Does Cocoa Grow?
Globally, cocoa grows in tropical climate regions and is successfully farmed in these areas, especially around the equator, between 20 degrees north and south latitudes. Major cocoa-producing countries include Ivory Coast, Ghana, Indonesia, Brazil, and Ecuador. The climate of these countries provides ideal temperature and humidity levels for cocoa trees. However, our country's climate is far from meeting the tropical conditions that are the natural requirements of cocoa trees. For this reason, cocoa cultivation is not very common. However, some farmers in regions of Turkey with a Mediterranean climate, such as Antalya, have started growing tropical plants like cocoa in greenhouses. This could increase production potential by allowing cocoa trees to be grown in an environment closer to tropical climate conditions. By providing controlled climate conditions in greenhouses, it is aimed that plants adapt more sensitively to factors such as temperature, humidity, and light.
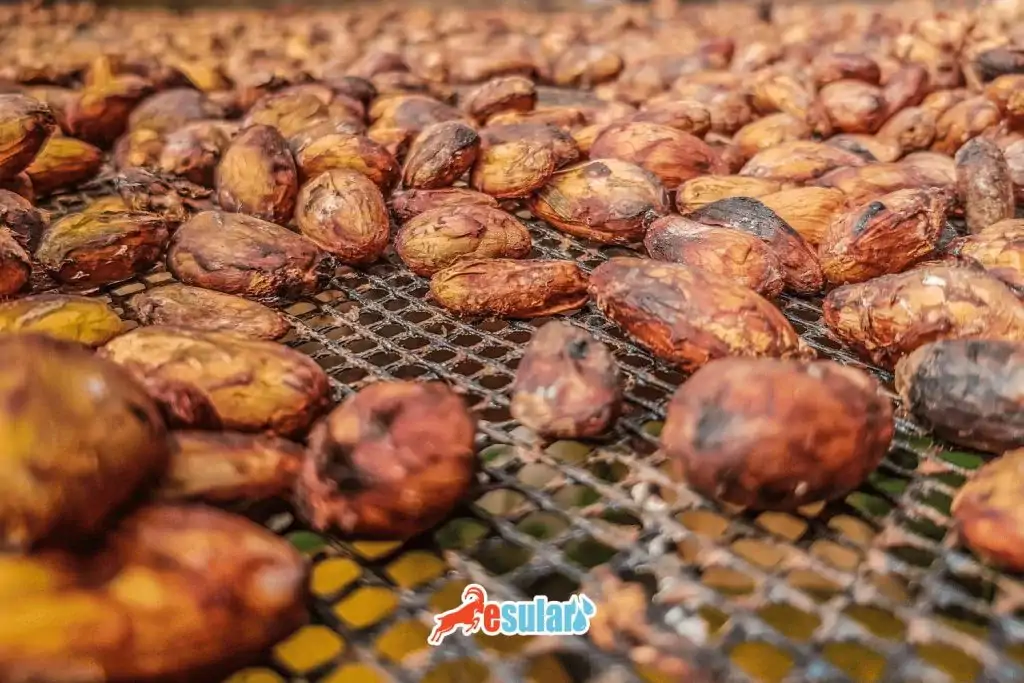

Climate and Soil Structure in Cocoa Cultivation
Cocoa cultivation is successfully carried out in tropical climates, particularly between 20 degrees north and south latitudes around the equator. The ideal temperature for cocoa trees is generally between 18-32°C. Extremely hot or cold conditions can negatively affect the plant's development. Additionally, the annual rainfall amount should generally be between 1500-2500 mm; regular rainfall is vital for the healthy growth and fruit yield of the plant. Soil structure is also a critical factor for cocoa cultivation. Cocoa trees thrive best in deep, well-drained soils rich in organic matter. Acidic or neutral pH levels (between 5.0-7.0) are considered suitable for plant health. Alkaline soils, on the other hand, are not suitable for cocoa cultivation and can negatively affect the plant's growth. Therefore, the climate and soil characteristics of the region where cocoa cultivation will be carried out should be meticulously evaluated.
How Many Years Do Cocoa Trees Bear Fruit?
Cocoa trees can bear fruit for about 25-30 years under the right conditions and with proper care. Cocoa trees start to bear fruit when they reach two to three years of age, and full yield is obtained after six to seven years. The productivity of the trees tends to decrease as they age, but this period can be extended with proper agricultural practices and regular maintenance. The economic life of cocoa trees is generally 25-30 years, during which fruit production continues.
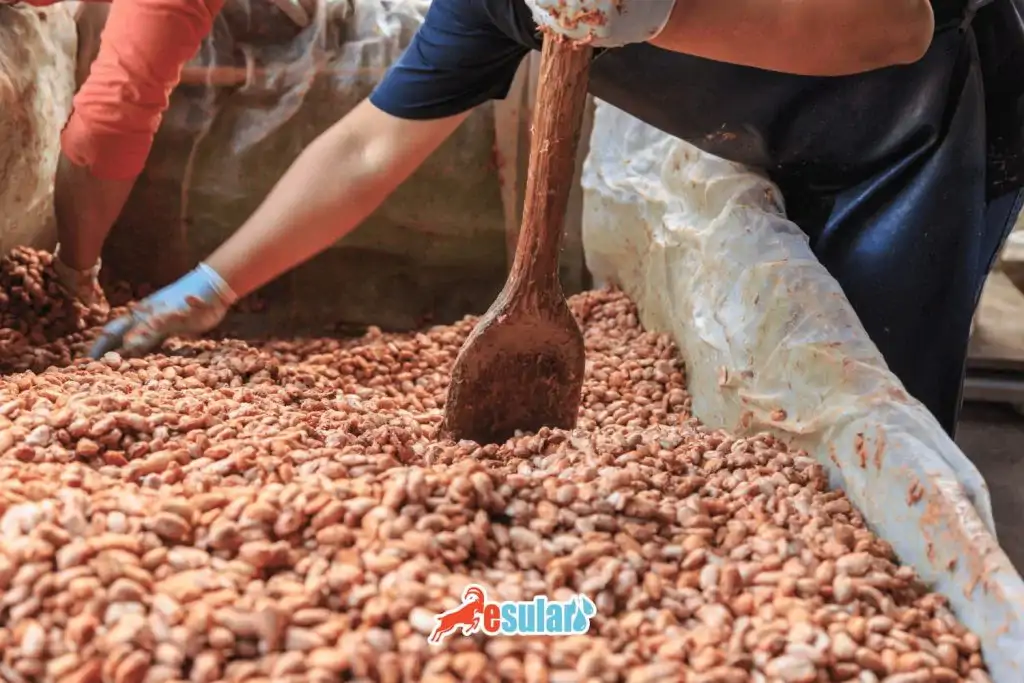

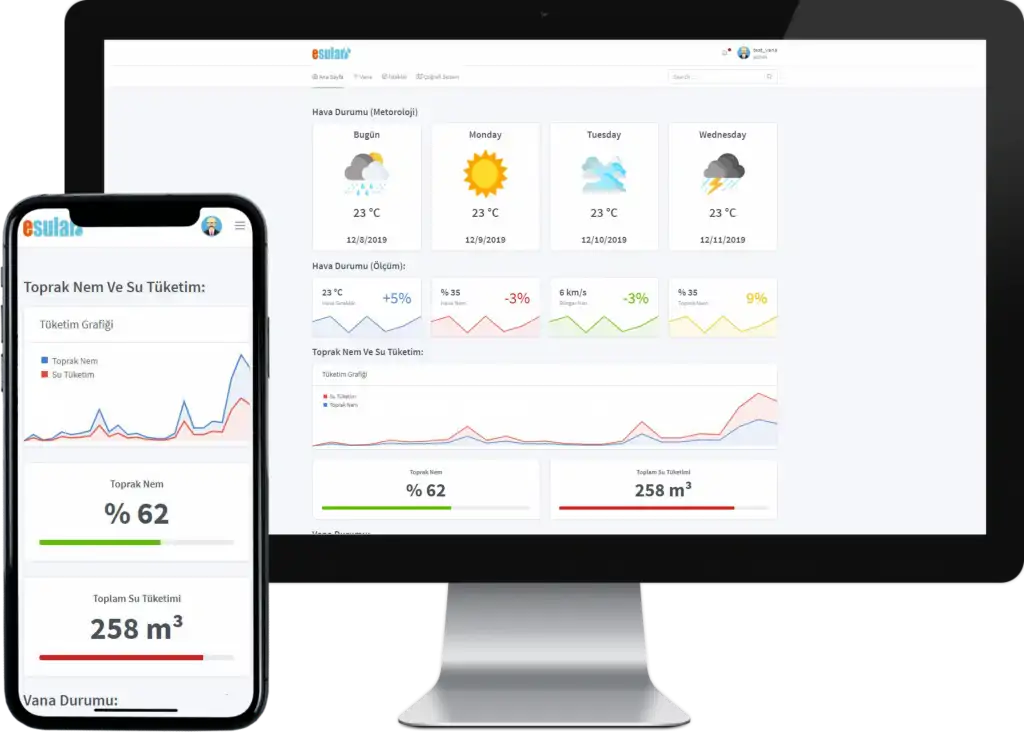
Smart Irrigation Systems in Cocoa Greenhouses
Cocoa cultivation requires the balance of humidity and temperature provided by tropical climates. However, in regions where climate conditions are not tropical, such as Turkey, growing these plants becomes possible through greenhouses. Irrigation is an important factor for the healthy growth and efficient yield of cocoa trees in these greenhouses. Traditional irrigation methods are increasingly being replaced by smart irrigation systems, and these systems increase efficiency and provide water savings. Smart irrigation systems offer great advantages in cocoa greenhouses by integrating technology into the agricultural sector. These systems continuously monitor and analyze the soil's moisture level, air temperature, and the plant's water needs. Thus, the amount of water needed by the plants is provided exactly on time and as much as necessary. While this supports the healthy growth of plants, it also significantly reduces water waste.
These systems also optimize irrigation plans by taking weather data into account. For example, the irrigation frequency is automatically reduced during a rainy period, while it is increased during dry periods. This dynamic irrigation management ensures more efficient use of water resources and contributes to environmental sustainability. Another important feature of smart irrigation systems is that they offer farmers remote access and control. Irrigation systems can be monitored and managed via smartphones or computers. In this way, farmers can check the status of their greenhouses at any time and intervene when necessary. This feature saves labor, especially in large-scale greenhouses, and increases operational efficiency. To get more detailed information, you can visit; https://esular.com/otomatik-sulama .
Cocoa Harvest
- Harvest Time and Process
Cocoa fruits are collected by hand by cutting the stem from the branches and trunk with a machete. Not all fruits ripen at the same time; therefore, the harvesting process takes several months and is usually done every 2-3 weeks. In Africa, the cocoa harvest usually starts at the beginning of October and continues until December. During the harvest, cocoa fruits are purchased from farmers, but the main purchases intensify in March.
- Collection and Opening of Fruits
Collected cocoa fruits are opened with a machete or a suitable wooden mallet, and the cocoa beans inside are removed. These beans are the basic material to be used in chocolate production. After the beans are separated from the fruit, they are made ready for processing.
- Yield and Maintenance
The yield of cocoa production varies greatly per hectare. In poorly maintained areas, 150-450 kg (as dried) of beans are obtained per hectare, while in well-maintained areas, this yield can go up to 2500 kg. Productivity can be significantly increased with correct agricultural practices and regular maintenance.
- Fermentation and Drying
Fermentation and drying of cocoa beans are carried out on farms immediately after harvest. These processes are necessary for the formation of cocoa flavor precursors. Drying is an ideal method for preserving the goods for small-scale growers. Cocoa beans are subjected to a fermentation process that ensures the breakdown of sugar and other substances thanks to natural yeasts and some bacteria. This process is usually carried out by keeping the cocoa beans in wooden boxes or piles for 5 days.
- Fermentation and Quality
During the fermentation process, cocoa beans are kept under piles covered with banana leaves or in wooden boxes. Fermentation improves the color and taste of the beans; unfermented cocoa beans are gray in color and bitter. After fermentation, the beans are left to dry. The drying process is usually done in the sun, but artificial drying methods can also be used.
- Storage and Shipping
Dried cocoa beans are bagged and made ready for sale after being cleaned of foreign substances. Cocoa beans produced on small farms are sold to cooperatives or traders, and these products are directed to larger buyers. Cocoa prices are determined by the New York and London stock exchanges and sold to different countries according to price movements. Shipping is mostly carried out by sea, and thus cocoa beans set off for the factories where chocolate production will take place.
Cocoa harvesting is a process that requires attention and care. With correct methods and regular maintenance, high-quality cocoa beans are obtained, contributing to the production of delicious chocolates. This journey from cocoa trees to our tables takes place thanks to the labor and expertise of cocoa farmers.



