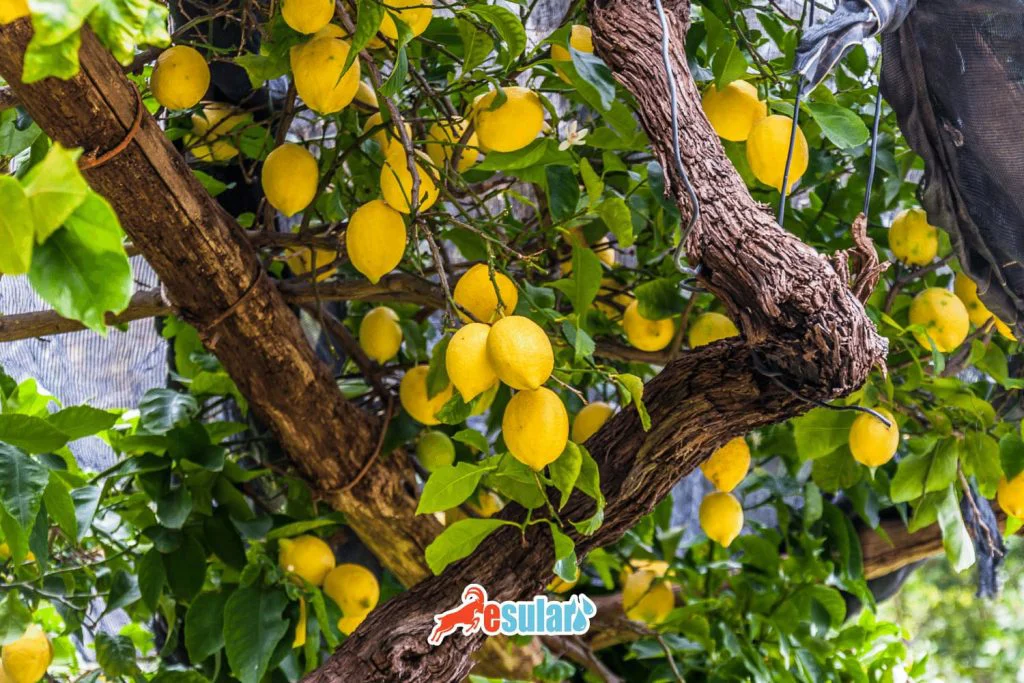
How to Cultivate Lemons?
Lemon cultivation is an important agricultural pursuit widely practiced worldwide and especially in regions with a Mediterranean climate. Lemon is a commercially valuable fruit and is in high demand for industrial uses as well as fresh consumption. It is particularly valuable for health due to its high vitamin C content. Lemon is generally grown intensively in subtropical and tropical climates. Regions such as the Mediterranean basin, the southern United States, India, China, and Southeast Asia are the main areas where lemon cultivation is intensive. The climate, soil structure, and geographical location of these regions offer ideal conditions for the healthy growth and development of lemon trees.
What are the Lemon Varieties?
Lemons are generally classified into three main groups: sour lemons, sweet lemons, and lemon-like fruits. Commercially, the most common ones generally belong to the sour lemon group. Within this group are the Eureka and Lisbon subgroups. Additionally, there are other lemon varieties. Prominent lemon varieties include:
Eureka Lemon: A variety widely grown in the coastal parts of the Mediterranean basin. The fruits are generally small with smooth skin. It is slightly more sensitive to cold.
Lisbon Lemon: A variety of Australian origin. The fruits are larger and thicker-skinned compared to Eureka. It is more resistant to cold.
Interdonato Lemon: A variety of Sicilian origin. It is frequently grown in Turkey and plays an important role in its export. The fruits are generally large, smooth, and have shiny skin.
Karalimon: A variety grown particularly in Antalya. It has medium-sized and yellowish-green fruits.
Meyer Lemon: A variety of Chinese origin. The fruits have a softer skin compared to other lemons and have a sweet flavor.
Kütdiken Lemon: A variety widely grown in Turkey. It is generally produced in large quantities in the provinces of Mersin and Hatay.
Each of these varieties has different characteristics and is preferred based on climate, growing conditions, and market demands.

Climate and Soil Structure in Lemon Cultivation
Climate is quite important in growing lemon trees. Factors such as temperature, frost, light, humidity, and day length directly affect the development and fruit quality of lemons. Lemon trees cannot withstand temperatures below 0°C, and frost events damage the trees. If there is fruit on the tree, the effect of frost increases even more. The growth temperature of the trees is generally accepted as 12.8 degrees. However, unlike other citrus fruits, lemons do not require a specific temperature total. In our country, lemons are generally grown in the Mediterranean and Aegean Regions because the climatic conditions of these regions are suitable for lemons. Lemons develop better in regions where summers are warm and humid, and winters are mild. The most suitable soils for cultivation are those that are rich in humus, deep, light, and have a well-drained structure. It is important that the pH level in the soil is between 5.5-6, the clay ratio does not exceed 20%, and the salt amount does not exceed 0.30%. Additionally, good drainage should be provided in the soil and the amount of ventilation should be sufficient.
Sapling Planting in Lemon Cultivation
The row spacing and on-row distances between saplings vary depending on the varieties, rootstocks used, soil characteristics, and climatic conditions. In planting, it is important to adjust appropriate distances to ensure the crown widths of the trees, their access to sunlight, moisture conservation in arid regions, and to prevent moisture accumulation in humid regions. Generally, square or rectangular planting systems are preferred in Turkey. The most suitable time for planting is generally the spring period and can last from mid-February to the end of April. Pruning should be done before planting the saplings. Before planting, farm manure is added to the pits where the saplings will be placed. Before the saplings are planted, root pruning is performed by watering them. During planting, the saplings are placed so that the root collar is at a certain distance from the soil level. After planting, the soil should be compacted and the saplings should be watered.

How is Irrigation Done in Lemon Cultivation?
The irrigation program may vary depending on climatic conditions, soil structure, the age of the tree, and the planting method. Generally, newly planted saplings should be watered frequently to ensure their roots are firmly established. Larger and mature trees should be watered at certain intervals according to the irrigation program. Common irrigation methods used in lemon cultivation include drip irrigation, furrow irrigation, and sprinkler irrigation. The amount of irrigation is adjusted based on soil moisture, climatic conditions, and the water needs of the tree. Over-irrigation can cause root rot and the development of fungal diseases, while insufficient irrigation can reduce fruit yield and negatively affect the quality of the fruits.
Smart Irrigation Systems in Lemon Cultivation
While the irrigation process with traditional irrigation methods can be time-consuming and require labor, smart irrigation systems make this process more efficient and easier. These systems measure the water needs of the plants through sensors and perform irrigation automatically. In this way, more efficient use of water is ensured and labor costs are reduced. Smart irrigation systems can be controlled remotely via mobile applications or the internet. Thus, farmers can monitor and manage irrigation processes remotely. These systems are becoming increasingly common in agricultural areas such as lemon cultivation to increase irrigation efficiency and use water resources more effectively. The use of these innovative technologies increases efficiency in agricultural production while reducing environmental impacts and contributing to sustainable agricultural practices. You can call us and browse our site to get more detailed information. https://esular.com/akilli-sulama-sistemleri
Fertilization in Lemon Cultivation
Fertilization is very important for the healthy growth of trees and quality fruit yield. In this process, leaf and soil analyses should be performed and the types and amounts of fertilizer should be determined according to the results. Fertilization is generally carried out in the months of November-December. Fertilizers are distributed by burying them in pits opened at the crown projections of the trees. Additionally, the most common nutrient deficiencies encountered by lemon trees are macro-nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Besides these, micro-nutrients such as zinc, manganese, and iron must also be provided regularly. Fertilization is a fundamental method to ensure the healthy growth of lemon trees and the production of quality fruit, but it is important to pay attention to the correct amount and type of fertilization. Following expert recommendations is important for a successful fertilization program.
Harvest in Lemon Cultivation
In lemon cultivation, harvest time, classification, packaging, and the characteristics of storage facilities are among the important factors affecting durability in storage. Harvest time, although varying by region and variety, should be done when the fruits are mature. Lemons should be collected before frosts and fruits should not be left on the tree unnecessarily. Harvesting should be done carefully to avoid damaging the fruits, and injuries to the skin during harvesting should be avoided. Collected fruits should be packaged and prepared for the market after waiting for at least one day. During the packaging process, steps such as pre-washing, degreening, selection, washing, waxing, pesticide application, grading, and packaging are followed. Fruits that need to be stored should be transported to storage quickly, and fruits to be offered for sale should be transported to the market. In this way, the durability and quality of the lemons are preserved and presented to the market.

How Much Lemon Does 1 Lemon Tree Yield?
The fruit yield of a lemon tree can vary depending on its variety, growing conditions, care, and climatic conditions. Generally, a minimum of 70 kilograms of fruit can be obtained from a healthy lemon tree that has reached 10 years of age. However, this amount may vary depending on various factors. Factors such as the region where the lemon tree is grown, irrigation, fertilization, and pruning are also effective on yield.
How Many Years After Does a Lemon Tree Bear Fruit?
It may generally be necessary to wait 2 to 3 years to get fruit from a lemon sapling grafted onto a sour orange rootstock. However, this period may vary depending on the type of sapling, growing conditions, and care. For example, some lemon saplings may grow faster and the fruit-bearing period may be shorter. In general, a period of about 3 to 4 years may be needed to obtain a lemon sapling and ensure its maturation. The important thing is to provide regular care to support the healthy growth and maturation of the sapling.

Diseases and Pests Seen in Lemon Cultivation
Diseases:
Mal Secco Disease (Phoma tracheiphila): This disease is seen on branches, and leaves fall while leaf stalks remain on the branches. When the infection is severe, total drying can be seen. It is common especially in citrus fruits, and lemon trees are among the most sensitive.
Brown Rot and Gummosis Disease (Phytophthora citrophthora): Brown spots and a leathery structure are observed in diseased fruits. Leaves fall before maturing and trees can remain completely leafless. The infection creates wounds on the trunk bark above the graft site. It is a disease frequently encountered in lemon cultivation.
Brown Spot Disease (Alternaria Alternata f.sp. citri): Generally seen on young shoot leaves and green fruit skin. Spots that initially appear very small on leaves grow over time. Sunken brown spots also form on the fruits. Rough lemon is particularly sensitive to this disease.
Citrus Blast (Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae): This disease is seen especially on branches and leaves. It spreads in hot and humid weather conditions and negatively affects the health of plants.
Pests:
Whiteflies: Citrus whitefly and citrus woolly whitefly are whitefly species frequently seen in lemon cultivation. They are leaf-sucking pests and cause damage by sucking the nutrients of plants.
Scale Insects: Scale insects such as California red scale, yellow scale, and citrus comma scale can cause serious damage on the fruit in lemon trees.
Akarlar: Mites such as citrus red mite and citrus rust mite are another group of pests that have harmful effects on lemon leaves and fruits.
Moths: Moths such as citrus flower moth and citrus leafminer can cause damage to leaves and shoots in lemon trees.
Aphids: Aphids such as citrus green aphid and citrus black aphid cause damage to the lower parts of leaves and shoots, consuming the plant's nutrients by sucking the leaves.
These diseases and pests can cause serious damage in lemon cultivation, so taking precautions is important. Control methods generally include various strategies such as cultural practices, biological control, and chemical control.



Yorumlar