How to Grow Forage Peas?
Forage pea cultivation can be carried out quite successfully in regions with suitable climate and soil conditions. Forage pea, besides being a rich source of protein, is a plant that improves the soil and has high nutritional value. Being a legume, it performs nitrogen fixation in the soil and therefore provides a suitable environment for other plants. At the same time, it provides high-quality feed raw material for various animals. With these features, forage pea plays an important role in sustainable agricultural practices.
What is Forage Pea?
Forage pea is a forage plant from the legumes known as Pisum arvense. Although it is less common in our country compared to the cultivation area of food peas, it has various areas of use. Forage pea can be used as a good preceding crop before cereal sowing. It can be grown as a winter catch crop in temperate climates and can be used for silage, as well as being evaluated by baling or grazing animals. The nutritional value of its seed and hay is high, making it extremely nutritious and palatable for animals. It is also rich in iron, potassium, and calcium. Forage pea can be fed to animals along with its straw and pods; it is also a good green manure plant. However, a point to note is that it is more suitable to sow forage peas together with cereals, because forage peas alone can cause bloating in animals. Forage pea is an important protein source for animals and has a wide range of uses.
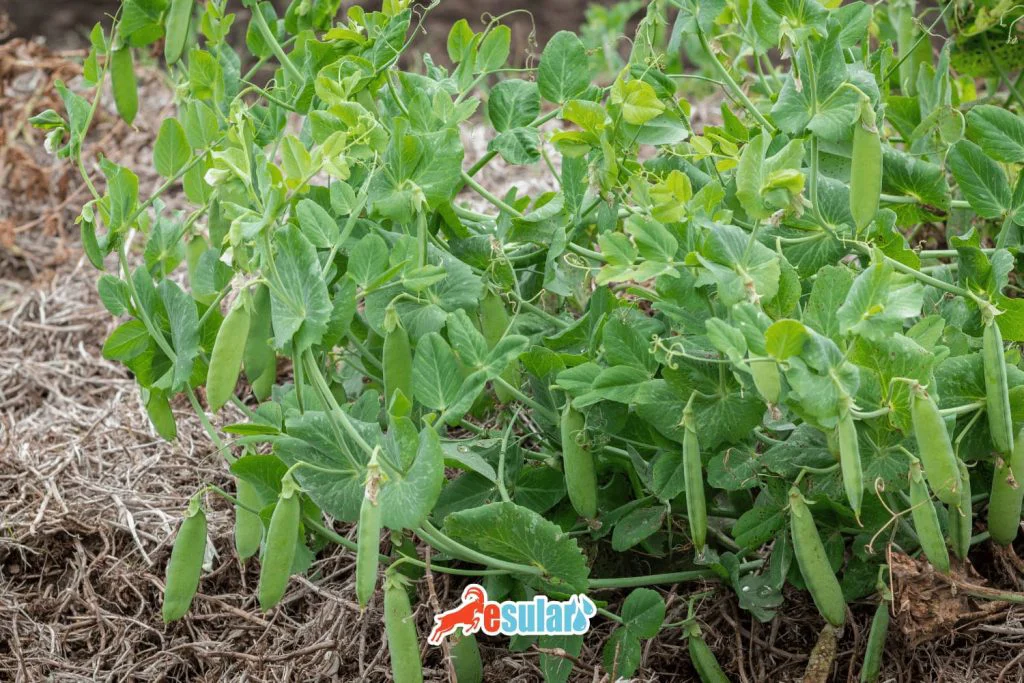

Climate and Soil Requirements of Forage Pea
Although forage pea is generally grown in temperate climates, it can adapt to various climatic conditions. It generally shows better development in temperate regions and likes cool, humid climates. It is resistant to cold and can tolerate short-term frosts. However, extreme weather conditions such as excessive heat and drought should be avoided because forage pea can lose its productivity in such conditions. In terms of soil preference, while it grows in well-drained, loamy-sandy, or clayey soils, heavy soils with high water-holding capacity should be avoided. The pH value of the soil should generally be neutral or slightly alkaline. Forage pea can grow healthily and high yield can be obtained under suitable climate and soil conditions.
What are the Benefits of Forage Pea?
Forage pea has an important role in agricultural production with its various advantages and areas of use. Firstly, it can be used as a good preceding crop before cereal sowing and can contribute to the enrichment of the soil in terms of nutrients. It can be grown as a winter catch crop in temperate climates and prevents soil erosion during this period. Additionally, it can be used as silage or hay, as well as being evaluated by baling. Forage pea seed and hay have high nutritional value. It is extremely nutritious and palatable for animals. It is especially rich in iron, potassium, and calcium. Forage pea can also be used as a good green manure plant. It increases the organic matter content of the soil and improves soil health. However, it should not be forgotten that forage peas can cause bloating in animals. Therefore, it may be more appropriate to sow it together with cereals. Its hay has a crude protein content between 15–20%, and this rate can go up to 20–30% in its grains.
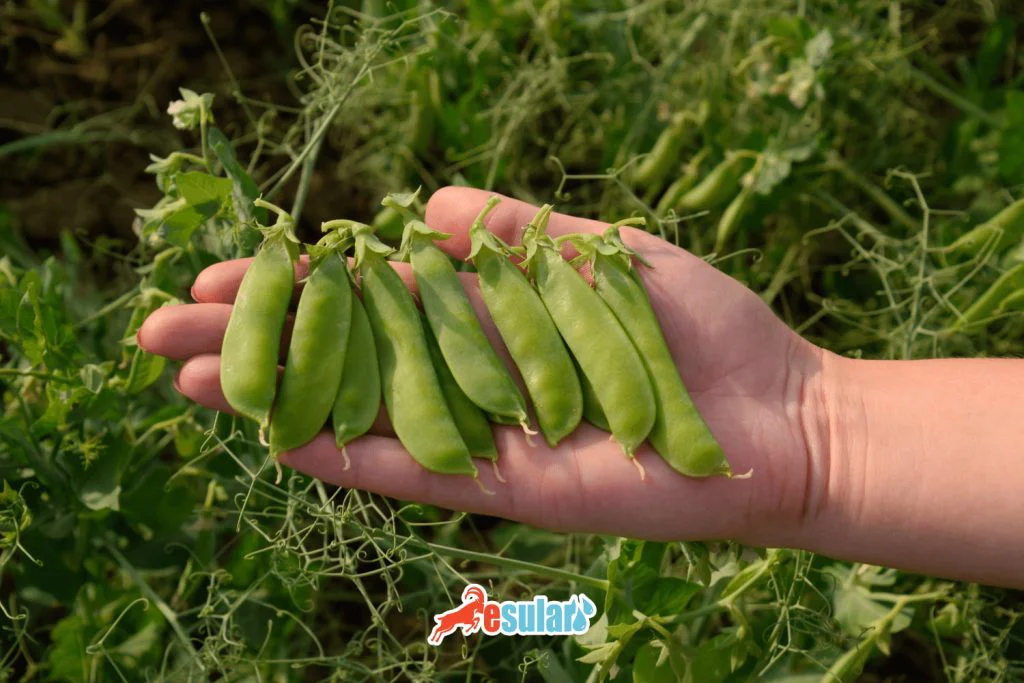

How to Plant Forage Peas?
Forage pea can be easily planted in autumn or spring. Thanks to its large seeds, the planting process is quite simple. In terms of productivity, the earlier the planting is done, the better. Having the soil deeply tilled and prepared provides an ideal environment for forage peas. After soil preparation is completed, it is sown 3-4 cm below the soil with a seed drill. Forage pea can generally be sown mixed with cereals. In this case, a certain amount of cereal seed is sown together with the forage pea. This increases soil fertility while also providing a balance between plants and helping to preserve nutrients in the soil. After planting, it is important that the seeds are well irrigated and proper care is provided.
How Much Forage Pea is Planted per Decare?
If it is to be planted for grain production, attention should be paid to the row spacing of the seeds. Row sowing at a density of 12-15 kg/decare or broadcast sowing at 15-20 kg/decare can be preferred. For green fodder production, a higher seed density is required. Row sowing at 15-20 kg/decare or broadcast sowing at 20-25 kg/decare is recommended. Row spacing being 15-20 cm is important for the healthy growth of the plants. The planting depth of the seeds should be around 5-6 cm. Forage pea is generally sown mixed with cereals. In this case, 10-13 kg of forage pea and 5-7 kg of cereal seed can be used per decare. These mixed sowings increase soil fertility and provide a natural harmony between plants.
Irrigation in Forage Pea Cultivation
Forage pea planting is generally done in the autumn months and does not need irrigation in temperate regions. However, yield increases can be achieved by irrigating in arid and dry regions. With irrigation, green fodder yield can reach up to 4 tons per decare. Using zinc leaf fertilizer after emergence in the autumn increases the plant's resistance to winter cold and ensures healthy development in the spring. These types of fertilizers, especially products like NitroZinc Fort and Potas Fort, which are special productions of Eşref Şekerli, support the growth and development of forage peas. In this way, it is ensured that the plants are stronger and healthier, productivity increases, and a high-quality harvest is obtained.

Fertilization in Forage Pea Cultivation
Forage pea planting is generally done in the autumn months and does not need irrigation in temperate regions. However, yield increases can be achieved by irrigating in arid and dry regions. With irrigation, green fodder yield can reach up to 4 tons per decare. Using zinc leaf fertilizer after emergence in the autumn increases the plant's resistance to winter cold and ensures healthy development in the spring. These types of fertilizers, especially products like NitroZinc Fort and Potas Fort, which are special productions of Eşref Şekerli, support the growth and development of forage peas. In this way, it is ensured that the plants are stronger and healthier, productivity increases, and a high-quality harvest is obtained.
Forage Pea Harvest
When planted for seed production, the most suitable harvest time is the period when the pods at the bottom of the plants turn yellow and the grains in the pods harden. At this stage, the grains reach full maturity and the seeds are of the best quality. When planted for fodder production, the most ideal harvest time is the period when the plants develop their first pods. During this period, 1 ton of green fodder or 250–300 kg of hay can be obtained per decare under dry and arid conditions. In regions with sufficient rainfall or irrigation, the green fodder yield per decare can vary between 2–4 tons.
In silage planting, the most suitable harvest time is the flowering stage of the plant. It is important that forage peas to be used for silage are first wilted after cutting and the dry matter content they contain is increased to over 25%. It is also necessary to use a suitable additive during silaging. Siloing in a mixture with plants such as cereals can increase silage quality. This method makes the silage more efficient by increasing nutritional value and durability.
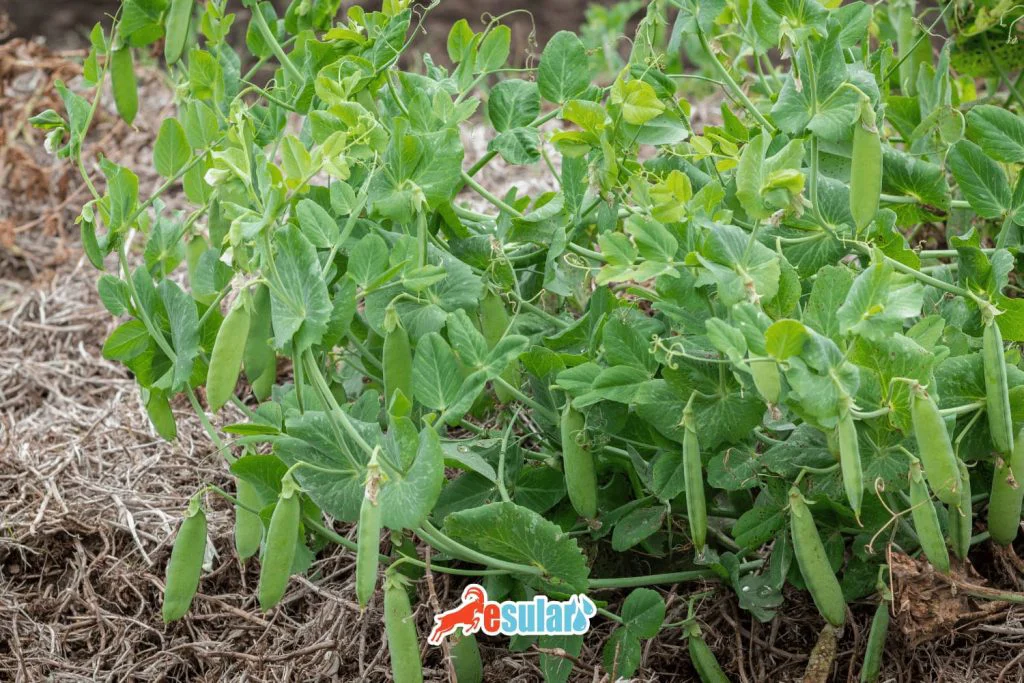

How Many Bales Does Forage Pea Yield per Decare?
This plant species generally offers a hay yield of between 30 and 40 bales per decare. This high productivity makes forage pea a fundamental component in animal feeding programs. High hay yield provides farmers with a valuable feed source while offering a healthy and nutritious food source for animals. Additionally, the productivity of forage pea encourages diversity in the agricultural field and can increase farm incomes. For this reason, forage pea is an important agricultural product that both farmers and animal breeders should consider.


Yorumlar