How is Cabbage Cultivation Done?
Cabbage cultivation is carried out in fertile soils rich in organic matter. Cabbage is a widely consumed and economically important vegetable belonging to the Brassicaceae family. It is generally known for its large, firm heads and dark green leaves. Originating from the Mediterranean region, cabbage is now widely grown throughout the world. Cabbage provides many benefits for health. It strengthens the immune system with the high amount of fiber, vitamin C, and folate it contains. Additionally, it is rich in vitamin A, vitamin K, and antioxidants. It is also known that the phytochemicals found in this vegetable have cancer-reducing effects. Economically, cabbage cultivation is one of the important sources of income for many countries. The fact that it is a vegetable in high demand, especially in local markets and supermarkets, makes it a profitable agricultural product for farmers.
What are the Cabbage Varieties?
There are many varieties of cabbage, and these are generally classified according to their head shape and colors. Here are some common cabbage varieties:
White Cabbage: One of the most common types, white cabbage is known for its large, tight heads and green outer leaves. It is mostly consumed by cooking in wraps and dishes.
Red Cabbage: This cabbage variety, which has a dark purple color, is generally used in pickles or salads. Its leaves are slightly crispier than white cabbage.
Savoy Cabbage: Known for its wavy, curly leaves, savoy cabbage has a crispier texture compared to other cabbage types. It is often preferred for making salads.
Brussels Sprouts: Brussels sprouts, which have small, round heads, grow in the leaf axils and are generally consumed roasted or boiled.
Kale: Often also called "leaf cabbage," kale is a cabbage variety with large, dark green leaves. It can be used in salads, soups, or wraps.
Black Cabbage: Black cabbage, which has dense, dark green leaves, is frequently used in making pickles or fermented cabbage.
These are just a few examples of some cabbage varieties, and many more varieties exist. Each variety has its own unique flavor and areas of use.

Climate and Soil Structure in Cabbage Cultivation
Suitable climate and soil conditions are important for success in cabbage cultivation. Climate is a fundamental factor affecting the growth process, development, and productivity of cabbages. Cabbage is generally considered a cool-climate vegetable and performs best in cool, humid climate conditions. Temperature plays a decisive role in the growth rate, head formation, and quality of cabbage. Most cabbage varieties develop best between 15°C and 20°C. However, temperatures above 25°C can negatively affect head formation and cause small heads to form. Therefore, the ideal temperature range for cabbage cultivation is important.
Soil structure also plays an important role in cabbage cultivation. Cabbages prefer soils that are rich in organic matter, well-drained, and capable of holding water. Soils with a pH level generally between 6 and 6.5 are considered suitable for cabbage. Sandy-loam or loamy soils allow the roots of cabbages to develop well and take in nutrients. Additionally, salty soils should be avoided because salty soils can negatively affect the quality of cabbage leaves. Cultivating in areas with suitable soil structure for cabbages can provide healthier plants and high productivity. Therefore, the climate and soil structure of the area where cabbage cultivation will be carried out should be carefully evaluated.
When and How are Cabbage Seedlings Planted?
Cabbage is among the cool-climate vegetables. Planting time generally varies from late spring to early summer or from late August to early autumn. Sowing of cabbage seeds should take place during the period when the soil temperature is between 10-15°C. This temperature range provides a suitable environment for germination. Cabbage generally grows in moist, well-drained soils rich in organic matter. Soil preparation before sowing is important and the pH level of the soil should be approximately between 6 and 6.5. Good preparation of the seedbed before sowing ensures that the seeds germinate well. Additionally, seasonal climate conditions and environmental factors should also be taken into account in cabbage cultivation. Therefore, careful planning should be made along with appropriate sowing time and soil preparation.

Irrigation in Cabbage Cultivation
Cabbage is a water-loving type of vegetable and needs sufficient irrigation to grow healthily. The first irrigation is usually carried out when cracks begin to occur around the root of the plant. However, the irrigation program is adjusted regularly depending on the soil structure, amount of precipitation, and the development status of the plant. Especially the yield and quality of cabbages grown in rainless, arid, and non-humid regions may be negatively affected. Therefore, irrigation is even more important in such regions.
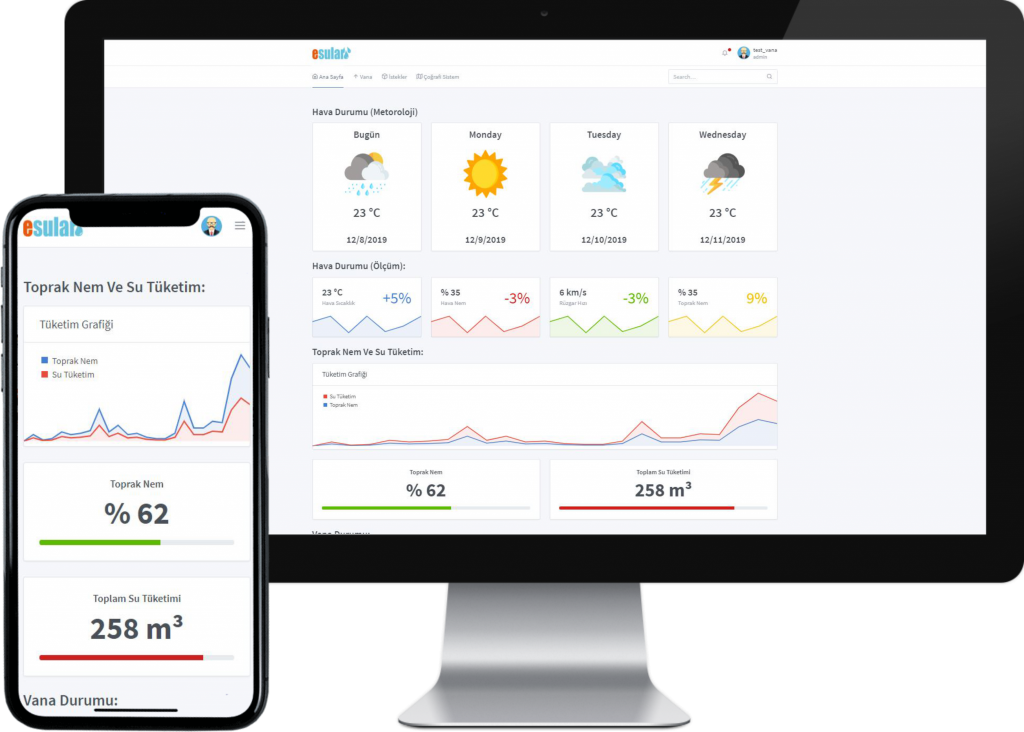
Smart Irrigation System in Cabbage Cultivation
Smart irrigation systems are an extremely effective tool for providing correct irrigation in cabbage cultivation. These systems determine the water need of the plant precisely, preventing water waste and increasing productivity. Additionally, they increase product quality, meeting the expectations of consumers and enabling them to obtain a better market share. Here are the important advantages of smart irrigation systems in cabbage cultivation:
Precise Irrigation: Smart irrigation systems determine the real-time water need of the plant by monitoring soil moisture sensors or weather conditions. In this way, water is ensured to be given in the correct amounts and at the right time.
Water Saving: Thanks to soil moisture sensors, the water need of the plant is determined and unnecessary irrigation is prevented. This prevents water waste and provides water savings.
Automatic Control: Smart irrigation systems have programmable features, and irrigation timing and amount can be easily adjusted. This automatic control saves labor and simplifies the irrigation process.
Productivity and Quality: Correct irrigation promotes the healthy growth of the plant and increases product yield. Additionally, it maintains the nutritional balance of the plant, which is important for obtaining a high-quality product.
Remote Monitoring and Control: Some smart irrigation systems offer remote monitoring and control possibilities. In this way, farmers can manage irrigation operations remotely and adjust systems when necessary.
Fertilization in Cabbage Cultivation
According to the results of soil analysis, all of the farm manure and half of the potassium fertilizer are generally applied before soil tillage. This application ensures the enrichment of the soil in terms of organic matter and nutrient elements and meets the nutrients needed by the plants. The remaining part of the potassium fertilizer is given during the head wrapping period of the cabbage, that is, the period when the plants wrap their head leaves. In this period, potassium helps the plants grow healthily and strongly. The remaining part of the nitrogen is generally applied at the last hoeing. This application ensures the provision of the nitrogen necessary for the plants to complete their development and increase product yield. Fertilization applications carried out in this way contribute to a healthy growth and high yield by ensuring that plants receive the nutrients they need at the most appropriate times and amounts.
Harvest in Cabbage Cultivation
Harvest in cabbage cultivation is carried out during the period when the plants reach the desired size and maturity. The harvest time of the heads may vary depending on factors such as the time elapsed since planting, variety characteristics, earliness or lateness. Cabbage heads generally mature between 3 to 5 months and become suitable for harvest. Heads that have reached harvest maturity are cut from the soil level, usually in a time frame determined according to their size and market conditions. During the harvest process, it is important that the heads are sound and undamaged. After cutting, damaged leaves are cleaned and the heads are made ready for sale by packaging or presenting to the market.
How Much Cabbage is Produced from 1 Decare?
On average, approximately 3 to 7 tons of product can be obtained from a one-decare area. If the harvest process is done with careful planning and correct timing, it is possible to obtain a high-quality and productive product

Diseases and Pests Seen in Cabbage Cultivation
Frequently seen diseases and pests in cabbage cultivation are as follows:
Diseases:
-
Leaf Spot in White Cabbage: A bacterial disease, leaf spot in white cabbage causes brown spots to form on the leaves.
-
Cabbage Canker: A bacterial disease, cabbage canker causes the plant to weaken by forming spots on the roots, stems, and leaves of the plants.
-
Fungal Leaf Spot Diseases: Fungal diseases such as Alternaria and Mycosphaerella species form spots on cabbage leaves and reduce the photosynthesis ability of the plant.
Pests:
-
Cabbage Moth: It is a pest that damages cabbage leaves and harms the plant with its larvae.
-
Aphids: These are small insects that damage cabbage plants by sucking their leaves. They negatively affect the growth and development of plants.
-
Mole Cricket: Larvae living underground cause yield loss by weakening the root system of the plant.
These diseases and pests can negatively affect the health of the plant and lead to yield loss. Therefore, identifying and combating diseases and pests is important.



Yorumlar