How is Mango Cultivation Done?
Mango cultivation is an agricultural practice successfully carried out in tropical and subtropical climates. In Turkey, mango cultivation is also carried out in some regions, especially in the Mediterranean and Aegean Regions. Mango is an exotic fruit species that grows in tropical and subtropical climates. Although there are different mango varieties, varieties such as Tommy Atkins, Kent, Keitt, Haden, and Irwin are generally preferred in our country. Mango is a very beneficial fruit for health because it contains high amounts of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. However, mango cultivation also faces certain risks. Factors such as diseases, pests, and transportation issues, as well as climate conditions, can affect the profitability of producers. Therefore, it is important for those who want to practice mango cultivation to plan carefully and take appropriate measures.
Where Does Mango Grow?
In Turkey, mango cultivation is generally carried out in the Mediterranean Region and some warm and humid parts of the Aegean Region. Among these regions, the Mediterranean coasts such as Antalya, Mersin, Adana, and some districts of Izmir are suitable regions for mango cultivation. However, mango production is more limited compared to other tropical and subtropical regions across Turkey and is not done on a commercial scale.
Climate and Soil Structure in Mango Cultivation
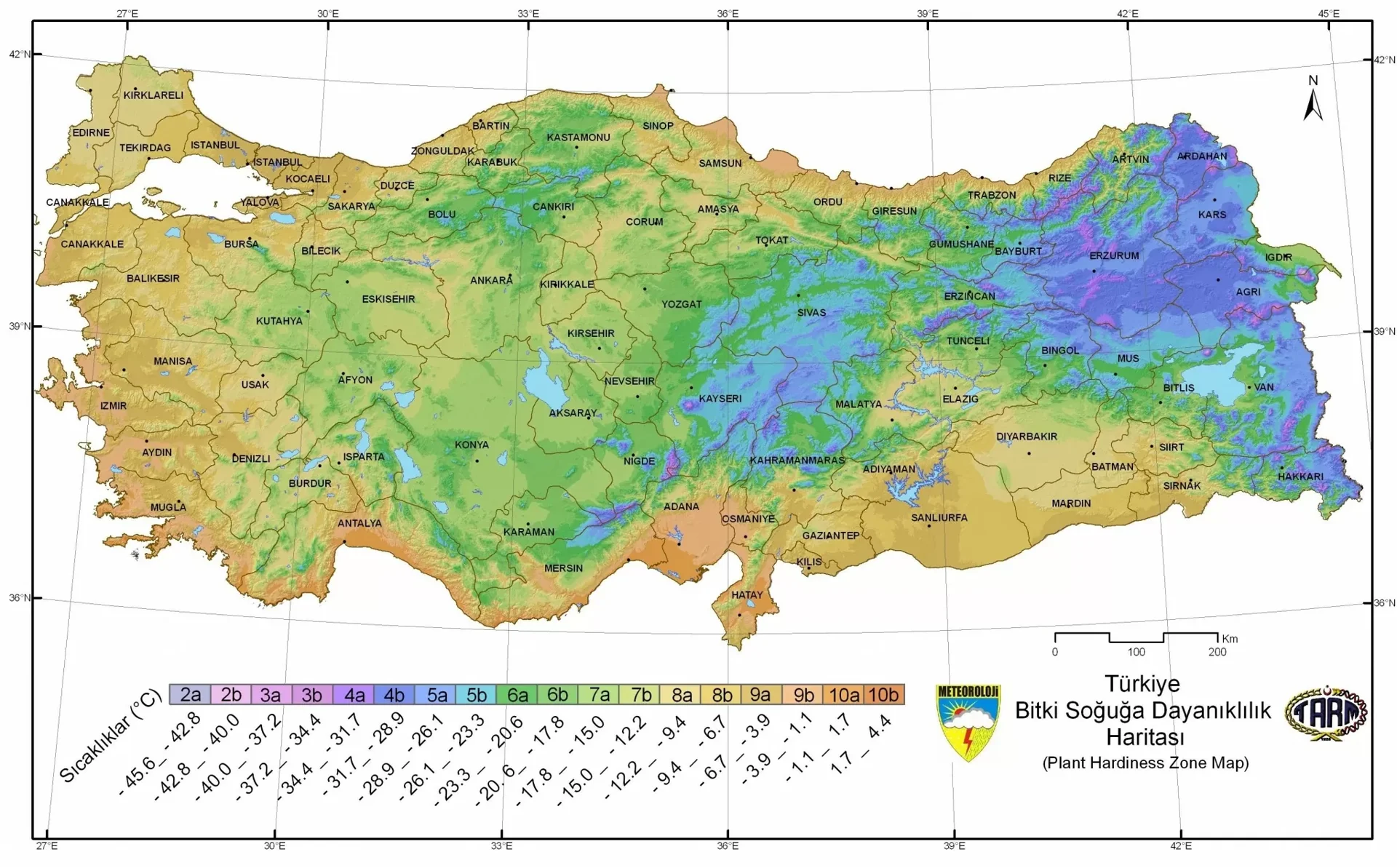
In mango cultivation, temperature is a very important factor. While young saplings are damaged in cold weather between -1.7 and -1.1 °C, this temperature drops to -3.9 °C in adult trees. For flowers and small fruits, the temperature falling below 4.4 °C increases the probability of damage. The average minimum temperature during winter should be above 5 °C. Otherwise, it may cause incomplete fruit formation during flowering time and a decrease in yield. For optimum growth, the temperature should be between 27-35 °C. However, it should not be forgotten that excessive temperature and low relative humidity can negatively affect vegetative growth. Problems such as chlorosis, flowering irregularities, and more frequent occurrence of male flowers may arise under the influence of low temperatures in winter months. Excessive humidity can cause many diseases in mango trees, and drying of young shoots can occur due to winds and cold weather, especially in regions close to the sea coasts. Therefore, it is important to monitor climate conditions carefully and take appropriate measures in mango cultivation.
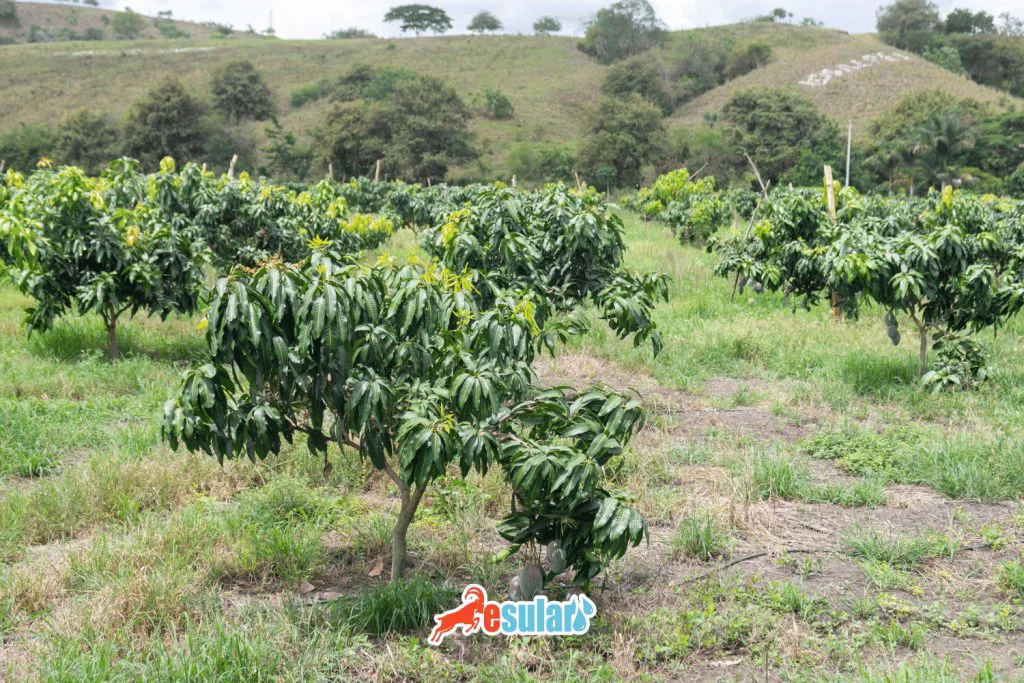

Orchard Establishment and Sapling Planting in Mango Cultivation
Orchard establishment and sapling planting in mango cultivation form the basis of a successful production process. Choosing the appropriate area for orchard establishment is of great importance. Therefore, regions with sunlight and soils that provide good drainage should be preferred for mango trees. Soil analysis should be performed before planting and the soil structure should be improved. In sapling planting, narrow spacings are generally preferred to increase fruit yield and benefit more from the total area. Saplings are generally planted in autumn or spring. Planting intervals may vary according to the variety used and soil structure. Root systems should be checked before saplings are planted and healthy saplings should be selected. Fidanlar properly placed, the soil should be compacted and watered. A healthy mango orchard can be created by using correct planning and appropriate planting methods in orchard establishment. This can increase productivity and provide profitable production.
Irrigation in Mango Cultivation
Mango trees need plenty of water, especially during fruit set and ripening periods. Irrigation should be planned considering soil structure, climate conditions, and available water resources. Soil moisture level should be checked regularly and the irrigation program should be adjusted accordingly. Drip irrigation systems promote efficient use of water by ensuring that water is delivered directly to the root zone of the plant. The irrigation process should be done especially in the early morning hours. Thus, water evaporation decreases and plants can take the water they need throughout the day.
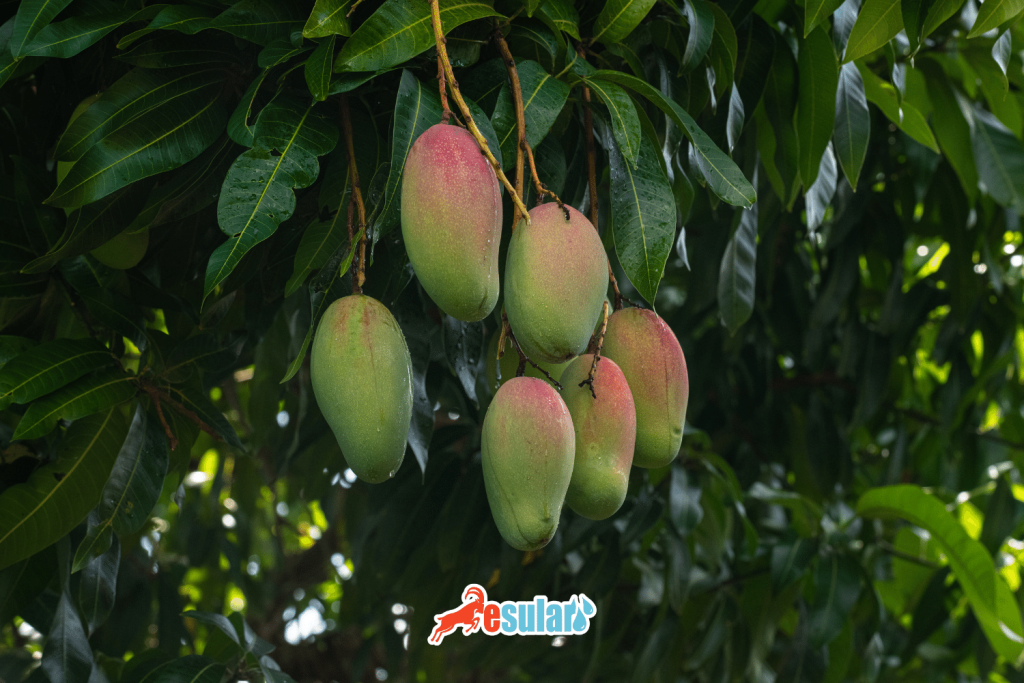

Smart Irrigation Systems in Mango Cultivation
Irrigation in mango cultivation can be made more efficient with smart irrigation systems provided by modern technology. Smart irrigation systems determine irrigation needs more precisely using components such as soil moisture sensors, weather forecasts, and automatic irrigation control devices. These systems monitor the real-time water needs of the plant and ensure efficient use of water. Additionally, it provides efficiency and savings related to water use to mango growers. These systems reduce plant stress and increase product quality by ensuring that water is given at the right time and in the right amount. Smart irrigation systems are also important for environmental sustainability because they help in the effective use of water resources. Therefore, the use of smart irrigation systems in mango cultivation is a practice that benefits both farmers and the environment.

Fertilization in Mango Cultivation
Fertilization in mango cultivation is important for healthy growth and obtaining efficient products. An appropriate fertilization program should be based on soil and plant analysis and should include basic nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Young trees are generally fed with fertilizers containing nitrogen, while phosphorus and potassium are important for older trees. The amount of fertilization should be determined by considering the nutrient content of the soil, plant condition, and growth period. Organic fertilizers are also commonly used and cause less harm to the environment while improving the structure of the soil. A correct fertilization program promotes healthy plant growth and supports high-quality fruit production.

Diseases and Pests Seen in Mango Cultivation
Diseases and pests seen in mango cultivation can negatively affect product yield and quality. These diseases include fungal diseases such as downy mildew, anthracnose, and alternaria spots. While downy mildew creates white spots and mold layers on leaves, anthracnose can create rot and brown spots on fruits. Alternaria spots also cause brown spots to form on leaves. Pests include Mediterranean fruit fly, thrips, and mango aphid. These pests damage the fruits by laying eggs inside them, feed on leaves and fruits, and can cause deformation. Growers should regularly monitor the symptoms of these diseases and pests and apply appropriate control methods. This is important for obtaining a healthy mango harvest and preventing yield loss.
Harvesting in Mango Cultivation
Mango is generally harvested in Turkey between August and December. This period is the time when the ripening process of the mango is most intense and the fruits are most delicious and aromatic. The harvest time between August and December constitutes the time frame when mango is offered to the market and preferred by consumers in Turkey. During this period, mango prices are generally at their highest level because the mango product is available in the market for a limited time and demand is quite high.
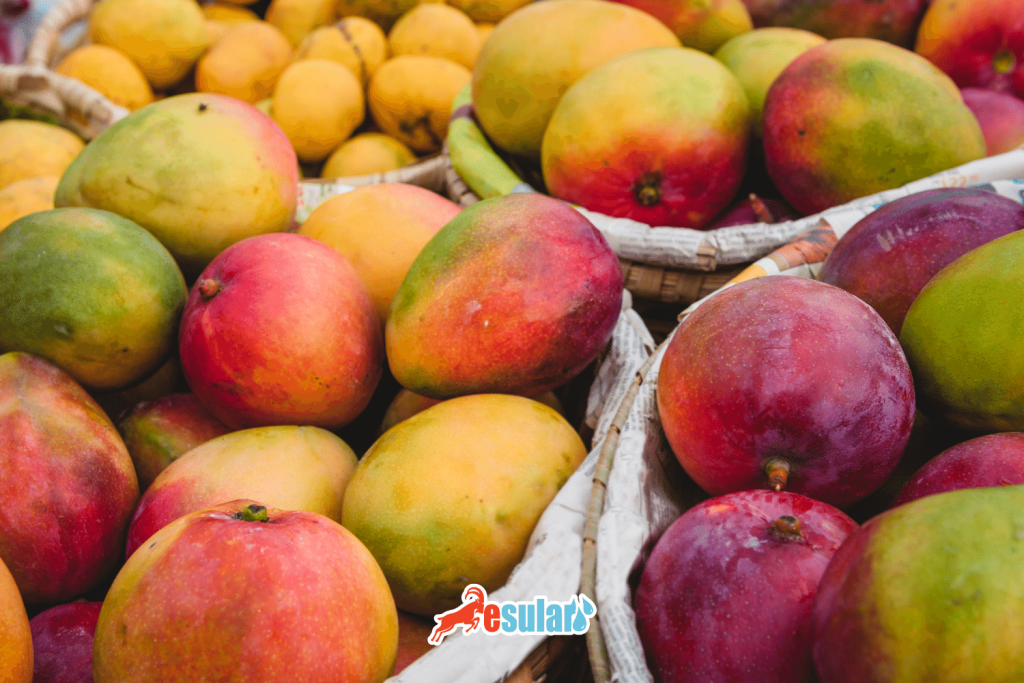

How Much Fruit Does 1 Mango Tree Produce?
Mango saplings start to give fruit from the age of 3 with correct care and management. This period can be even shorter in grafted varieties. Generally, approximately 100 mango fruits can be obtained from a mango tree that has reached the age of 5. However, this amount may vary depending on the variety, climate conditions, quality of care, and growing methods. Additionally, approximately 1000 mango fruits can be obtained from a mango tree that has reached the age of 10. This shows that there is a high yield potential in mango cultivation.


Yorumlar