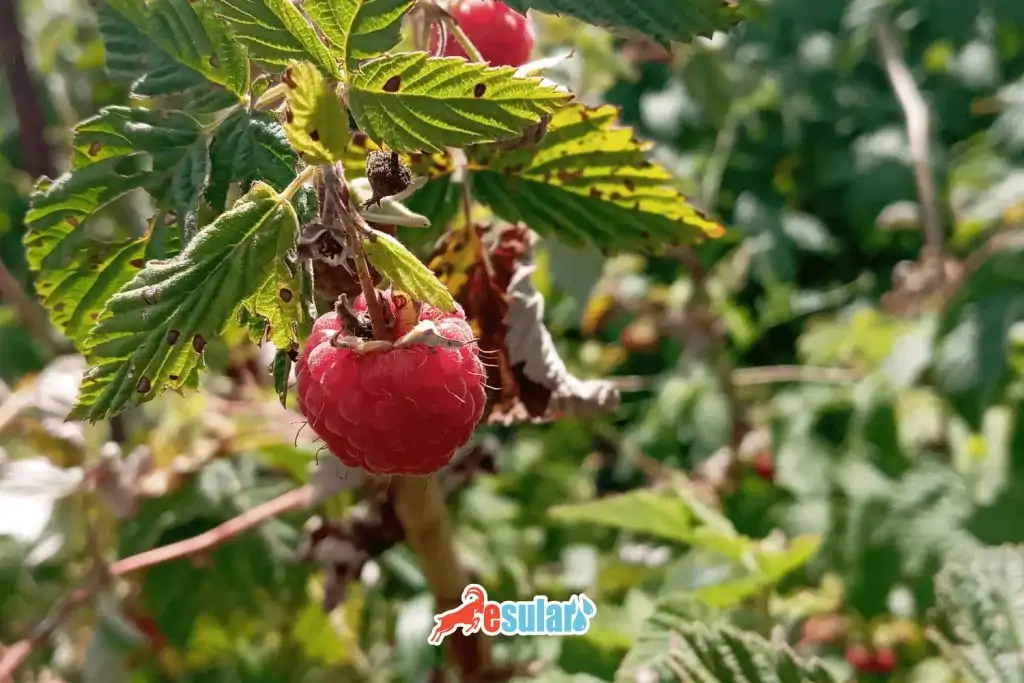
How to Grow Raspberries?
Raspberry cultivation is an area gaining increasing interest in the agricultural sector. Due to being highly valuable for health, this fruit is in high demand. Additionally, besides fresh consumption, it is also used in industrial production. Raspberry cultivation carried out under the right conditions is a quite profitable business. However, good planning and correct agricultural practices are necessary to be successful.
What are the Benefits of Raspberries?
Besides being a nutritious and delicious fruit, raspberries provide many benefits for health. Rich in antioxidants, raspberries protect the body against free radicals, reducing cellular damage and minimizing the risk of chronic diseases. Additionally, thanks to its high fiber content, it supports digestive health, regulates digestion, and increases the feeling of fullness. Due to being rich in Vitamin C, it strengthens the immune system and provides protection against infections. Raspberries may also be potentially beneficial in fighting cancer. It keeps blood sugar levels in balance and supports skin health. With all these benefits, raspberries can be an important part of a healthy lifestyle.
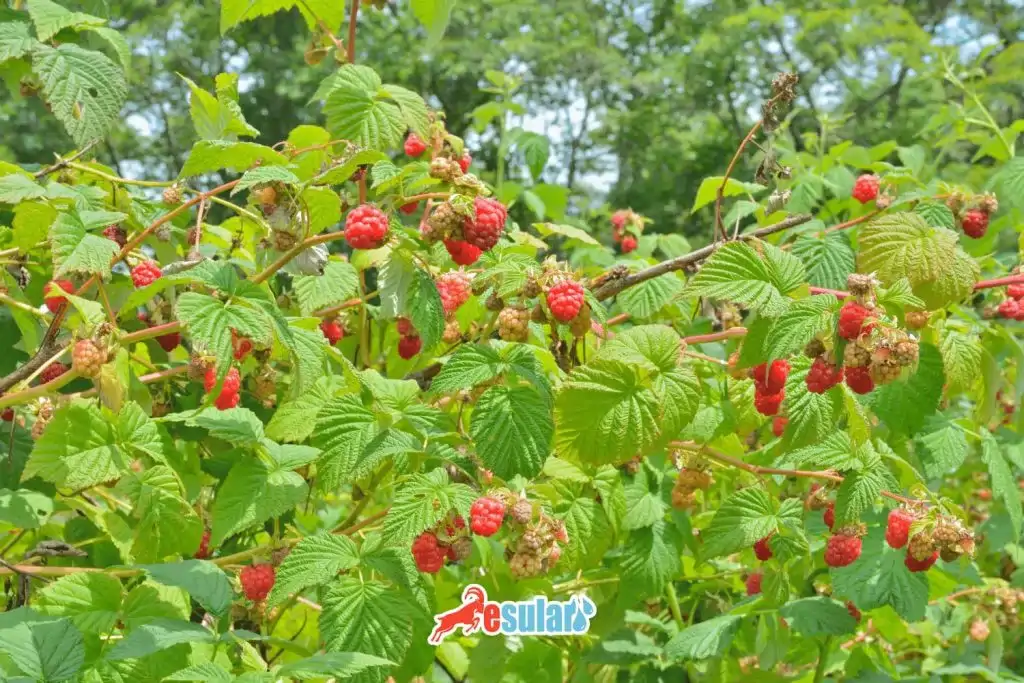

How Should the Climate and Soil Structure Be in Raspberry Cultivation?
The raspberry plant generally prefers temperate climate conditions. For good raspberry cultivation, the annual precipitation amount should be between 800-1200 mm. However, raspberries also have drought tolerance, but long-term drought periods can negatively affect productivity. Temperature is an important factor for raspberry cultivation. The plant prefers mild temperatures in the summer months and can be damaged by extreme temperatures. For ideal growth, daytime temperatures should be between 20-25°C and nighttime temperatures should not drop too low. Deep, well-drained soils rich in organic matter and with slightly acidic or neutral pH are ideal. Additionally, soils must be free from negative characteristics such as salinity and calcification.
Where Do Raspberries Grow?
Raspberry is a fruit widely grown in temperate climate regions. Globally, raspberry farming is conducted in Europe, North America, and certain parts of Asia. In Europe, it has significant production potential in countries like England, Germany, and France. In Turkey, raspberry cultivation is carried out especially in the Eastern and Western Black Sea regions of the Black Sea Region and some parts of the Marmara Region. Provinces like Rize, Trabzon, and Artvin are important production areas. The climate and soil structure of the Black Sea are favorable for raspberry cultivation. In Turkey, raspberries are utilized for industrial uses such as fruit juice, jam, and ice cream, in addition to fresh consumption. In recent years, with the increase in local production and the realization of its economic value, raspberry cultivation has gained importance in Turkey.
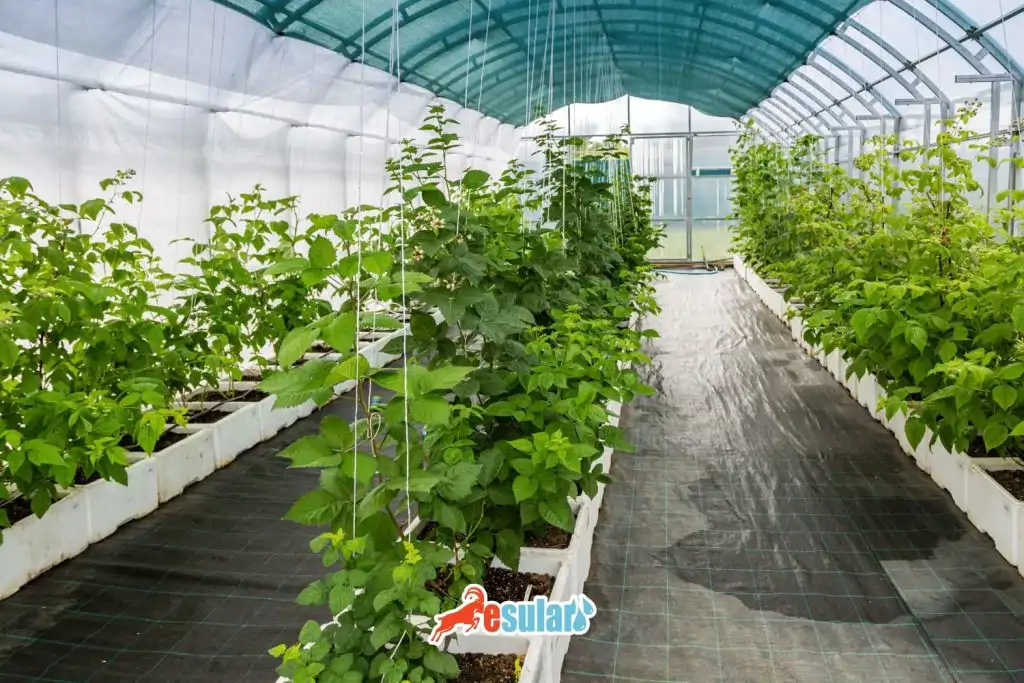

Sapling Planting in Raspberry Cultivation
Raspberry sapling planting is generally carried out in late autumn or winter months. After soil preparation is completed, saplings are planted at distances determined according to row spacing. Saplings are kept with their roots immersed in water where they will be planted, and wounded or dry parts of the roots are cut before planting in the soil. After the planting process, saplings are watered to ensure better contact of the roots with the soil. Planting intervals are generally determined as 2-2.5 meters between rows and 0.4-1 meter on the row. After planting, the care of saplings includes processes such as regular irrigation, fertilization, and pruning when necessary. Raspberry saplings generally grow and become productive in a short time, so a careful planting and maintenance process ensures the healthy development of the saplings.
How Many Raspberry Saplings are Planted per 1 Decare?
In raspberry cultivation, a planting distance of 2x4 meters is generally preferred. Considering this distance, 125 raspberry saplings can be planted on one decare of land. However, the planting distance and therefore the number of saplings may vary depending on the climate and soil conditions of the cultivation region, the variety used, and the cultivation technique. Proper spacing and care are important in raspberry planting because they are necessary for the plants to grow healthily and bear fruit productively.
Smart Irrigation Systems in Raspberry Cultivation
Irrigation in raspberry cultivation is very important for the healthy growth of saplings and productive production. Especially in dry periods, regular irrigation increases fruit yield by meeting the water needs of the plants. While the irrigation process with traditional irrigation methods can take time and require labor, smart irrigation systems make this process more efficient and easier. These systems measure the water needs of plants through sensors and perform irrigation automatically. In this way, more efficient use of water is ensured and labor costs are reduced. Smart irrigation systems can be controlled remotely via mobile applications or the internet. Thus, farmers can monitor and manage irrigation processes remotely. These systems are becoming increasingly common in agricultural areas such as raspberry cultivation to increase irrigation efficiency and use water resources more effectively. The use of these innovative technologies increases productivity in agricultural production while contributing to sustainable agricultural practices by reducing environmental impacts. For more detailed information, you can call us and browse our site. https://esular.com/akilli-sulama-sistemleri
Fertilization in Raspberry Cultivation
After selecting a suitable field for raspberry cultivation, it is important to conduct a soil analysis. Soils rich in organic matter are especially necessary for the healthy growth and productive output of the raspberry plant. According to the soil analysis results, the status of the soil in terms of basic nutrients such as phosphorus and potassium is determined. Phosphorous and potassium fertilizers can be applied once or twice during the year according to the needs of the soil. Fertilizer application is generally done in the winter months, and fertilizers are applied by burying them 20-30 cm below the soil. This ensures that the fertilizers mix better with the soil and that the roots of the plants have better access. It is important that fertilization in raspberry cultivation is done in a balanced and controlled manner. Therefore, a fertilization program should be determined according to the soil analysis results. In this way, healthy growth and high yield are achieved by providing suitable nutrients for raspberry plants.
Harvest in Raspberry Cultivation
Harvest time is when the fruits reach full maturity and should be done carefully during this process. Harvesting generally starts in June for early species and starts in August for late species, continuing until the end of September. Fruits reach harvest maturity approximately 20-25 days after flowering. Fruits can be gently picked by hand when they ripen. The harvesting process should be done in the early hours of the morning. This time frame helps the fruits stay fresher and sweeter. Additionally, since the fruits are collected in a cooler environment with the sunrise, they remain durable for longer. Collected raspberry fruits are filled into small plastic containers with a capacity of 500 to 1000 grams. The fruits are packaged by covering them with gelatin and arranged in crates in a single layer. Fruits packaged in this way maintain their freshness and the risk of damage during transport is reduced. The harvesting process is generally repeated at 2-3 day intervals. This process may vary depending on the length of the ripening period of the fruits and the yield.

How Much Raspberry is Produced from 1 Decare?
In raspberry cultivation, when done according to the technique, approximately 1.5 to 2 tons of fruit can be obtained from a 1-decare raspberry orchard in its full-yield age. This amount is a typical estimate for a healthy orchard supported by correct agricultural practices, proper fertilization, irrigation, and pest and disease control. However, the yield can vary depending on many variables such as climate conditions, soil structure, varieties used, and cultivation technique, in addition to these factors. With good management and care, raspberry cultivation can be a profitable business.
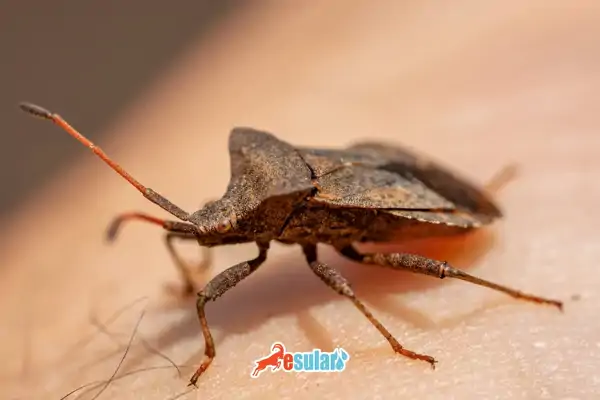
What are the Diseases and Pests Seen in Raspberry Cultivation?
Some diseases and pests that may be encountered in raspberry cultivation are:
Anthracnose: This fungal disease causes brown spots on leaves and fruits. It spreads in humid weather conditions.
Cane Blight / Mummy Rot: This bacterial disease causes a wax-like formation on fruits and shoots. This leads to the rotting and damage of the fruits.
Mildew Fungi: Raspberry plants are sensitive to mildew fungi, especially on leaves and fruits. These fungi spread in humid conditions and weaken the plant.
Gray Mold: This fungal disease creates a gray mold layer on leaves, shoots, and fruits. It causes the fruits to rot and reduces harvest yield.
Dark Pear Scale Beetle: These harmful insects infest the plant with egg groups located under the leaves. They consume the plant's nutrient resources by opening holes in the leaves.
Spider Mite: These pests infest the plant with spider webs located on the lower surface of the leaves.
Raspberry Beetle: This insect damages the inner parts of the fruits and causes the fruits to rot. Larvae feed by entering inside the fruits.
To combat these diseases and pests in raspberry cultivation, it is important to use appropriate agricultural practices, correct fertilization and irrigation techniques, cleaning of diseased and pest-infested areas, and the use of chemical control methods. Additionally, to protect plant health, it is necessary to regularly observe the plant and take necessary precautions.



