What is Soil and Water Salinity? How to Combat It?
Salinity is defined as high concentrations of salts found dissolved in soil and water resources. Soil salinity is generally caused by factors such as excessive irrigation, incorrect irrigation techniques, or the use of high-salinity irrigation waters. This situation prevents plant growth and negatively affects agricultural productivity. There are several important strategies in combating soil and water salinity. First, by establishing effective drainage systems, the removal of salts accumulated in the soil can be ensured. In addition, the impact of saline water resources can be minimized by optimizing water use with appropriate irrigation management. For soil improvement, methods such as desalination techniques and the selection of salt-tolerant plant species can be applied. These strategies aim to increase agricultural sustainability by reducing the negative effects of soil and water salinity. With the right measures applied, the fertility of the soil can be preserved and agricultural productivity can be increased in a sustainable manner.
What is Salinity?

Why Does Salinity Occur?
The main causes of soil and water salinity are as follows:
Excessive Irrigation: When incorrect irrigation methods or more irrigation than necessary is applied, salts in the irrigation water can seep into the soil and accumulate, leading to salinity.
High-Salinity Irrigation Waters: High salt content in the water used for irrigation can cause salt accumulation in the soil over time.
Soil Drainage Problems: If the soil cannot drain sufficiently, salts carried by rainwater or irrigation water can accumulate in the soil and cause salinity.
Industrial and Urban Wastes: The mixing of wastewater or waste materials into the soil can increase soil salinity.
Natural Processes: In some regions, the use of water resources that naturally have high salt content or salt accumulations arising from the natural structure of the soil.
These factors play an important role in the formation of soil and water salinity and can have serious effects on agricultural production, environmental sustainability, and economic activities.
What are the Sources of Water Salinity?
Natural Sources: Natural water sources with high salt content are naturally found particularly in seawater and drinking water sources. Seawater generally contains 3-4% salt, and these salts can be transported to terrestrial water sources.
-
Human Impact: Human activities can increase the salinity of water resources. These impacts may include:
- Agriculture: Incorrect irrigation methods, excessive irrigation, and the salt content in irrigation water can increase water salinity in agricultural areas.
- Industry: Industrial wastewater can increase the salinity of water resources due to the chemicals and salts they contain.
- Urbanization: Wastewater from cities can increase water salinity when discharged into agricultural areas or natural water sources without treatment.
-
Soil and Geological Processes: In some regions, soil and geological structures may harbor high salt content. This situation can increase water salinity by being transported to soils via precipitation or irrigation water.
-
Climatic Effects: In arid and semi-arid climates, low precipitation amounts and high evaporation rates can increase the salinity of water resources. In these conditions, salts in water resources become more concentrated.
The combination of these factors can lead to an increase in water salinity in natural water resources and agricultural irrigation waters. This situation can cause significant problems in terms of both environmental health and agricultural production.

What are the Economic and Environmental Effects of Salinity?
The economic and environmental effects of salinity have a deep and wide-ranging impact on the sustainability of water resources. High salt levels lead to a decrease in product quantity and quality by lowering agricultural productivity, which can cause serious losses in agricultural income and food security. At the same time, it increases the maintenance costs of irrigation infrastructure and can affect the drinking water supply by making the management of water resources difficult. Environmentally, saline water damaging ecosystems and lowering water quality can reduce biodiversity and disrupt ecosystem services. These situations emphasize the broad impacts of water salinity on both economic activities and natural systems; therefore, effective water resources management and keeping salinity under control are of great importance.
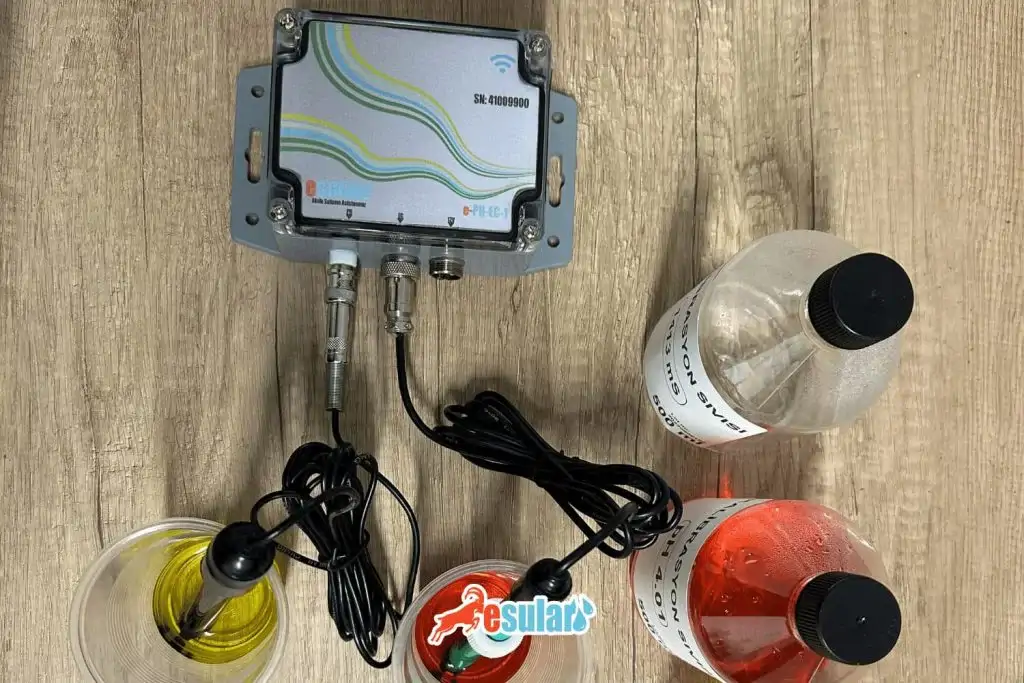
How is Soil and Water Salinity Measured?
Soil and water salinity measurement is an important parameter in agricultural production and can be done through various methods. Here are some common methods used to make these measurements:
Soil Salinity Measurement:
- Electrical Conductivity (EC) Method: In this method, a soil sample is taken and the electrical conductivity of the soil is measured with a special device. The EC value reflects the amount of dissolved salts present in the soil. A higher EC value means higher salinity.
- Soil Salinity Sensors: These are sensors that continuously measure the soil EC value at the location where they are placed. These sensors collect data from different points within the field, thus allowing for the mapping and monitoring of soil salinity.
Water Salinity Measurement:
- EC and pH Sensors: These are sensors that continuously measure the EC and pH values of irrigation water. EC sensors determine the salt concentration in the irrigation water, while pH sensors show the acidity or alkalinity of the irrigation water. The data from these sensors are used to evaluate whether the irrigation water is suitable for plants and to make adjustments if necessary.
These measurements are important for increasing plant health and productivity in agricultural production. The EC and pH measuring sensors offered by Esular automate these processes and offer farmers the opportunity to optimize irrigation management by providing continuous and reliable data. In this way, keeping water and soil salinity under control and the healthy growth of plants are supported.

How to Combat the Salinity Problem?
Various methods can be used to combat soil and water salinity. Here are some commonly applied combat methods:
Establishing Drainage Systems: Especially in high-saline areas, drainage systems are used to ensure the removal of excess water from the soil. With this method, it can be ensured that salts accumulated under the soil surface come to the surface and become available for uptake by plants.
Regular Irrigation: Irrigating at the right timing and in the correct amounts can help balance the salts in the soil. By avoiding excessive irrigation, the accumulation of salts in the soil is prevented.
Salt-Removing Plants: Some plant species can grow specifically in saline soils and can absorb the salts in the soil through their roots. These plants can reduce or keep salt accumulation in the soil under control.
Soil Management: Appropriate agricultural practices carried out to increase organic matter content in the soil, improve soil structure, and control the movement of salt are important.
Fertilization and Nutrition Management: A correct fertilization program and nutrient management can keep the salt concentration in the soil in balance while providing the nutrients that plants need.
Improving Irrigation Water Quality: Treatment methods or less saline water sources can be used to increase the quality of irrigation water. This is an important factor in controlling soil salinity.
Genetic and Agricultural Practices: The use of plant varieties that are resistant to salt stress or can cope with salt, along with appropriate agricultural practices, can be effective in combating soil salinity.
These methods can be integrated to keep soil and water salinity under control and to make agricultural production sustainable. Each method should be applied appropriately according to local conditions and salinity levels.



Yorumlar