How is Cherry Cultivation Done?
Cherry cultivation is generally carried out intensively in regions with a Mediterranean climate and in the temperate climate zone. Turkey is one of the world's leading cherry producers and cherry cultivation is widely carried out in many regions of the country. Turkey's southern regions, especially the Marmara, Aegean, Mediterranean, and Central Anatolia regions, have ideal climate and soil conditions for cherry cultivation. Cherry is a commercially important fruit and provides significant income sources to producers. However, cherry cultivation is quite sensitive to seasonal factors, especially climate changes, and natural events such as frost negatively affect the product quantity. Nevertheless; with correct agricultural techniques, irrigation methods, and disease control, cherry cultivation can be quite profitable. Cherry cultivation has been carried out for thousands of years in various regions of Anatolia, which is considered the homeland of cherries. Cherry cultivation makes significant contributions to the country's economy both for fresh consumption in the domestic market and through exports.
What are the Cherry Varieties?
There are many different varieties in cherry cultivation. Some popular cherry varieties grown in Turkey and worldwide are as follows:
Bing: A variety that is quite popular in the USA, with large, bright red color and sweet fruit.
Lambert: This variety, which has large, dark red color and a sweet-tart flavor, grows in a short season and has a short shelf life.
Van: Named after the city of Van in Turkey, this variety has medium-sized and bright red fruits. It is also grown in Central Anatolia regions.
Stella: Medium-sized, bright red and sweet fruit, this variety is self-fertile and easily grown.
0900 Ziraat: This variety, which is very widely grown in Turkey, has large, firm, and sweet fruit flesh. It stands out with its fruit resistant to cracking.
Kordia: This variety, which has large, black-colored and sweet fruit, ripens late and has a long shelf life.
Regina: This variety, which has medium-sized, bright red and sweet fruit, has a durable tree structure and is compatible with cold climates.
In addition to these varieties, different cherry varieties can be grown according to the climate and soil conditions of each region. Variety selection in cherry cultivation should be made by considering factors such as climate conditions, soil structure, and market demands.

How Should Climate and Soil Structure Be in Cherry Cultivation?
Since cherry is a deciduous fruit species, they need a warm growing season and a certain period of rest in winter. A growing season without frost events and a rain-free harvest period to prevent cracking are required. However, one of the most important factors limiting cherry cultivation is late spring frosts. While cherry flower buds can generally withstand up to -2°C, open flowers may be damaged at -2°C. Winter chilling is necessary for breaking dormancy and for growth to continue in the spring. Cherries generally have a chilling requirement of 400-1500 hours spent below 7.2°C. Soil structure is also important for cherry cultivation. Well-drained soils with a pH value between 5.5-7.5 are suitable for cherry cultivation. However, cherry roots are sensitive to excessively moist soils, and root diseases can be more common in such soils. Therefore, in addition to suitable climate and soil conditions, correct irrigation and disease control are of great importance in cherry cultivation.
Sapling Planting in Cherry Cultivation
Determining the appropriate rootstock-variety combination for cherry cultivation and obtaining saplings from reliable sources is quite important. The fact that the saplings are certified is necessary for the establishment of a healthy and high-quality orchard. Depending on the climate conditions, the planting time should also be well planned. In places where spring is harsh, autumn should be preferred, and in places where it is mild, autumn should be preferred. Root pruning should be done before planting and they should be planted at the same depth they were removed from the nursery parsel. Adding farm manure to the planting holes positively affects sapling development. Giving life water to the saplings immediately after planting helps the roots settle and the new orchard to develop healthily. It is important to implement these steps meticulously for a successful planting and maintenance process in cherry cultivation.

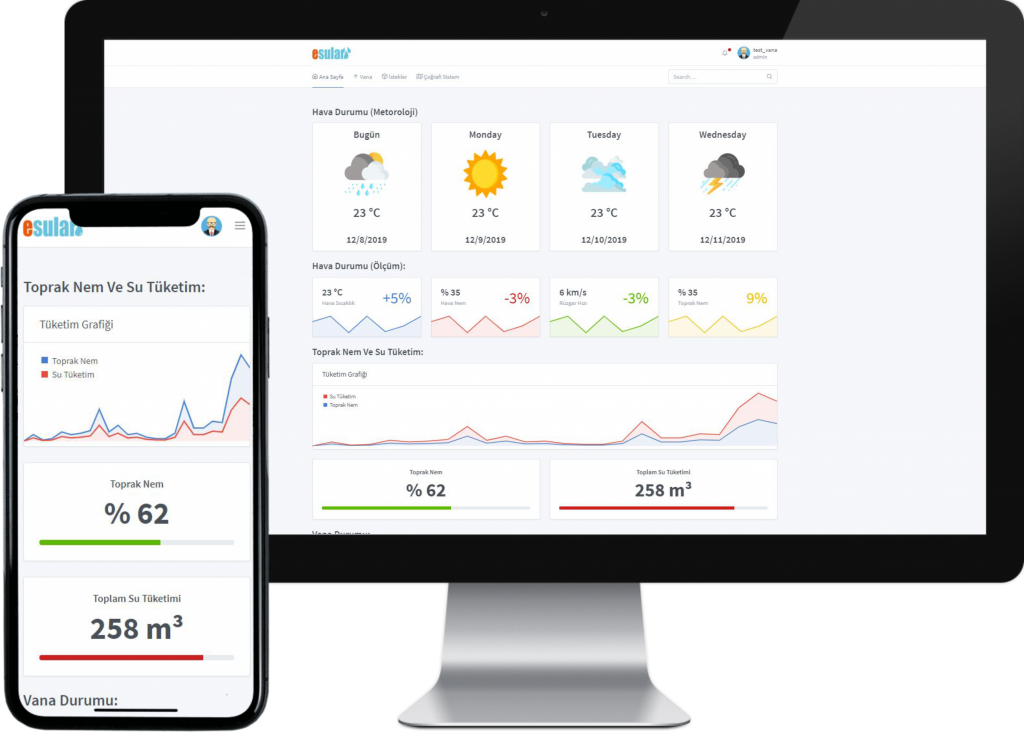
Smart Irrigation Systems in Cherry Cultivation
Cherry trees need a regular and sufficient amount of water throughout the growing season. Especially during the flowering and fruit development periods, their water needs increase even more. Water also helps to obtain larger and sweeter fruits by increasing the fruit juice during the fruit ripening process.
Smart irrigation systems in cherry cultivation allow irrigation processes to be carried out more effectively and efficiently. These systems automatically adjust the irrigation amount and timing based on plant needs. In this way, while preventing the waste of water, it also correctly meets the water needs of the plants. Another advantage of smart irrigation systems is that it reduces the workload. Automatic irrigation programs reduce the time and labor farmers spend to organize irrigation processes. This allows farmers to focus more on other agricultural activities. These systems help improve water management in cherry cultivation and obtain healthier and more productive cherry crops. You can contact us to get more detailed information on this subject.
Fertilization in Cherry Cultivation
To determine the soil characteristics of the land where the cherry orchard will be established, soil samples should be taken from different depths and analyzed. These analyses provide information about the soil's pH level, nutrient content, organic matter amount, and other important characteristics. Based on the soil analysis results obtained, an appropriate fertilization program should be determined and the nutrient elements needed by the trees should be added to the soil. It is important for cherry trees to form a sufficient amount of flower buds to yield fruit at a commercial scale. This requires providing water and nutrients in correct proportions. Basic nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are necessary for the growth and fruit formation of cherry trees. In addition, microelements also play an important role. Especially; deficiencies such as boron, iron, and zinc should be monitored regularly. After harvest, foliar applications and fertilizations should be made to ensure the nutrition of the trees. This process continues until the trees' dormant period and ensures the nutrition of next year's fruit buds. In this way, cherry trees can grow healthily and gain resistance against diseases.
How to Prune a Cherry Tree?
Pruning and training in cherry cultivation are quite important in terms of early fruit formation, productivity, and fruit quality. Cherry trees generally form a vertically growing canopy. For this reason, the central leader system is preferred for pruning. According to this system, after the first planting, the tops of the saplings are cut from a height of 75-85 cm. In the spring, after the buds swell, 2 buds at the tip are left and 5-6 buds below it are plucked. With this application, the competition of the shoots at the top of the tree is reduced. When the shoots reach 7-10 cm in length, 4-5 branches are selected from a height of 45-50 cm and the branch angles are widened to make an angle of 80-90 degrees with the trunk. In this way, early fruit formation is encouraged. After the first tier is formed, the same process is repeated in subsequent years until a total of 4-5 tiers and 17-21 side branches are formed. Pruning time should be delayed, especially in harsh winter regions.
How Many Years After Does a Cherry Tree Bear Fruit?
A cherry tree generally starts to bear fruit between 3 to 5 years after planting. However, this period may vary depending on the variety, growing conditions, and climate conditions. Some fast-growing and early cherry varieties may bear fruit earlier, while other varieties may take longer.
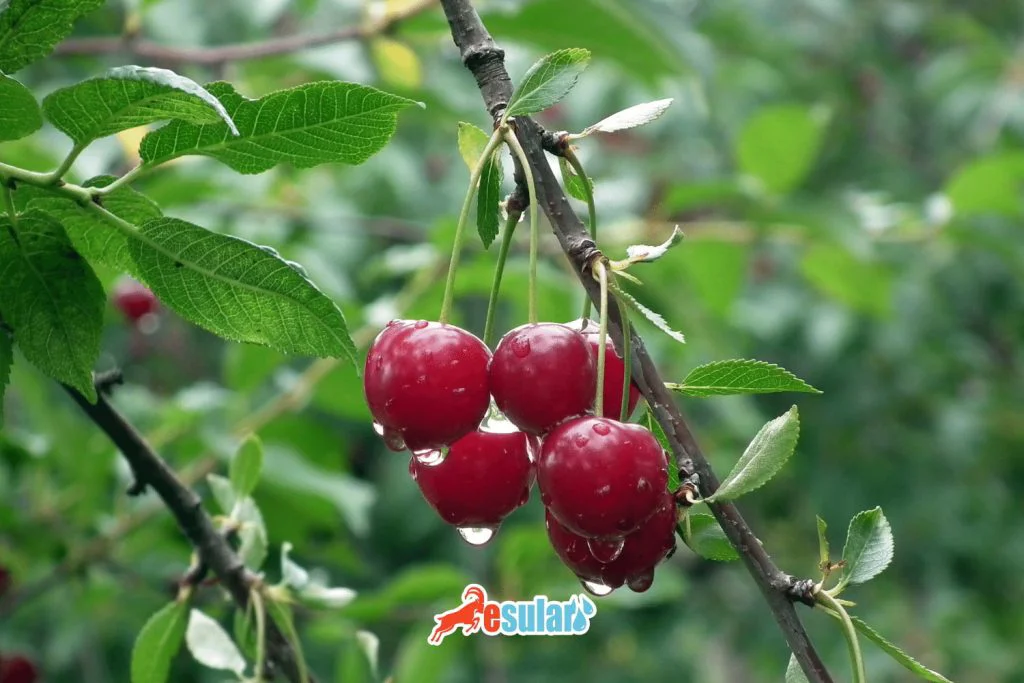

Harvest in Cherry Cultivation
Harvest is one of the most important stages of the process. Because the unique physical characteristics and delicate structure of cherries require extremely careful behavior during harvest. When cherries reach maturity, they should be collected in the early hours of the day. Because as the temperature increases, the quality and durability of the fruits may decrease. Also, the harvest should not be delayed to protect ripening cherries from birds. During harvest, not only the fruit but also the stems must be carefully plucked. This helps both in protecting the fruits and in preparing the tree for next year's yield; because if fruit buds are damaged during harvest in cherry trees, the next season's yield can be seriously affected. Therefore, the harvest process should be carried out meticulously and with care, so that both the fruits and the trees can continue their development healthily.
How Much Cherry Comes Out of 1 Dönüm?
In cherry cultivation, the amount of product that can be obtained from an area of one dönüm varies. According to TUIK's 2012 data, the average yield per tree is 28 kilograms. Based on this data, the amount of product that can be obtained from a one-dönüm area can be between 420 and 3000 kilograms.

Diseases and Pests Seen in Cherry Cultivation
Some diseases and pests seen in cherry cultivation are as follows:
Diseases:
- Monilia Disease: It is a fungal disease seen in flowers and fruits. It causes the fruits to turn brown and rot.
- Bacterial Canker and Gummosis: It is a disease that is especially effective on the trunk, young shoots, branches, fruit stems, buds, leaves, and fruits. It shows symptoms in the form of circular and longitudinal wet spots.
- Root Fungal Diseases: Fungal diseases such as root rot and crown rot can damage the root system in cherry trees and prevent growth and nutrient uptake.
Pests:
- Cherry Fly: It is a pest that causes larvae to feed inside the fruit by laying its eggs on cherry fruits. It can cause fruit drop and loss of quality.
- Spotted Wing Drosophila: It causes larvae to develop inside them by laying eggs on ripened fruits. This leads to the rotting of the fruits.
- Red Spider Mite: Red spider mite, which is harmful to cherry trees especially in summer months, can cause yellowing, drying, and shedding in leaves.
- Aphids and Scale Insects: Aphids and scale insects can cause yellowing of leaves and deformation of fruits.
These diseases and pests can cause serious economic losses in cherry cultivation, so it is important to control them using effective struggle methods.


