Long-Term Water Saving Strategies for Avocado
Install valves for each plant row bed
To ensure that crop water needs match irrigation practices more accurately, separate valves should be installed in blocks or plant row beds with different water requirements. Water use varies between varieties and with tree age. If canopy reduction is adopted in a section of a patch, the irrigation system should be modified to accommodate significant differences in resulting water requirements.
Install more advanced planning equipment
More sophisticated scheduling equipment (e.g., capacitance probes) will allow for much more accurate irrigation applications and assessment of additional rainfall effectiveness. While ensuring irrigations are fully effective, leaching losses can be completely avoided. This equipment is more expensive and requires some time to learn how to use and understand the information produced.
Switching to more efficient irrigation systems
When managed correctly, drip irrigation is potentially the most efficient irrigation system currently available. When water allocations are low or predicted to be low, converting to drip is often a standard horticultural recommendation. Avocado growers' personal experiences with drip irrigation are mixed. Proper management is crucial because avocado trees are very unforgiving.
Without any prior experience with this system, a quick switch to drip in a low-water situation can cause problems. Managers in this situation should consider sticking with a system they are familiar with. A change to drip can cause significant crop loss. Many who have tried drip return to low-level sprinklers for these reasons.
If you want to convert to drip, remember that a new permanent drip system requires a significant investment and must be professionally designed.
It is important to know that switching from a full-coverage irrigation system to drip irrigation changes the water distribution in the root zone. It takes time for roots to respond to a change in water distribution, and trees will experience stress until the root system adapts. Plenty of drip irrigation is recommended in the first year after the switch in a normal season. In low-water conditions, adding a water deficit on top of the conversion will likely lead to significant stress.
Avocado Young Tree (0-6 years) management
If water is applied efficiently, significant water savings can be made in young trees. Young trees have a smaller canopy and root zone than older trees and require less water in proportion to their reduced canopy sizes.
Key water saving practices for young trees include:
- reducing leaching losses below the root zone
- building a small basin around newly planted trees to trap water (low-level sprinklers)
- spreading mulch around the tree to reduce evaporation from the soil surface
- In-line dripper clips (C-clips) can be used to block drippers between trees where roots are not yet established.
- installing additional sub-pipes and valves to separate young plantings from mature trees
- installing sprinkler heads with smaller throw patterns and
- installing a soil moisture monitoring system to accurately and safely determine water demand from young trees.
Tree water use is directly related to canopy size, so reducing the canopy reduces water use. The relationship between canopy size and water use occurs primarily through the interception of solar radiation (sunlight).
Consequently, for a 50 percent reduction in water availability, for example, reducing the tree canopy to reduce the shaded area under the trees by 50 percent will match water demand with availability.
If a patch of trees needs pruning due to row access issues or if older trees need rejuvenation due to declining productivity, this presents itself as an opportunity. However, if pruning is used only as a water-saving strategy, it should be carefully considered as part of the overall farm strategy, as it will significantly affect production levels for the next few years even if allocations return to normal immediately. Alternatively, old or unproductive blocks can be abandoned in preparation for replanting when water availability increases.
Unlike citrus, avocados are not suited to stag-horning or skeletonizing, but some work has recently been done on selective limb removal.
Severe selective branch pruning to remove 50 percent of the wood produced ensures that the remaining 50 percent of the tree remains productive. Whitewashing all remaining branches will be necessary.
Reducing the height of trees and removing large branches in older trees will also allow some production to continue while reducing irrigation requirements.
The decision to remove the canopy should be based on tree age, crop load, growth stage, on-off crop load cycle, long-term block viability, water and commodity prices (consider the possible impact of low water supply on the county and basin. Wide avocado production levels and subsequent fruit prices) and how much water needs to be saved. Trees are given sufficient levels of water and nutrients they need to recover to form a strong canopy that produces quality fruit.
It is important to treat entire irrigation units (e.g., not alternate rows) so that a reduced irrigation application can be confidently applied to the patch and regrowth occurs evenly without excessive shading from unpruned neighboring trees. If an entire irrigation unit cannot be pruned, the irrigation system must be modified to match; otherwise, the full benefits of reduced irrigation demand cannot be achieved. Soil moisture monitoring also becomes important to validate reduced water demands and ensure appropriate irrigation scheduling occurs.
Deep Pruning in Avocado Trees
Deep pruning involves cutting trees down to a stump above the graft union to revitalize orchards or allow new varieties to be top-worked. It can also be an option if water resources are severely reduced

Deeply pruned trees will require whitewashing of exposed limbs to prevent sunburn. Damage can occur within a day in hot weather, and the risk increases significantly as temperatures rise. Adding a copper fungicide treatment can help control disease on the pruned surface.
Trees may remain out of production for 2-4 years after stag-horning. If nurse limbs are kept, recent trials have found that trees can return to production within 1-2 years with proper management and canopy regrowth manipulation.
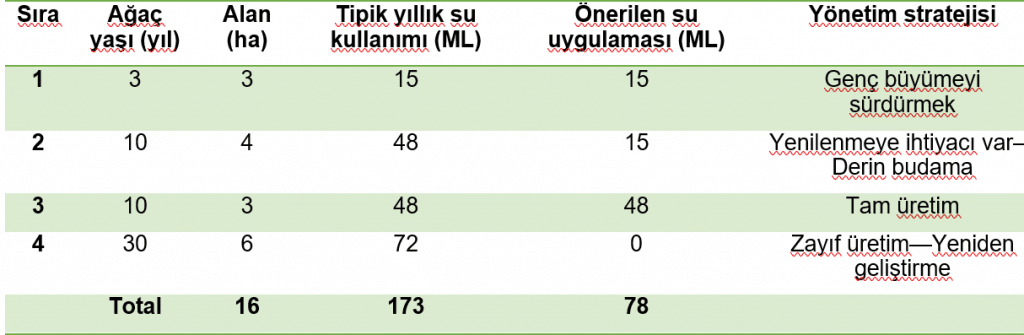
Water Budget Planning
Table 1 is a sample water budget for a 16-hectare avocado orchard irrigated with a sprinkler system. The property has a 200 ml entitlement. The table addresses a scenario where the orchard allocation reaches only 40 percent and 80 ml remains available.
The first step is to prioritize plant row beds and determine appropriate management strategies. Discussions should be held with packers. Typical annual water use for each block should be determined from previous records and experience. The recommended allocation for each plant row and the management strategy to be implemented should then be determined.
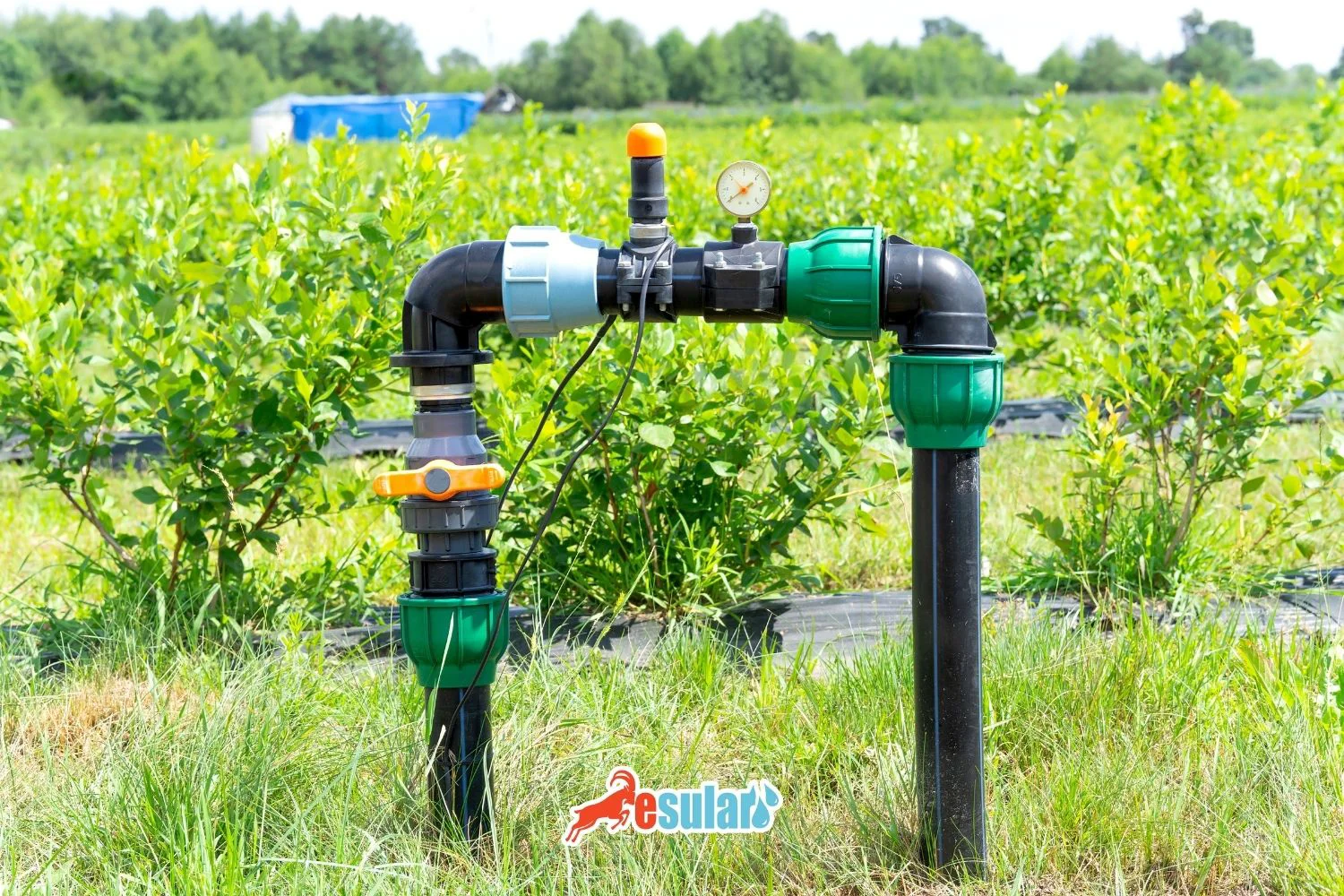
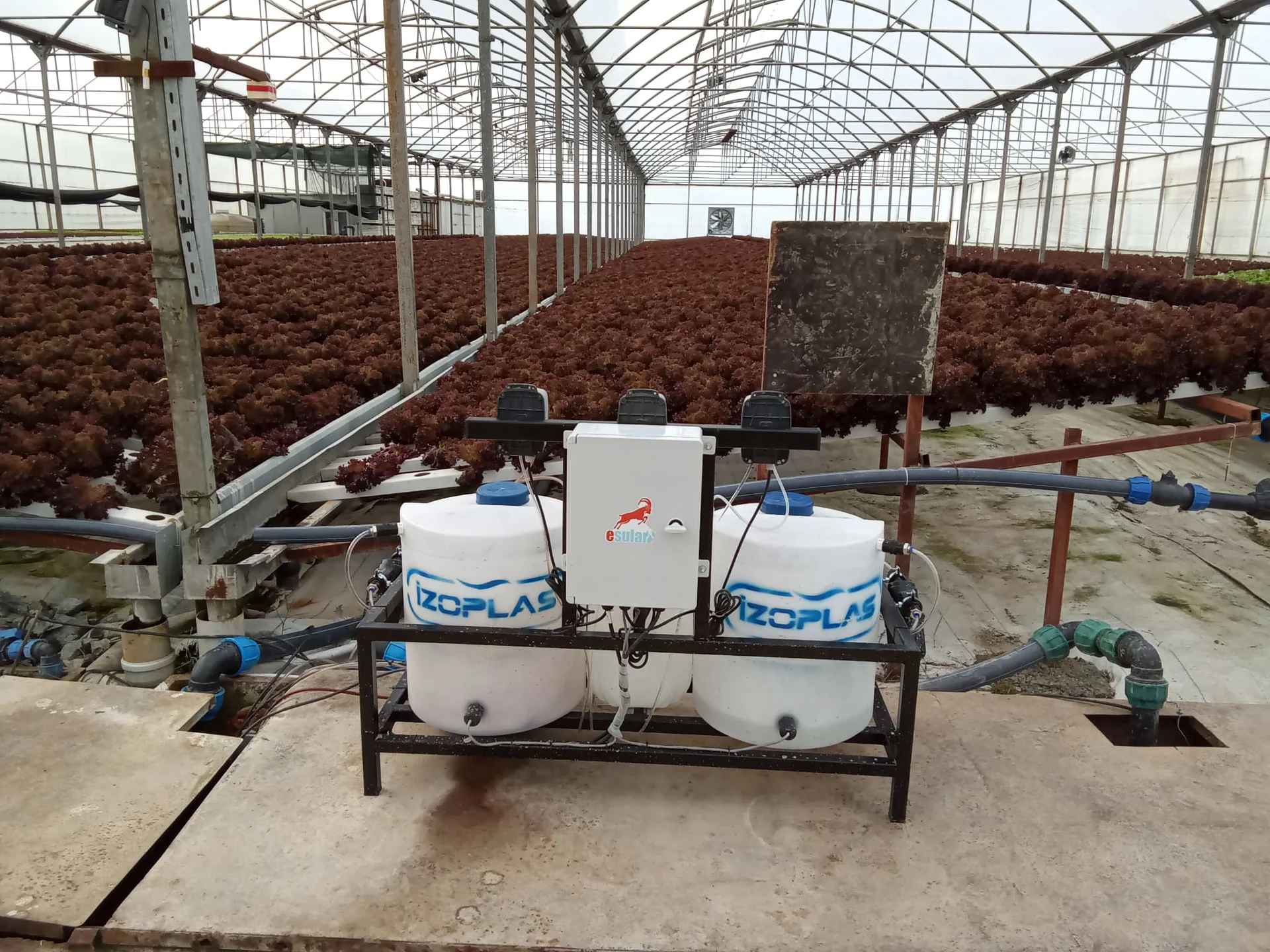
In avocado plant irrigation, the drip irrigation system is an indisputable system for both point water application and weed control. In addition; with a smart irrigation system, the most optimum irrigation is achieved in the avocado plant, which has a fibrous root structure, with data received from soil moisture sensors and EC meters to be placed at depths of 20 cm and 50 cm. The smart irrigation system is integrated with smart meter, central station, soil moisture and EC sensor units. This system minimizes risks by providing real-time detailed data and alerts from the field, and also maximizes savings in personnel, water, and electricity consumption. By ensuring the healthy development of the plant and ensuring the use of plant nutrients in the most appropriate amounts, it prevents salinity/nutrient leaching in the soil. Since the plant root zone is not over-irrigated, "root rot" disease is also prevented in the avocado plant grown in hot regions.



Yorumlar